Autonomous Aircraft Market by Technology (Increasingly Autonomous, and Fully Autonomous), End Use (Commercial, Combat & ISR, Cargo, Passenger Air Vehicle, Personal Air Vehicle, Air Medical Services), Component, and Region (2025-2035)
The aviation industry stands at the threshold of a new era where autonomy is redefining how aircraft operate, navigate, and perform missions. The Autonomous Aircraft Market, once confined to conceptual visions, has become a key segment of modern aerospace innovation. With rapid advances in artificial intelligence, sensor fusion, and flight control systems, aircraft are moving toward complete autonomy. Between 2025 and 2035, the market is expected to expand substantially, driven by commercial air mobility programs, defense modernization, and increased demand for cost efficient, safe, and sustainable air transport.
Autonomous aircraft are designed to perform critical flight operations without direct human input. These systems rely on onboard sensors, advanced communication networks, machine learning algorithms, and robust data processing to execute real time decisions. As governments, startups, and major aerospace manufacturers continue investing in autonomy, the industry is poised to witness transformative growth across commercial, defense, and urban air mobility sectors.
Download PDF Brochure: https://www.marketsandmarkets.com/pdfdownloadNewNew.asp?id=79798352
Understanding the Core of Autonomous Aircraft Systems
An autonomous aircraft is equipped with systems capable of independent navigation, obstacle avoidance, and operational decision making. The level of autonomy ranges from “increasingly autonomous” where systems assist or share control with pilots to “fully autonomous,” where human involvement is limited to mission programming and oversight.
Key technological enablers include artificial intelligence, flight management software, computer vision, LIDAR, radar, satellite based navigation, and cloud connectivity. These technologies allow aircraft to interpret environmental conditions, manage flight paths, and adapt to real time airspace changes with minimal human intervention.
The journey toward autonomy began with automated flight control systems in commercial aircraft. However, the integration of AI has accelerated the evolution toward self flying capabilities. From pilot assist systems to drone based logistics and passenger air taxis, the vision of a self operating aircraft ecosystem is becoming reality.
Market Segmentation by Technology: Increasingly Autonomous vs. Fully Autonomous
The increasingly autonomous segment dominates the current market landscape. These aircraft incorporate advanced automation that assists pilots with flight control, navigation, collision avoidance, and landing procedures. Most commercial aircraft today already operate with high levels of automation, reducing pilot workload and improving safety through redundant flight systems.
Over the next decade, these technologies will evolve into fully autonomous systems. Fully autonomous aircraft are capable of takeoff, en route navigation, and landing without human input. Development in this category is accelerating across both commercial and defense sectors. Companies such as Boeing, Airbus, and autonomous air mobility firms like Wisk Aero and Xwing are conducting flight tests to validate self piloting software capable of handling complex airspace interactions and emergency procedures.
The transition to fully autonomous operations will depend on regulatory approvals, robust data links, cybersecurity frameworks, and advancements in detect and avoid technology. Between 2025 and 2035, as AI models mature and 5G/6G communication infrastructure expands, fully autonomous flight will become viable for a wide range of applications including cargo transport, surveillance, and passenger mobility.
End Use Segmentation: Transforming Air Operations Across Sectors
The autonomous aircraft market serves diverse end use sectors, each driving unique technological requirements and operational models.
Commercial Applications
Commercial aviation is at the forefront of adopting autonomy to improve safety, efficiency, and cost effectiveness. Automated flight systems are already integrated into airliners, but the next decade will see the introduction of pilotless cargo planes and eventually passenger carrying air taxis. Companies like Reliable Robotics and Merlin Labs are developing retrofittable autonomy kits for existing aircraft, enabling pilot optional operations for regional routes.
Autonomous commercial aircraft will also reduce operational costs by minimizing crew requirements, optimizing routes using AI driven analytics, and reducing fuel consumption through precision navigation. As urban air mobility expands, autonomous commercial platforms will become an essential component of future air transport networks.
Combat and ISR (Intelligence, Surveillance, and Reconnaissance)
In defense, autonomy is revolutionizing combat and ISR operations. Autonomous military aircraft can perform high risk missions, collect intelligence, and conduct electronic warfare without endangering pilots. Systems like the U.S. Air Force’s Skyborg and Australia’s Loyal Wingman are leading examples of combat autonomy, where unmanned aircraft operate in coordination with manned platforms.
