Marine Engines Market by Engine (Propulsion and Auxiliary), Type (Two Stroke and Four Stroke), Power Range (Up to 1,000 hp, 1,001-5,000 hp, 5,001-10,000 hp, 10,001-20,000 hp, and Above 20,000 hp), Fuel, Vessel and Region - Global Forecast to 2029
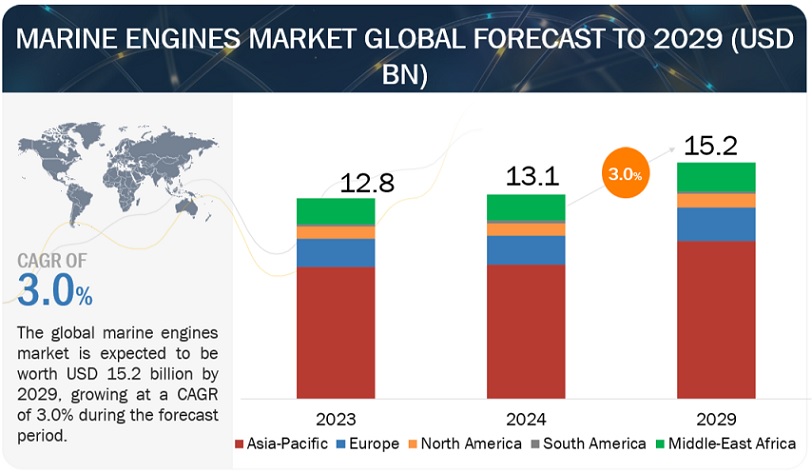
[280 Pages Report] The global marine engines market is estimated at USD 13.1 billion in 2024, with a projected growth to USD 15.2 billion by 2029, exhibiting a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 3.0%. The marine engines market is currently at a crossroads, navigating a complex interplay between the established needs of global trade and the growing urgency for cleaner operations. The global marine engines market is expected to experience moderate growth in the coming years. As international trade continues to expand, the demand for efficient and reliable propulsion systems for cargo ships and tankers will remain high. Replacement of aging engines in existing vessels creates a steady demand for new, more efficient models. Ship owners are constantly seeking ways to optimize fuel consumption and reduce operating expenses, driving demand for engines with improved fuel efficiency.
Despite a push for cleaner alternatives, Heavy Fuel Oil (HFO) remains a significant player due to its cost-effectiveness. LNG offers a cleaner burning alternative to HFO, particularly for new vessels. However, infrastructure for LNG bunkering (refueling) needs further development. Biofuels and synthetic fuels derived from renewable sources hold promise for the future, but cost reduction and production scalability remain challenges. The dominance of HFO is expected to wane as regulations tighten and cleaner options become more viable. LNG is likely to solidify its position as a leading fuel choice, particularly for larger vessels.
Advancements in production methods and cost reduction could make these options more competitive in the long run. Manufacturers will develop engines capable of operating on multiple fuel types, offering ship owners greater flexibility and adaptability. Engines with lower fuel consumption and optimized performance will be crucial for reducing operating costs and emissions. Technologies like exhaust gas aftertreatment systems will be essential for complying with stricter environmental regulations. Integration of sensors, advanced controls, and remote monitoring will enable predictive maintenance and optimize engine performance. Collaboration between various stakeholders - engine manufacturers, shipbuilders, fuel suppliers, and regulators - will be crucial for achieving a sustainable future. This includes development of carbon-neutral fuels, investment in shore-side power infrastructure for ports, and creation of regulations that incentivize cleaner technologies and practices.
The future of the marine engines market is one of transformation. As environmental concerns take center stage, cleaner fuels, smarter engines, and alternative propulsion technologies hold immense promise. The industry is on a trajectory towards powering a more responsible and sustainable maritime transportation sector.
