
Biopesticides to Lead the Charge in Sustainable Agriculture & Integrated Pest Management Globally
Increasing awareness of the environmental and health concerns of synthetic pesticides is prompting farmers to seek more sustainable solutions. Biopesticides, derived from natural sources, offer a suitable alternative, promoting crop protection by fostering beneficial microorganisms in the soil while minimizing negative environmental impact. Further, their integration into integrated pest management (IPM) strategies allows for targeted pest control, contributing to sustainable agricultural practices globally.
According to MarketsandMarkets, the biopesticides market is projected to reach USD 15.66 billion by 2029 from USD 7.72 billion by 2024, at a CAGR of 15.2% during the forecast period in terms of value. Supported by the stringent regulations on synthetic pesticides and growing demand for organic food, biopesticide usage remained prominent in North America and Europe. Technological advancements in biopesticide development, the growing organic food industry, and increasing awareness about sustainable practices are anticipated to further propel market growth in developing countries such as Brazil, Argentina, China, and India.
Focus on sustainable agricultural practices to support biopesticides growth
The demand for organic and sustainably produced food is growing as consumers become more conscious of the environmental impact of conventional farming practices, driving the demand for crops grown using biopesticides. Governments worldwide are encouraging the use of biopesticides by implementing supportive regulatory frameworks. It includes incentives, subsidies, and streamlined registration processes for biopesticide products. Registration of biopesticides in the US takes around 12 to 18 months compared to approximately 36 months for conventional pesticides. The registration fees are also comparatively lower. Ongoing research & development efforts are expanding the range and efficacy of biopesticides as part of integrated pest management (IPM). Companies such as Bayer AG, Syngenta, and Corteva Agrisciences are investing in innovative formulations to improve biopesticide products’ shelf life and efficiency.
Biopesticides for sustainable agriculture and Integrated Pest Management (IPM)
Considered part of sustainable agriculture practices, biopesticides are derived from natural materials such as animals, microbes, plants, bacteria, and certain minerals. The use of biopesticides is becoming more popular due to their safer and environmentally friendly nature compared to traditional pesticides. This trend aligns with the global push for sustainable agriculture, where eco-friendly solutions are key to minimizing harm to the ecosystem. Biopesticides are an essential component of Integrated Pest Management (IPM) as they help to reduce chemical inputs, promoting a balanced and resilient agroecosystem.
Advancement in microbial research to support future growth of biopesticides
Extensive research undertaken by the major players in the crop protection industry has encouraged the effective use of biological signals to trigger RNAi-specific genes, which would help in disease and pest resistance and increase yield and quality. Bayer AG (Germany) is advancing in microbial and RNA interference (RNAi) technology, allowing farmers to adopt better alternatives for applying biological products. Companies such as Greenlight Biosciences are focusing on the invention of RNAi-based biopesticides for biological crop protection. Monsanto Company (US) got approval from the EPA in 2017 for genetic engineering technology using RNA interference to kill insect pests. Corteva Agriscience (US) also licensed two insect traits from Monsanto Company (US), which contained an RNAi rootworm trait. Regulated under biopesticides in the US, this technology is witnessing increased adoption in the industry, as it is a novel solution available for specific pest traits in specific crops.
Technological limitations for the use of biological products
Biological products have a short or limited shelf life and a high probability of contamination. One of the significant problems with agricultural inoculation technology is the survival of microorganisms during storage. The other issues include exposure to sunlight, culture mediums, the physiological state of microorganisms when harvested, temperature maintenance during storage, and water activity of inoculants that have an influence on their shelf life. Compatibility with other agricultural products, such as chemical fungicides and herbicides, also poses problems with using microbial inoculants in the soil. Some of the major technological constraints with the use of biological products include the following:
- Use of improper and inefficient strains for production
- Lack of experienced, skilled, and technical personnel
- Unavailability of high-quality carrier materials or the use of different carrier materials by producers without ascertaining the quality of the material
- Short shelf life due to the influence of various abiotic and biotic stress factors
Effectiveness of foliar application to drive the demand for biopesticides
Foliar mode of application has become increasingly popular in recent years as it allows for more targeted and efficient use of inputs. This application mode improves the effectiveness of biopesticide products through direct application to the leaves. When applied directly to the grass plant leaves, these products can be absorbed more quickly and efficiently, allowing for faster results and better overall performance.