ISR missions benefit greatly from autonomy, as AI driven flight systems can process sensor data, identify threats, and relay critical information in real time. The integration of autonomous aircraft in defense strategies enhances situational awareness, speeds up decision cycles, and ensures mission persistence in contested environments.
Cargo Operations
Autonomous cargo aircraft represent one of the most promising commercial opportunities within this market. By eliminating pilot requirements, these aircraft can operate continuously, reduce turnaround times, and access remote areas with minimal infrastructure. Companies such as Natilus, Elroy Air, and Dronamics are developing large scale autonomous cargo systems designed to bridge logistical gaps in freight networks.
The expansion of e-commerce and supply chain digitization further accelerates this trend, as fully autonomous cargo operations offer cost savings and sustainability benefits through optimized flight planning and reduced emissions.
Passenger Air Vehicles (Urban Air Mobility)
Passenger air vehicles, often referred to as urban air taxis, are a central element of the future air mobility ecosystem. These aircraft are designed to transport individuals or small groups within urban and regional environments. Autonomous operation is key to making these systems scalable, safe, and economically viable.
Companies like Joby Aviation, Wisk Aero, and Archer Aviation are actively developing eVTOL (electric vertical takeoff and landing) aircraft that rely on advanced autonomy to manage navigation and airspace coordination. Regulatory agencies such as the FAA and EASA are working toward certification frameworks to ensure the safety of autonomous passenger operations.
Personal Air Vehicles
Beyond commercial air taxis, personal autonomous air vehicles are being designed for private ownership and point to point travel. These aircraft integrate intuitive AI based flight control systems that enable passengers to input destinations, after which the system autonomously manages flight execution. This emerging segment blends convenience, speed, and sustainability for individual mobility.
As energy storage technologies improve, personal autonomous aircraft will become a practical alternative to automobiles for short and medium distances, particularly in regions with high population density.
Air Medical Services
Autonomous aircraft are increasingly being adopted for emergency medical services and humanitarian operations. These systems can deliver critical supplies, transport organs for transplantation, and provide rapid medical evacuation in disaster zones. By removing the dependency on human pilots, autonomous aircraft ensure consistent operations even in dangerous or remote conditions.
In North America and Europe, pilot projects are underway for using autonomous drones and fixed wing platforms in air medical logistics, supporting hospitals and emergency response units with faster, safer, and cost efficient aerial delivery systems.
Component Segmentation: Building the Foundation of Autonomy
The performance of autonomous aircraft depends on a complex ecosystem of components that ensure real time perception, decision making, and control. These include sensors, actuators, flight control computers, communication systems, and software architectures that work in synchronization.
AI enabled flight computers act as the aircraft’s brain, processing inputs from multiple sensors including radar, LIDAR, infrared, GPS, and visual cameras. This data is used to create a live digital map of the environment, allowing the aircraft to navigate safely. Advanced algorithms ensure redundancy, fault tolerance, and adaptive learning capabilities that enhance safety even in unpredictable conditions.
Electric propulsion systems, lightweight composite structures, and distributed power architectures further complement the autonomous framework. The integration of these components with secure communication links and cybersecurity systems is essential to ensure operational reliability in both civil and military airspace.
Regional Analysis: Global Growth Dynamics (2025–2035)
North America
North America leads the global autonomous aircraft market due to strong investment from both defense and commercial sectors. The United States, through the Department of Defense and NASA, supports major autonomous aviation programs aimed at developing pilot optional combat and cargo aircraft. Commercial players such as Boeing, Joby Aviation, and Reliable Robotics are pioneering large scale autonomous flight tests, while regulatory agencies work to establish safety frameworks for autonomous operations.
Europe
Europe’s autonomous aviation ecosystem is driven by innovation in electric and sustainable flight systems. Airbus, Volocopter, and Lilium are leading European initiatives in autonomous urban air mobility and short haul transport. European Union programs such as SESAR are promoting the integration of autonomous aircraft into shared airspace, emphasizing safety, sustainability, and air traffic management harmonization.