To know about the assumptions considered for the study, Request for Free Sample Report

To know about the assumptions considered for the study, download the pdf brochure
Marine Engines Market Dynamics
Driver: Growth in international marine freight transport
The growth of international marine freight transport acts as a critical driver for the marine engines market, fueling demand for powerful and reliable propulsion systems. The interconnectedness of global economies necessitates the efficient movement of goods across vast distances. Maritime transportation remains the most cost-effective and reliable method for bulk cargo like raw materials, manufactured products, and agricultural goods. The rise of economies in Asia, Africa, and South America has led to an increase in import and export activity, further amplifying the demand for maritime freight transport. The expansion of international marine freight transport translates to a greater need for ships. This, in turn, drives demand for marine engines larger fleets and variety of vessel types.The global maritime fleet consists of a significant number of older vessels. As these engines reach the end of their lifespan, they need to be replaced with newer, more fuel-efficient, and environmentally friendly models. The future of international maritime freight transport is likely to see continued growth, driven by globalization and economic development. This will keep demand for marine engines high, pushing manufacturers towards innovation in terms of efficiency, cleaner burning fuels, and alternative propulsion technologies. As the maritime industry strives for sustainability, the marine engine market will play a critical role in powering a future of reliable and environmentally responsible international trade.
Restraints: Stringent environmental regulations
Stringent environmental regulations are a double-edged sword for the marine engine market. While they act as a restraint on traditional engine technologies, they also present a significant opportunity for innovation and the development of cleaner solutions. The shipping industry is a major contributor to air and water pollution, emitting pollutants like sulfur oxides (SOx), nitrogen oxides (NOx), and particulate matter. This has led to stricter regulations from international bodies like the International Maritime Organization (IMO) aimed at reducing emissions and protecting the environment. The IMO has designated specific areas around the world as Emission Control Areas (ECAs), where stricter emission limits are enforced. This necessitates the use of cleaner burning fuels or exhaust gas aftertreatment systems for vessels operating within these zones.
Traditional marine engines, particularly those relying on Heavy Fuel Oil (HFO), struggle to comply with increasingly stringent regulations. This creates a restraint on the market for these older technologies. Regulations incentivize the adoption of cleaner burning fuels like Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG) and biofuels. This pushes engine manufacturers to develop engines compatible with these alternative fuels or modify existing models for better fuel efficiency. Engine manufacturers are actively researching and developing new technologies like dual-fuel engines capable of operating on both traditional and cleaner fuels, offering ship owners greater flexibility. The future of the marine engine market lies in embracing these regulations and fostering innovation to create a more sustainable maritime industry. In the long run, stricter environmental regulations can lead to a more robust market driven by advanced, eco-friendly engine technologies.
Opportunities: Rising demand for duel fuel and hybrid engines
The marine engine market is witnessing a surge in demand for dual-fuel and hybrid engine systems. This trend presents a significant opportunity for manufacturers and reflects the growing focus on cleaner and more sustainable maritime operations. Dual-fuel engines are designed to operate on two different fuel types, typically a traditional fuel like Marine Gas Oil (MGO) and a cleaner alternative like Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG) or biofuel. This adaptability offers ship owners greater flexibility when it comes to complying with evolving regulations in different regions. They can choose the most economical and environmentally friendly option depending on fuel availability, operational requirements, and emission control area (ECA) restrictions. Stringent environmental regulations, particularly those targeting sulfur and nitrogen oxide emissions, are driving the adoption of cleaner burning fuels.
Dual-fuel engines allow ship owners to comply with these regulations by switching to cleaner fuels in ECAs or opting for traditional fuels in other areas. Hybrid propulsion systems combine internal combustion engines with electric motors and battery banks. This configuration allows for significant emission reductions, particularly when operating in electric mode within ports or harbor areas. By utilizing electric motors for low-speed maneuvers and harbor operations, hybrid systems can significantly reduce fuel consumption compared to traditional engines. Additionally, regenerative braking can capture energy during deceleration and store it in batteries for later use, further enhancing efficiency. The demand for dual-fuel and hybrid engines represents a promising avenue for growth and innovation in the marine engine market. By embracing these technologies, manufacturers can cater to the evolving needs of the maritime industry while contributing to a more sustainable future for our oceans.