Use of microbial-based biopesticides to boost the market growth
Microbial-based biopesticides are highly specific in their action, targeting only the pests they are designed to control while leaving beneficial insects and organisms unharmed, hence integrating sustainable approaches to farming. Microbials, including bacteria, fungi, viruses, and protozoa, can act as natural enemies of pests by directly infecting and killing them or interfering with their life cycles and behavior. This targeted approach helps preserve the ecological balance and reduces the risk of resistance development in pests. Additionally, microbial products have a lower environmental impact, as they degrade naturally without leaving harmful residues in the soil, water, or air.
Growth opportunities in developing regions such as Asia Pacific and South America
According to FAOSTAT, China, India, Brazil, and Argentina have emerged as major consumers of pesticides. As the demand for food has risen in these regions, the use of pesticides has increased consequently to achieve higher crop yields. However, pollution, soil contamination, and concerns about the harmful effects of chemical pesticides on the food chain have become significant issues in these areas. To address these concerns, governments are promoting the adoption of integrated pest management practices (IPM) and sustainable crop protection practices.
FIGURE 1Top 10 countries for total pesticide usage in agriculture,
2020 (‘000 tonnes)
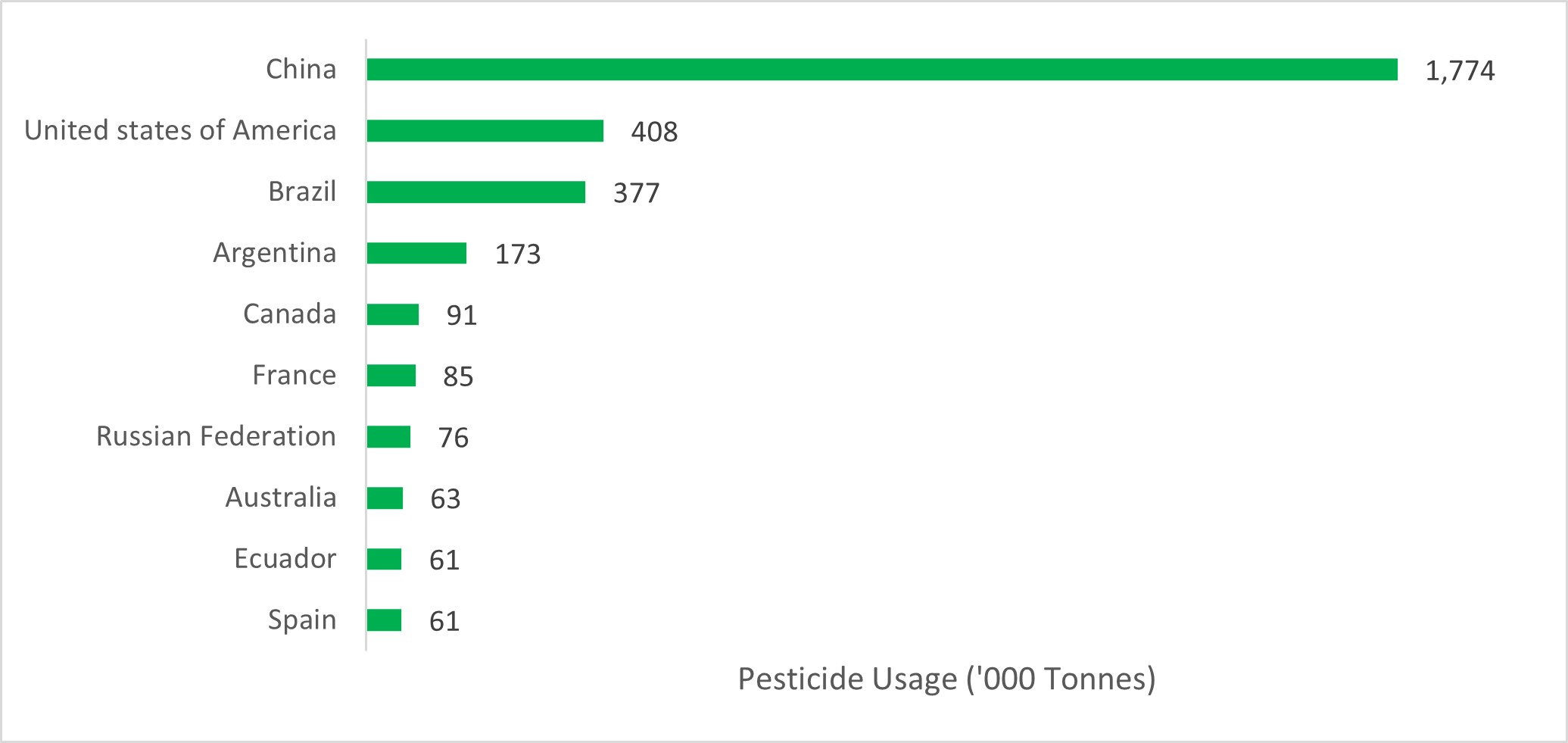
Source: FAOSTAT
Developing regions such as the Asia Pacific are poised for strong growth due to the availability of biopesticide products, the extent of organic farming, farmers’ awareness, cultivation of high-value cash crops, and effective promotion and marketing of biopesticides.