Asia-Pacific
Asia Pacific is emerging as a key growth region due to increasing investments in autonomous drone and passenger air mobility systems. China, Japan, and South Korea are actively developing domestic solutions for logistics, surveillance, and passenger transport. The expansion of smart city projects and regional air mobility networks supports strong market potential for autonomous aviation in this region.
Middle East and Africa
The Middle East’s focus on advanced air mobility and defense modernization drives autonomous aircraft adoption, particularly for surveillance and cargo applications. The region’s growing interest in AI driven infrastructure aligns with the development of autonomous aviation ecosystems.
Latin America
Latin America’s adoption of autonomous aircraft is slower but steadily increasing in cargo delivery and humanitarian aid operations. Nations such as Brazil and Chile are exploring pilot programs for integrating autonomous aircraft into commercial and defense operations.
Technological Trends: AI, Connectivity, and Safety Systems
Artificial intelligence remains the backbone of autonomous aviation. Machine learning algorithms enable decision making, route optimization, and predictive maintenance. Combined with advanced connectivity technologies such as 5G and satellite communication, autonomous aircraft can exchange data with ground control stations, other aircraft, and air traffic management systems in real time.
Cybersecurity is another critical area of focus. As aircraft become more connected, protecting data integrity and preventing unauthorized access becomes paramount. Manufacturers are implementing encryption protocols and blockchain based authentication to safeguard mission critical systems.
Redundancy and fail safe design principles ensure operational safety. Multiple independent control systems provide backup in case of component failure, ensuring that autonomous aircraft can complete missions safely even under abnormal conditions.
Market Forecast and Future Outlook (2025–2035)
The autonomous aircraft market is expected to grow at a remarkable rate between 2025 and 2035 as autonomy transitions from experimental technology to mainstream adoption. Market growth will be fueled by rising demand for urban air mobility, logistics optimization, defense modernization, and AI driven efficiency improvements.
Fully autonomous operations are anticipated to become commercially viable in logistics and surveillance sectors by the early 2030s, followed by passenger operations once regulatory frameworks mature. Defense agencies will increasingly adopt autonomous systems for strategic missions, particularly in ISR and combat support roles.
Manufacturers will continue focusing on modularity, scalability, and energy efficient designs. Partnerships between aerospace firms, AI developers, and telecom providers will play a vital role in enabling large scale autonomous flight ecosystems.
The Dawn of Autonomous Aviation
The decade from 2025 to 2035 will mark a paradigm shift in global aviation. Autonomous aircraft will redefine how humanity perceives air travel, logistics, and defense operations. From increasingly autonomous commercial jets to fully self piloting cargo and passenger air vehicles, autonomy will reshape safety, efficiency, and sustainability across the aviation value chain.
As technology, regulation, and public trust align, autonomous aircraft will transition from innovation to integration, ushering in a new age of intelligent air mobility. This transformation represents not just an evolution of aircraft but a redefinition of flight itself where the sky is managed by algorithms, powered by AI, and driven by a vision of connected, sustainable, and autonomous aviation.