Challenges: Volatile oil & gas prices
The marine engine market operates in a world of fluctuating fuel costs, with volatile oil and gas prices presenting a significant challenge for ship owners and engine manufacturers. Fuel represents one of the largest operational costs for ship owners. Fluctuations in oil and gas prices can have a significant impact on profitability, especially for vessels with traditional, fuel-intensive engines. The volatile nature of oil and gas prices makes it difficult for ship owners to plan their budgets and routes effectively. Sudden price spikes can disrupt operations and erode profit margins. Volatile fuel prices incentivize ship owners to seek more fuel-efficient engines. This drives manufacturers to invest in research and development of engines with improved combustion processes, reduced friction losses, and optimized performance across varying operating conditions. While traditional fuels like HFO are often the most cost-effective option, stricter regulations and volatile oil prices are pushing the industry towards cleaner alternatives. This creates a demand for engines compatible with fuels like LNG or biofuels, which may offer greater price stability in the long run. The volatility of oil and gas prices will continue to be a challenge for the marine engine market. However, it also creates opportunities for innovation and the development of more efficient and adaptable engine technologies. By embracing these advancements, the industry can build resilience against fluctuating fuel costs and contribute to a more sustainable future for maritime transportation.
Marine Engines Market Ecosystem
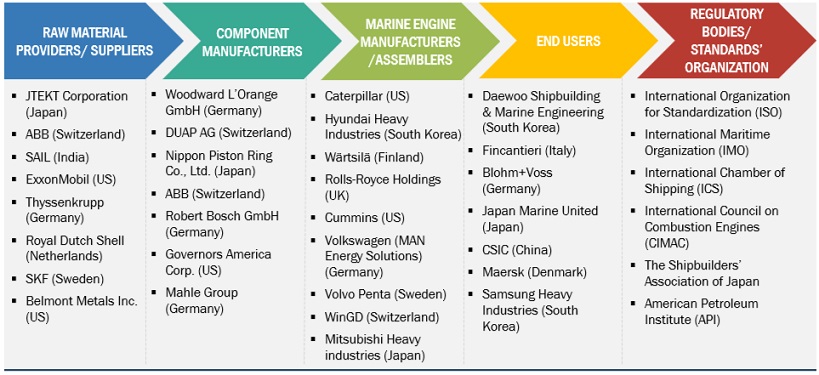
The market for marine engines is marked by the participation of leading companies that are firmly established, financially robust, and possess substantial expertise in the production of marine engines. These companies hold a significant market presence and provide a wide array of product offerings. They harness advanced technologies and maintain extensive global sales and marketing networks. Among the notable players in this market are Caterpillar (US), Wärtsilä (Finland), Man Energy Solutions (Germany), AB Volvo Penta (Sweden), Rolls-Royce Plc (UK), Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. (Japan), HDHyundai Heavy Industries Co., Ltd. (South Korea), Cummins Inc. (US), Daihatsu Diesel Mfg. Co., Ltd. (Japan), and Deutz AG (Germany).
Propulsion segment, by engine, to have the largest market share during forecast period.
The propulsion engine segment reigns supreme in the marine engine market, claiming the largest market share for a few compelling reasons. The primary function of any marine vessel, be it a colossal container ship or a nimble tugboat, is propulsion. Propulsion engines are the workhorses that convert fuel into power, driving propellers and enabling the vessel to move through water. Without reliable propulsion, a ship is essentially a stationary structure. This centrality to a vessel's core function translates to a naturally high demand for propulsion engines compared to other engine types used onboard.
The propulsion engine segment encompasses a diverse range of engine types catering to various needs. From colossal, two-stroke, low-speed diesel engines powering massive cargo ships to high-speed gas turbines propelling ferries and patrol boats, the propulsion segment offers solutions for all sizes and operational profiles of vessels. This variety ensures the segment caters to the vast spectrum of the marine industry. Propulsion engines are designed to generate significantly higher power outputs compared to auxiliary engines used onboard ships. Auxiliary engines handle tasks like generating electricity, powering winches, and operating onboard equipment. The sheer power needed to propel a vessel through water necessitates a larger and more powerful engine type, driving up the market share of the propulsion segment.
The propulsion engine segment's dominance in the marine engine market stems from its central role in ship operations, the variety of engine types offered, higher power outputs compared to auxiliary engines, and the ongoing demand for replacements, maintenance, and technological advancements. As the maritime industry strives for cleaner operations and greater efficiency, the propulsion engine segment will continue to be a focal point for innovation and hold the largest market share in the foreseeable future.