In countries such as India, China, and Brazil, where farmers typically have smaller landholdings and face economic challenges, government agencies provide subsidies and implement favorable regulatory policies to support large-scale production and encourage the use of biopesticides. The biopesticide market in these regions presents opportunities for new entrants due to a relatively small number of producers and low entry barriers.
Biopesticides market ecosystem
Prominent companies operating in the market possess a diversified product portfolio, state-of-the-art technologies, and strong global sales and marketing networks. The key players in this include BASF SE (Germany), Bayer AG (Germany), Syngenta (Switzerland), UPL Limited (India), FMC Corporation (US), Marrone Bio Innovations, Inc. (US), Novozymes (Denmark), Nufarm (Australia), Isagro S.p.A (Italy), Certis USA L.L.C. (US), Koppert (Netherlands), Biobest Group NV (Belgium), SOM Phytopharma (India) Limited (India), Valent BioSciences LLC (US), and STK Bio-Ag Technologies (Israel). These players in this market are focusing on increasing their presence through agreements and collaborations. These companies have a strong presence in North America, Asia Pacific, and Europe. They also have manufacturing facilities along with strong distribution networks across these regions.

Source: Company Websites and MarketsandMarkets Analysis
80% of the Forbes Global 2000 B2B companies rely on MarketsandMarkets to identify growth opportunities in emerging technologies and use cases that will have a positive revenue impact.
- Food Packaging Market Size Set for Strong Growth Through 2030 Amid Rising Demand for Convenience Foods
- Fertilizers Industry Set to Grow at 4.1% CAGR Through 2030
- Leading Automated Guided Vehicle Companies 2024: An In-depth Analysis
- CHARGED UP: SHIFT TO E-MOBILITY AND THE EVOLUTION OF TRANSPORTATION
- Global Automotive Market: Predictions For 2024
The surge in biopesticide adoption globally reflects the growing emphasis and a fundamental shift toward sustainable and environmentally conscious agriculture. As the world faces the challenges of growing population, shrinking farmland, growing concern over chemical pesticide contamination, and the need for better farm productivity, biopesticides offer a viable solution that aligns with the principles of integrated pest management, effective crop protection, and overall agricultural sustainability. With supportive regulatory frameworks, ongoing research, and the commitment of industry leaders, the biopesticide market is poised for high growth that will help shape the future of sustainable agriculture.

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What is the role of biopesticides in Integrated Pest Management Practices (IPM) and sustainable crop protection globally?
Along with IPM principles, biopesticides offer targeted pest control with lower environmental and health risks than conventional chemical pesticides. They provide a variety of control mechanisms, such as direct toxicity to pests, disruption of their growth and development, or pest repellent. This diversity helps prevent resistance development and facilitates a long-term sustainable approach.
- How do biopesticides improve the efficacy and efficiency of Integrated Pest Management Practices (IPM)?
IPM programs integrating biopesticides can significantly lower the overall usage of synthetic crop protection chemicals. Biopesticides can be used effectively alongside other IPM tactics, improving the process efficiency by multi-fold:
- Cultural Practices: Crop rotation, sanitation, and habitat manipulation
- Biological Control: Introduction of beneficial predators and parasites
- Physical Controls: Barriers, traps, and manual removal