Table of Contents
1 Introduction (Page No. - 17)
1.1 Objectives of the Study
1.2 Market Definition
1.3 Market Scope
1.3.1 Regional Scope
1.3.2 Years Considered
1.4 Currency & Pricing
1.5 Limitations
1.6 Market Stakeholders
2 Research Methodology (Page No. - 21)
2.1 Research Data
2.1.1 Secondary Data
2.1.1.1 Key Data From Secondary Sources
2.1.2 Primary Data
2.1.2.1 Key Data From Primary Sources
2.1.2.2 Breakdown of Primaries
2.2 Market Size Estimation
2.2.1 Market Definition & Scope
2.2.2 Exclusions
2.3 Research Approach & Methodology
2.3.1 Bottom-Up Approach
2.3.1.1 Regional Autonomous Aircraft Market
2.3.1.2 Autonomous Aircraft Size
2.3.1.3 Autonomous Aircraft for End Use
2.3.1.4 Autonomous Aircraft for Futuristic Technologies
2.3.2 Top-Down Approach
2.4 Market Breakdown and Data Triangulation
2.5 Assumptions
3 Executive Summary (Page No. - 31)
4 Premium Insights (Page No. - 35)
4.1 Autonomous Aircraft Overview
4.2 Autonomous Aircraft Growth, By Autonomy Component
4.3 Autonomous Aircraft, By Technology
4.4 Autonomous Aircraft in Asia Pacific
4.5 Autonomous Aircraft Regional Analysis
4.6 Autonomous Aircraft, By End Use
5 Market Overview (Page No. - 39)
5.1 Introduction
5.2 Market Dynamics
5.2.1 Drivers
5.2.1.1 Increasing Operating Efficiency and Cost Savings
5.2.1.2 Reduced Human Error
5.2.1.3 Advancements in Artificial Intelligence (Ai)
5.2.2 Restraints
5.2.2.1 Safety During Emergency Situations
5.2.3 Opportunities
5.2.3.1 Reduced Emissions
5.2.3.2 on Demand Availability
5.2.4 Challenges
5.2.4.1 Public Acceptance
5.2.4.2 Infrastructure
5.2.4.3 Regulations
6 Industry Trends (Page No. - 43)
6.1 Introduction
6.2 Megatrends That Drive the Autonomous Aircraft
6.2.1 Artificial Intelligence
6.2.2 Big Data Analytics
6.2.3 Internet of Things (IoT)
6.3 Technology Trends
6.3.1 Smart Drones
6.3.1.1 Evolution of Smart Drones
6.3.2 Increasingly Autonomous (IA) Systems
6.3.2.1 Characteristics and Functions of IA Systems
6.3.3 Electric Propulsion
6.4 Innovations & Patent Registrations, 2008–2018
7 Autonomous Aircraft, By Technology (Page No. - 49)
7.1 Introduction
7.2 Increasingly Autonomous (IA)
7.2.1 Semi Autonomous Aircraft
7.3 Fully Autonomous
7.3.1 Aircraft Operations Without Any Human Intervention, But Remote Monitoring
8 Autonomous Aircraft, By End Use (Page No. - 52)
8.1 Introduction
8.2 Commercial Aircraft
8.2.1 Increasingly Autonomous Capability
8.3 Cargo & Delivery Aircraft
8.3.1 Package Pick Up and Delivery, Cargo Transport
8.4 Air Medical Services
8.4.1 Emergency Medical Services in Remote, Non-Accessible, Or Heavy Traffic Areas
8.5 Passenger Air Vehicle
8.5.1 Urban Air Mobility – Passenger Travel, Air Taxi
8.6 Personal Air Vehicle
8.6.1 One and Two Seater Aircraft for Intracity Travel
8.7 Combat and Isr
8.7.1 Military Operations With Autonomous Capabilities
8.8 Others
8.8.1 Agriculture, Science and Research, Survey, Mapping and Photography
9 Autonomous Aircraft, By Autonomy Component (Page No. - 58)
9.1 Introduction
9.2 Flight Management Computers
9.2.1 Processing Unit for Autonomous Operations
9.3 Air Data Inertial Reference Units (ADIRU)
9.3.1 Collecting Data to Provide Input to Efis and Flight Management Computer
9.4 Sensors
9.4.1 Advancements in Sensor Technology is Driving the Market
9.5 Actuation System
9.5.1 Driven By Increase in Number of Fully Autonomous Aircraft
9.6 Software
9.6.1 Algorithms That Drive Autonomous Aircraft
9.7 Intelligent Servos
9.7.1 Controls the Flight Control Autonomously
9.8 Cameras
9.8.1 Input Provider to the Display System
9.9 Radars & Transponders
9.9.1 Sense and Avoid System
9.10 Propulsion Systems
9.10.1 Advancements in Technology and Introduction of Evtols is Driving the Growth