Two stroke segment, by type, to emerge as largest segment of marine engines market.
Within the type segment, the two-stroke engine reigns supreme, holding the largest market share in the marine engine market. Two-stroke engines are renowned for their ability to generate immense power at relatively low engine speeds. This characteristic makes them ideal for propelling large vessels like container ships, tankers, and bulk carriers, which require tremendous power to overcome drag and navigate vast distances. Their simple design with fewer moving parts also contributes to their robustness and reliability, crucial qualities for long ocean voyages.
Despite a perception of being less fuel-efficient than their four-stroke counterparts, two-stroke engines offer a surprising advantage when it comes to large, slow-speed applications. Their simpler design translates to lower internal friction losses, which can improve overall fuel efficiency for these massive engines. Additionally, two-stroke engines can operate efficiently on lower-grade fuels like Heavy Fuel Oil (HFO), which is often the most cost-effective option for large commercial vessels. The simpler design of two-stroke engines compared to four-stroke models translates to lower manufacturing costs. This affordability factor makes them an attractive choice for shipbuilders and owners, particularly for large vessels where initial engine cost is a significant consideration. Additionally, their simpler design can sometimes lead to easier and potentially less expensive maintenance procedures.
While two-stroke engines hold the current market share, stricter environmental regulations and a growing focus on sustainability are pushing the industry towards cleaner burning fuels and alternative propulsion technologies. Four-stroke engines tend to offer lower emissions and are finding favor in smaller vessels. Additionally, advancements in areas like electric and hybrid propulsion systems pose a potential challenge to the long-term dominance of two-stroke engines.
The two-stroke engine's reign in the marine engine market stems from its exceptional power output, surprising fuel efficiency for large engines, lower costs, and historical dominance. However, the future of marine propulsion is likely to see a diversification of engine types with a growing emphasis on cleaner burning fuels and alternative technologies. While two-stroke engines will likely continue to play a vital role in powering large commercial vessels for the foreseeable future, their dominance may gradually wane as the industry strives towards a more sustainable future.
Marine diesel oil segment, by fuel, to hold the largest market share in marine engines market.
Within the fuel segment of the marine engine market, Marine Diesel Oil (MDO) reigns supreme, holding the largest market share. MDO is a lighter and cleaner-burning fuel compared to its heavier cousin, Heavy Fuel Oil (HFO). This versatility allows it to be used in a wider range of marine engines, including both high-speed four-stroke and some two-stroke engines. This adaptability makes MDO a suitable choice for various vessel types, from smaller ferries and tugs to medium-sized cargo ships and tankers. MDO has a lower pour point, meaning it remains liquid at lower temperatures, facilitating easier engine starts in colder climates. MDO burns cleaner, leading to better engine performance, less wear and tear, and potentially lower maintenance costs.
MDO produces fewer pollutants compared to HFO, contributing to cleaner air and reduced environmental impact. While cleaner burning fuels like Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG) are emerging, MDO offers a good balance between cost and emissions. For many ship owners, particularly those operating smaller or regional vessels, MDO remains a more cost-effective option compared to LNG, which requires additional infrastructure for bunkering (refueling). Current international maritime regulations allow the use of MDO in most Emission Control Areas (ECAs), which are designated zones around the world with stricter emission limits. Additionally, MDO is readily available at most ports worldwide, unlike LNG which requires specialized bunkering facilities. This existing infrastructure makes MDO a more accessible and convenient fuel choice for many ship owners.
MDO's versatility, operational advantages, cost-effectiveness, and compatibility with existing regulations and infrastructure solidify its position as the leading fuel choice in the marine engine market. However, the future of marine fuels is likely to see a shift towards cleaner options as the industry strives for a more sustainable future. MDO will likely remain a significant player for the foreseeable future, particularly for smaller and regional vessels, but its market share might gradually decrease as cleaner alternatives become more viable and infrastructure expands.