10 Regional Analysis (Page No. - 65)
10.1 Introduction
10.2 North America
10.2.1 US
10.2.2 Canada
10.3 Europe
10.3.1 UK
10.3.2 France
10.3.3 Germany
10.3.4 Russia
10.3.5 Sweden
10.3.6 Rest of Europe
10.4 Asia Pacific
10.4.1 China
10.4.2 Japan
10.4.3 India
10.4.4 Australia
10.4.5 Rest of Asia Pacific
10.5 Rest of the World
10.5.1 Middle East
10.5.2 Africa
10.5.3 Latin America
11 Competitive Landscape (Page No. - 94)
11.1 Overview
11.2 Competitive Leadership Mapping
11.2.1 Autonomous Aircraft Industry Landscape
11.2.1.1 Visionary Leaders
11.2.1.2 Innovators
11.2.1.3 Dynamic Differentiators
11.2.1.4 Emerging Companies
11.3 Company Ranking Analysis: 2018
11.4 Competitive Scenario
11.4.1 Mergers & Acquisitions
11.4.2 New Product Launches
11.4.3 Contracts, Partnerships, & Agreements
12 Company Profiles (Page No. - 99)
(Business Overview, Products Offered, Recent Developments, SWOT Analysis, MnM View)*
12.1 Introduction
12.2 Northrop Grumman
12.3 Elbit Systems
12.4 Aerovironment
12.5 Lockheed Martin
12.6 Boeing
12.7 Aeronautics
12.8 Raytheon
12.9 Saab
12.10 BAE Systems
12.11 General Atomics Aeronautical Systems
12.12 Airbus
12.13 Embraer
12.14 Bell Helicopter
12.15 Startup Company Profiles
12.15.1 Volocopter GmbH
12.15.2 Kitty Hawk
12.15.3 Joby Aviation
12.15.4 Aston Martin
12.15.5 Wing
12.15.6 Karem Aircraft Inc.
12.15.7 Lift
*Details on Business Overview, Products Offered, Recent Developments, SWOT Analysis, MnM View Might Not Be Captured in Case of Unlisted Companies.
13 Appendix (Page No. - 137)
13.1 Discussion Guide
13.2 Knowledge Store: Marketsandmarkets’ Subscription Portal
13.3 Available Customizations
13.4 Related Reports
13.5 Author Details
List of Tables (75 Tables)
Table 1 Comparison of Advanced Automation and Autonomy
Table 2 Innovations & Patent Registrations
Table 3 Autonomous Aircraft Size, By Technology, 2016–2030 (USD Million)
Table 4 Increasingly Autonomous Aircraft, By Region, 2016–2030 (USD Million)
Table 5 Fully Autonomous Aircraft, By Region, 2016–2030 (USD Million)
Table 6 Autonomous Aircraft Size, By End Use, 2018–2030 (USD Million)
Table 7 Autonomous Aircraft for Commercial Aircraft, By Region, 2016–2030 (USD Million)
Table 8 Autonomous Aircraft for Commercial Aircraft, By Region, 2016–2030 (USD Million)
Table 9 Autonomous Aircraft for Air Medical Services, By Region, 2016–2030 (USD Million)
Table 10 Autonomous Aircraft for Air Taxi, By Region, 2016–2030 (USD Million)
Table 11 Autonomous Aircraft for Personal Air Vehicles, By Region, 2016–2030 (USD Million)
Table 12 Autonomous Aircraft for Combat and Isr, By Region, 2016–2030 (USD Million)
Table 13 Autonomous Aircraft for Others, By Region, 2016–2030 (USD Million)
Table 14 Autonomous Aircraft Size, By Autonomy Component, 2018–2030 (USD Million)
Table 15 Autonomous Aircraft for Flight Management Computers, By Region, 2016–2030 (USD Million)
Table 16 Autonomous Aircraft for Air Data Inertial Reference Unit, By Region, 2016–2030 (USD Million)
Table 17 Autonomous Aircraft for Sensors, By Region, 2016–2030 (USD Million)
Table 18 Autonomous Aircraft for Actuation System, By Region, 2016–2030 (USD Million)
Table 19 Autonomous Aircraft for Software, By Region, 2016–2030 (USD Million)
Table 20 Autonomous Aircraft for Intelligent Servos, By Region, 2016–2030 (USD Million)
Table 21 Autonomous Aircraft for Cameras, By Region, 2016–2030 (USD Million)
Table 22 Autonomous Aircraft for Radars & Transponders, By Region, 2016–2030 (USD Million)
Table 23 Autonomous Aircraft for Propulsion Systems, By Region, 2016–2030 (USD Million)
Table 24 Autonomous Aircraft Size, By Region, 2018-2030 (USD Million)
Table 25 North America: Autonomous Aircraft Size, By Technology, 2016–2030 (USD Million)