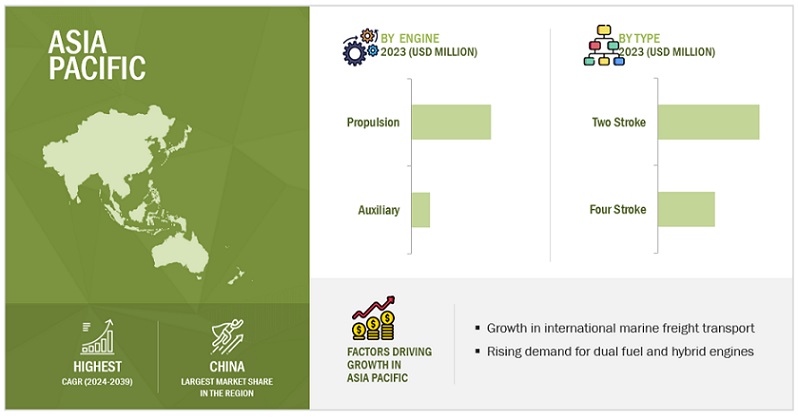
The Asia Pacific marine engines market is poised to achieve the highest CAGR throughout the forecast period.
The Asia Pacific region reigns supreme in the marine engine market, holding the largest market share by a significant margin. This dominance can be attributed to a confluence of factors that create a thriving ecosystem for shipbuilding and engine production. Asia Pacific has emerged as a global manufacturing hub, particularly for ships and maritime equipment. Renowned shipyards like those in China, South Korea, and Japan boast established expertise in shipbuilding. This naturally translates to a high demand for marine engines within the region itself. Shipbuilders often require a steady supply of engines to meet their production quotas, and with a well-developed domestic engine manufacturing base, Asia Pacific fulfills this demand efficiently.
As international commerce continues to experience steady growth, the demand for cargo ships to transport goods across vast distances rises. Building new vessels necessitates a corresponding demand for marine engines. Many Asian governments actively support their shipbuilding industries through subsidies and tax incentives. This financial backing creates a more favorable environment for shipbuilders to operate, further propelling growth in the industry and consequently, the demand for marine engines. Asian shipyards cater to a wide range of vessel types, from massive container ships and tankers to smaller ferries, fishing boats, and offshore service vessels. This necessitates a diverse range of engine types and power outputs. The ability to produce a variety of engines allows Asian manufacturers to cater to the specific needs of different shipbuilders and vessel types, contributing significantly to their dominant market share.
The confluence of a thriving shipbuilding industry, diverse engine production, cost-competitiveness, and advancements in engine technology all contribute to Asia Pacific's leading position in the marine engine market. However, the region must navigate competition and balance cost efficiency with environmental considerations to ensure its continued dominance in the future.
Key Market Players
Caterpillar (US), Wärtsilä (Finland), Man Energy Solutions (Germany), AB Volvo Penta (Sweden), Rolls-Royce Plc (UK), Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. (Japan), Cummins Inc. (US), Daihatsu Diesel Mfg. Co., Ltd. (Japan), Deutz AG (Germany), and others.
Get online access to the report on the World's First Market Intelligence Cloud
- Easy to Download Historical Data & Forecast Numbers
- Company Analysis Dashboard for high growth potential opportunities
- Research Analyst Access for customization & queries
- Competitor Analysis with Interactive dashboard
- Latest News, Updates & Trend analysis
Request Sample Scope of the Report
Get online access to the report on the World's First Market Intelligence Cloud
- Easy to Download Historical Data & Forecast Numbers
- Company Analysis Dashboard for high growth potential opportunities
- Research Analyst Access for customization & queries
- Competitor Analysis with Interactive dashboard
- Latest News, Updates & Trend analysis
|
Report Metric |
Details |
|
Market Size available for years |
2020–2029 |
|
Base year considered |
2023 |
|
Forecast period |
2024–2029 |
|
Forecast units |
Value (USD Million) |
|
Segments covered |
By Engine, By Type, By Power Range, By Fuel, By Vessel |
|
Geographies covered |
Asia Pacific, North America, Europe, Middle East and Africa, and South America |
|
Companies covered |
Caterpillar (US), Wärtsilä (Finland), Man Energy Solutions (Germany), AB Volvo Penta (Sweden), HDHyundai Heavy Industries Co., Ltd. (South Korea), Mitsubishi Heavy Industries, Ltd. (Japan), Cummins Inc. (US), Daihatsu Diesel Mfg. Co., Ltd. (Japan), and Deutz AG (Germany) |
The marine engines market is classified in this research report based on engine, type, power range, fuel, vessel, and region.
Based on engine, the marine engines market has been segmented as follows:
- Propulsion Engine
- Auxiliary Engine
Based on type, the marine engines market has been segmented as follows:
- Two Stroke
- Four Stroke
Based on power range, the marine engines market has been segmented as follows:
- Up to 1,000 hp
- 1,001-5,000 hp
- 5,001-10,000 hp
- 10,001-20,000 hp
- Above 20,000 hp
Based on fuel, the marine engines market has been segmented as follows:
- Marine Diesel Oil
- Others
- Heavy Fuel Oil
- Marine Gas Oil
Based on regions, the marine engines market has been segmented as follows:
- North America
- Asia Pacific
- South America
- Europe
- Middle East and Africa
Recent Developments
- In February 2024, Caterpillar and Solstad Offshore ASA (Solstad) and Cat® dealer Pon Power AS comes into partnership where Caterpillar Marine is committed to helping vessel owners increase fuel efficiency and reduce GHG emissions and offer pathways to support these operational and sustainability targets by providing a range of solutions for alternative fuels and powertrain integration.
- In December 2023, MAN Energy Solutions has announced an agreement with Alfa Laval, the Swedish industrial concern, to develop a methanol fuel-supply solution for MAN four-stroke engines and its fuel-injection technology. As a result, the first four-stroke engine types will be capable of retrofit to methanol operation from 2025.
- In August 2022, Leisure, and Volvo Penta joined forces to develop near-silent, eco-friendly boats. Leiser's sleek designs paired with Volvo's hybrid electric technology aim to reduce emission. This collaboration pushes boundaries in sustainable boating, offering a glimpse into the future of the industry..
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ):
What is the current size of the global marine engines market?
The global marine engines market is estimated to be USD 12,894 million in 2024.
What are the major challenges for marine engines market?
The marine engine market faces a complex web of challenges. Stricter environmental regulations demanding cleaner burning fuels and reduced emissions push for innovation but can also raise costs. Volatile fuel prices create uncertainty for ship owners, while the need to balance efficiency with affordability can hinder the adoption of some cleaner technologies. Additionally, competition from established players and the pressure to maintain cost-effectiveness in engine production necessitate continuous advancements for Asian manufacturers to retain their dominance.
Which type has the largest market share in the marine engines market?
Two-stroke engines dominate the marine engine market due to their exceptional power output at low speeds, ideal for propelling massive cargo ships. Despite a perception of lower fuel efficiency, their simpler design translates to surprisingly good efficiency for these large engines, especially when running on cost-effective Heavy Fuel Oil. Lower manufacturing and maintenance costs coupled with their historical prevalence further solidify their dominance. However, stricter environmental regulations and a growing focus on sustainability might see their market share gradually wane in favor of cleaner burning alternatives.
Which region holds second largest market share in the marine engines market?
Europe holds the second-largest market share in the marine engine market due to a combination of factors. It boasts the world's largest shipping fleet, with many ship owners operating some of the newest and most innovative vessels. Stringent environmental regulations in the region incentivize the development and adoption of cleaner burning engines, like those using LNG or biofuels. Additionally, established European manufacturers have a long-standing reputation for technological leadership, offering high-quality and reliable engines despite potentially higher costs compared to Asian counterparts. This combination of a large existing fleet, focus on innovation and cleaner technologies, and strong manufacturing base positions Europe as a key player in the marine engine market.
Which is the largest segment, by power range in the marine engines market during the forecast period?
The above 20,000 horsepower segment reigns supreme in the marine engine market due to its dominance in powering the workhorses of global trade: massive cargo ships, tankers, and container vessels. These giants require immense power to overcome drag and navigate vast distances efficiently. Two-stroke engines, often found in this segment, excel at delivering this exceptional power output at relatively low engine speeds. Additionally, for these large engines, their simpler design can offer surprisingly good fuel efficiency, especially when running on cost-effective heavy fuel oil. This combination of factors makes the above 20,000 hp segment the engine room of global maritime commerce. .