Table 26 North America: Autonomous Aircraft Size, By End Use, 2016–2030 (USD Million)
Table 27 North America: Autonomous Aircraft Size, By Autonomy Component, 2016–2030 (USD Million)
Table 28 North America: Autonomous Aircraft Size, By Country, 2016-2030 (USD Million)
Table 29 US: Autonomous Aircraft Size, By Technology, 2016–2030 (USD Million)
Table 30 US: Autonomous Aircraft Size, By End Use, 2016–2030 (USD Million)
Table 31 Canada: Autonomous Aircraft Size, By Technology, 2016–2030 (USD Million)
Table 32 Canada: Autonomous Aircraft Size, By End Use, 2016–2030 (USD Million)
Table 33 Europe: Autonomous Aircraft Size, By Technology, 2016–2030 (USD Million)
Table 34 Europe: Autonomous Aircraft Size, By End Use, 2016–2030 (USD Million)
Table 35 Europe: Autonomous Aircraft Size, By Autonomy Component, 2016–2030 (USD Million)
Table 36 Europe: Autonomous Aircraft Size, By Country, 2016-2030 (USD Million)
Table 37 UK: Autonomous Aircraft Size, By Technology, 2016–2030 (USD Million)
Table 38 UK: Autonomous Aircraft Size, By End Use, 2016–2030 (USD Million)
Table 39 France: Autonomous Aircraft Size, By Technology, 2016–2030 (USD Million)
Table 40 France: Autonomous Aircraft Size, By End Use, 2016–2030 (USD Million)
Table 41 Germany: Autonomous Aircraft Size, By Technology, 2016–2030 (USD Million)
Table 42 Germany: Autonomous Aircraft Size, By End Use, 2016–2030 (USD Million)
Table 43 Russia: Autonomous Aircraft Size, By Technology, 2016–2030 (USD Million)
Table 44 Russia: Autonomous Aircraft Size, By End Use, 2016–2030 (USD Million)
Table 45 Sweden: Autonomous Aircraft Size, By Technology, 2016–2030 (USD Million)
Table 46 Sweden: Autonomous Aircraft Size, By End Use, 2016–2030 (USD Million)
Table 47 Rest of Europe: Autonomous Aircraft Size, By Technology, 2016–2030 (USD Million)
Table 48 Rest of Europe: Autonomous Aircraft Size, By End Use, 2016–2030 (USD Million)
Table 49 Asia Pacific: Autonomous Aircraft Size, By Technology, 2016–2030 (USD Million)
Table 50 Asia Pacific: Autonomous Aircraft Size, By End Use, 2016–2030 (USD Million)
Table 51 Asia Pacific: Autonomous Aircraft Size, By Autonomy Component, 2016–2030 (USD Million)
Table 52 Asia Pacific: Autonomous Aircraft Size, By Country, 2016-2030 (USD Million)
Table 53 China: Autonomous Aircraft Size, By Technology, 2016–2030 (USD Million)
Table 54 China: Autonomous Aircraft Size, By End Use, 2016–2030 (USD Million)
Table 55 Japan: Autonomous Aircraft Size, By Technology, 2016–2030 (USD Million)
Table 56 Japan: Autonomous Aircraft Size, By End Use, 2016–2030 (USD Million)
Table 57 India: Autonomous Aircraft Size, By Technology, 2016–2030 (USD Million)
Table 58 India: Autonomous Aircraft Size, By End Use, 2016–2030 (USD Million)
Table 59 Australia: Autonomous Aircraft Size, By Technology, 2016–2030 (USD Million)
Table 60 Australia: Autonomous Aircraft Size, By End Use, 2016–2030 (USD Million)
Table 61 Rest of Asia Pacific: Autonomous Aircraft Size, By Technology, 2016–2030 (USD Million)
Table 62 Rest of Asia Pacific: Autonomous Aircraft Size, By End Use, 2016–2030 (USD Million)
Table 63 Rest of the World: Autonomous Aircraft Size, By Technology, 2016–2030 (USD Million)
Table 64 Rest of the World: Autonomous Aircraft Size, By End Use, 2016–2030 (USD Million)
Table 65 Rest of the World: Autonomous Aircraft Size, By Autonomy Component, 2016–2030 (USD Million)
Table 66 Rest of the World: Autonomous Aircraft Size, By Country, 2016-2030 (USD Million)
Table 67 Middle East: Autonomous Aircraft Size, By Technology, 2016–2030 (USD Million)
Table 68 Middle East: Autonomous Aircraft Size, By End Use, 2016–2030 (USD Million)
Table 69 Africa: Autonomous Aircraft Size, By Technology, 2016–2030 (USD Million)