To speak to our analyst for a discussion on the above findings, click Speak to Analyst
This study encompassed significant efforts in determining the present size of the marine engines market. It commenced with a thorough secondary research process to gather data related to the market, similar markets, and the overarching industry. Subsequently, these findings, assumptions, and market size calculations were rigorously validated by consulting industry experts across the entire supply chain through primary research. The total market size was assessed by conducting an analysis specific to each country. Following that, the market was further dissected, and the data was cross-referenced to estimate the size of various segments and sub-segments within the market.
Secondary Research
In this research study, a wide range of secondary sources were utilized, including directories, databases, and reputable references such as Hoover's, Bloomberg BusinessWeek, Factiva, World Bank, the US Department of Energy (DOE), and the International Energy Agency (IEA). These sources played a crucial role in gathering valuable data for a comprehensive analysis of the global marine engines market, covering technical, market-oriented, and commercial aspects. Additional secondary sources included annual reports, press releases, investor presentations, whitepapers, authoritative publications, articles authored by well-respected experts, information from industry associations, trade directories, and various database resources.
Primary Research
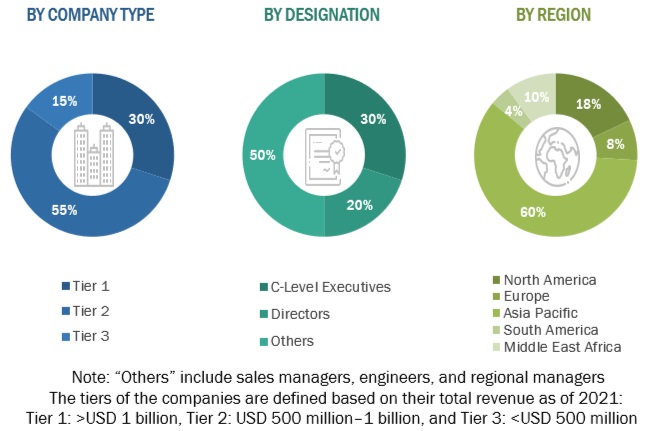
The marine engines market involves a range of stakeholders, including raw material suppliers, component manufacturers, marine engine manufacturers/assemblers, distributors, end users, and post-sale services within the supply chain. The demand for this market is primarily driven by end users such as shipbuilding, maritime logistics firms operating different types of vessels, and ferry & cruise operators On the supply side, there is a notable trend of heightened demand for contracts from the industrial sector and a significant presence of investments and expansions among major players.
To gather qualitative and quantitative insights, various primary sources from both the supply and demand sides of the market were interviewed. The following breakdown presents the primary respondents involved in the research study.
To know about the assumptions considered for the study, download the pdf brochure
Market Size Estimation
The estimation and validation of the marine engines market size have been conducted using a bottom-up approach. This approach was rigorously employed to ascertain the dimensions of multiple subsegments within the market. The research process comprises the following key stages.
In this method, the production statistics for each type of marine engines have been examined at both the country and regional levels.
Thorough secondary and primary research has been conducted to gain a comprehensive understanding of the global market landscape for various segments of marine engines.
Numerous primary interviews have been undertaken with key experts in the field of marine engines development, encompassing important OEMs and Tier I suppliers.
When calculating and forecasting the market size, qualitative factors such as market drivers, limitations, opportunities, and challenges have been taken into account.
Global Marine Engines Market Size: Bottom-Up Approach
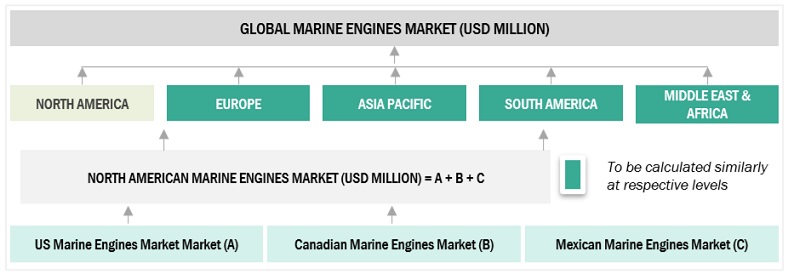
To know about the assumptions considered for the study, Request for Free Sample Report
Data Triangulation
The process of determining the overall market size involved the methodologies described earlier, followed by segmenting the market into multiple segments and subsegments. To finalize the comprehensive market analysis and obtain precise statistics for each market segment and subsegment, data triangulation and market segmentation techniques were applied, as appropriate. Data triangulation was accomplished by examining various factors and trends from both the demand and supply perspectives within the ecosystem of the marine engines market.
Market Definition
The marine engine market deals with the development, manufacturing, sales, and after-sales services of engines specifically designed for powering seafaring vessels. These engines are the workhorses that propel various types of ships, from the colossal container ships traversing vast oceans to smaller fishing vessels navigating local waters. Marine engines come in a wide range of power outputs, catering to the diverse needs of different vessel types. Large container ships require immensely powerful engines to overcome drag and efficiently navigate long distances. Conversely, smaller vessels prioritize fuel-efficient engines for cost-effective operation on shorter routes. The harsh marine environment with its constant exposure to saltwater, extreme weather conditions, and varying loads demands exceptional durability from marine engines.
These engines are designed and built to withstand continuous operation for extended periods, ensuring reliable performance at sea. Unlike land-based engines, marine engines need to adapt to varying operational demands. They must efficiently handle maneuvers in harbors, navigate diverse sea conditions, and sometimes operate at different engine speeds depending on the route or cargo requirements. Strict environmental regulations governing air and water pollution emissions from ships significantly impact the marine engine market. Manufacturers constantly innovate and develop engines that comply with these regulations, such as those limiting sulfur and nitrogen oxide emissions in designated Emission Control Areas (ECAs). The marine engine market caters to a variety of fuel options. While Heavy Fuel Oil (HFO) remains the most economical choice for some large vessels, stricter regulations and a growing focus on sustainability are driving the adoption of cleaner alternatives like Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG), biofuels, and synthetic fuels
Key Stakeholders
- Government & research organizations
- Institutional investors
- Investors/shareholders
- Environmental research institutes
- Manufacturers’ associations
- Marine engine raw material and component manufacturers
- Marine engine manufacturers, dealers, and suppliers
- Consulting companies in the shipping sector
- Shipbuilding and maritime industry associations
- Shipbuilding and shipyard industries
- State and national regulatory authorities
- Manufacturing industry
- Energy efficiency consultancies
- Vessel designers, owners, and operators
Objectives of the Study
- To describe and forecast the marine engines market, in terms of value, by engine, type, power range, fuek, vessel, and region
- To forecast the market for various segments, in terms of value, with regard to five regions: North America, South America, Europe, Asia Pacific, and the Middle East & Africa, along with their key countries
- To provide detailed information about the key factors, such as drivers, restraints, opportunities, and challenges, influencing the market’s growth
- To strategically analyze the subsegments with respect to individual growth trends, prospects, and contributions of each segment to the overall market size
- To study the complete supply chain and allied industry segments and perform a supply chain analysis of the marine engines landscape
- To strategically analyze the regulatory landscape, tariff, standards, patents, Porter’s five forces, import and export scenarios, trade values, and case studies pertaining to the market under study
- To analyze the opportunities in the market for various stakeholders by identifying the high-growth segments of the marine engines market
- To profile the key players and comprehensively analyze their market position in terms of ranking and core competencies1, along with detailing the competitive landscape for the market leaders
- To analyze competitive developments such as agreements, partnerships, product launches, acquisitions, contracts, expansions, and investments in the marine engines market
Available Customization
With the given market data, MarketsandMarkets offers customizations based on the company’s specific needs. The following customization options are available for the report:
Product Analysis
- Product Matrix, which provides a detailed comparison of the product portfolio of each company
Company Information
- Detailed analyses and profiling of additional market players (up to 5)




 Generating Response ...
Generating Response ...







Growth opportunities and latent adjacency in Marine Engines Market