Table 70 Africa: Autonomous Aircraft Size, By End Use, 2016–2030 (USD Million)
Table 71 Latin America: Autonomous Aircraft Size, By Technology, 2016–2030 (USD Million)
Table 72 Latin America: Autonomous Aircraft Size, By End Use, 2016–2030 (USD Million)
Table 73 Mergers & Acquisitions, 2016-2018
Table 74 New Product Launches, 2016-2018
Table 75 Contracts, Partnerships, & Agreements, 2016-2018
List of Figures (45 Figures)
Figure 1 Autonomous Aircraft Segmentation
Figure 2 Research Process Flow
Figure 3 Research Design
Figure 4 Bottom-Up Approach
Figure 5 Top-Down Approach
Figure 6 Data Triangulation Methodology
Figure 7 Regional Analysis: Autonomous Aircraft CAGR, 2018
Figure 8 Fully Autonomous Segment of Autonomous Aircraft, By Technology, Estimated to Account for A Major Share in 2018
Figure 9 Flight Management Computers Segment of Autonomous Aircraft, By Component, to Lead Globally in 2018
Figure 10 Air Medical Services Segment of Autonomous Aircraft, By End Use, Projected to Grow at Highest CAGR, During Forecast Period
Figure 11 Advancements in Artificial Intelligence Expected to Drive Market Growth From 2018 to 2030
Figure 12 Propulsion Systems Segment to Grow at Highest CAGR During Forecast Period
Figure 13 Fully Autonomous Segment of Autonomous Aircraft to Grow at Highest CAGR During Forecast Period
Figure 14 China Accounted for A Major Market Share of Asia Pacific Autonomous Aircraft in 2017
Figure 15 North America Accounted for Largest Share of Global Autonomous Aircraft in 2017
Figure 16 Combat & ISR Aircraft Projected to Lead Market During Forecast Period
Figure 17 Reduced Accidents Between 2008 and 2018
Figure 18 Autonomous Aircraft Size, By Technology, 2018–2030 (USD Million)
Figure 19 Autonomous Aircraft Size, By End Use, 2018–2030 (USD Million)
Figure 20 Autonomous Aircraft Size, By Autonomy Component, 2018–2030 (USD Million)
Figure 21 Rest of the World Autonomous Aircraft to Grow at the Highest CAGR During the Forecast Period
Figure 22 North America Autonomous Aircraft Snapshot (2018)
Figure 23 Europe: Autonomous Aircraft Snapshot (2018)
Figure 24 Asia Pacific Autonomous Aircraft Snapshot (2018)
Figure 25 Rest of the World Autonomous Aircraft Snapshot (2018)
Figure 26 Key Developments By Leading Players in the Autonomous Aircraft Between 2016 and 2018
Figure 27 Autonomous Aircraft Market Industry Competitive Leadership Mapping, 2018
Figure 28 Northrop Grumman: Company Snapshot
Figure 29 Northrop Grumman: SWOT Analysis
Figure 30 Elbit Systems: Company Snapshot
Figure 31 Elbit Systems: SWOT Analysis
Figure 32 Aerovironment: Company Snapshot
Figure 33 Aerovironment: SWOT Analysis
Figure 34 Lockheed Martin: Company Snapshot
Figure 35 Lockheed Martin: Company Snapshot
Figure 36 Boeing: Company Snapshot
Figure 37 Boeing: SWOT Analysis
Figure 38 Raytheon: Company Snapshot
Figure 39 Saab: Company Snapshot
Figure 40 BAE Systems: Company Snapshot
Figure 41 BAE Systems: SWOT Analysis
Figure 42 General Atomics Aeronautical Systems: Company Snapshot
Figure 43 Airbus: Company Snapshot
Figure 44 Airbus: SWOT Analysis
Figure 45 Embraer: Company Snapshot
The study involved 4 major activities in estimating the current market size for autonomous aircraft. Exhaustive secondary research was done to collect information on the market, peer market, and parent market. The next step was to validate these findings, assumptions, and sizing with industry experts across the value chain through primary research. Both, top-down and bottom-up approaches were employed to estimate the complete market size. Thereafter market breakdown and data triangulation were used to estimate the market size of segments and sub- segments.
Secondary Research
In the secondary research process, various secondary sources, such as Hoovers, Bloomberg BusinessWeek, and Dun & Bradstreet have been referred to, so as to identify and collect information for this study. These secondary sources included annual reports, press releases & investor presentations of companies, white papers, certified publications, articles by recognized authors, gold standard & silver standard websites, regulatory bodies, trade directories, and databases.
Primary Research
Prominent companies that manufacture autonomous aircraft, Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs), distributors, and end-customers (aircraft manufacturers and airline companies) are the key stakeholders in the supply chain of the autonomous aircraft market. The demand side of this market is characterized by increase in reduced emissions, and on-demand availability. The supply side is characterized by increased cost savings, reduction in human error due to increased autonomy, and advancements in artificial intelligence. Various primary sources from both, the supply and demand sides of the market were interviewed to obtain qualitative and quantitative information. Following is the breakdown of primary respondents.
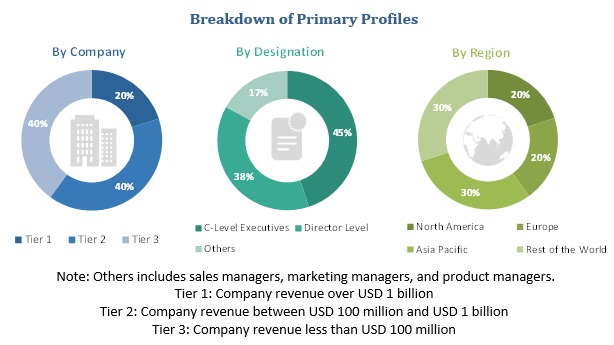
To know about the assumptions considered for the study, download the pdf brochure
Market Size Estimation
Both, top-down and bottom-up approaches were used to estimate and validate the total size of the autonomous aircraft market. These methods were also used extensively to estimate the size of various subsegments in the market. The research methodology used to estimate the market size includes the following:
- The key players in the industry and markets have been identified through extensive secondary research.
- The industry’s supply chain and market size, in terms of value, have been determined through primary and secondary research processes.
- All percentage shares, splits, and breakdowns have been determined using secondary sources and verified through primary sources.
Data Triangulation
After arriving at the overall market size—using the market size estimation processes as explained above—the market was split into several segments and subsegments. In order to complete the overall market engineering process and arrive at the exact statistics of each market segment and subsegment, data triangulation and market breakdown procedures were employed, wherever applicable. The data was triangulated by studying various factors and trends from both, the demand and supply sides.
Report Objectives
- To define, segment, and project the global market size of autonomous aircraft
- To understand the structure of the autonomous aircraft market by identifying its various subsegments
- To provide detailed information about the key factors influencing the growth of the market (drivers, restraints, opportunities, and industry-specific challenges)
- To analyze micromarkets with respect to individual growth trends, future prospects, and their contribution to the total market
- To project the size of the market and its submarkets, in terms of value, with respect to the 4 regions (along with their respective key countries)
- To profile key players and comprehensively analyze their core competencies
- To understand the competitive landscape and identify major growth strategies adopted by players across key regions
- To analyze competitive developments, such as expansions & investments, new product launches, mergers & acquisitions, joint ventures, and agreements in the autonomous aircraft market
Available Customizations
With the given market data, MarketsandMarkets offers customizations according to the company’s specific needs.
The following customization options are available for the report:
Product Analysis
- Product matrix, which gives a detailed comparison of the product portfolio of each company.
Regional Analysis
- Further breakdown of the autonomy component at country-level.
Company Information
- Detailed analysis and profiles of additional market players (up to 5).














Growth opportunities and latent adjacency in Autonomous Aircraft Market