
PFAS Filtration Market
PFAS Filtration Market by Technology (Water Treatment Systems, Water Treatment Chemicals), Place of Treatment (In-situ, Ex-situ), Remediation Technology (Activated Carbon, Ion Exchange Resin, RO Membrane & Nanofiltration), Contaminant Type, Environmental Medium, Service Type, End-use Industry, & Region - Global Forecast to 2031




OVERVIEW

Source: Secondary Research, Interviews with Experts, MarketsandMarkets Analysis
The PFAS filtration market is projected to reach USD 3.28 billion by 2031 from USD 2.34 billion in 2026 at a CAGR of 7.0% from 2026 to 2031. The market is experiencing strong growth due to many factors, such as stringent environmental regulations, growing public awareness, technological advancements, and government grants for PFAS research and removal. Industries across the chemicals manufacturing and water treatment sectors are implementing advanced filtration and destruction technologies to achieve compliance, decrease liabilities, and attain sustainability objectives.
KEY TAKEAWAYS
-
By RegionNorth America accounted for ~42% revenue share of the global PFAS filtration market in 2025.
-
By Remediation TechnologyBy remediation technology, the RO membrane & nanofiltration segment is expected to register the highest CAGR of 7.7%.
-
By TechnologyBy technology, the water treatment systems segment is projected to witness the highest growth rate from 2026 to 2031.
-
By Environmental MediumBy environmental medium, the groundwater segment is estimated to dominate the market.
-
By Place of TreatmentBy place of treatment, the ex-situ segment will grow at a high rate during the forecast period.
-
By Service TypeBy service type, the on-site segment is estimated to lead the market.
-
By End-use Industry TypeBy end-use industry type, the municipal segment is estimated to lead the market.
-
Competitive LandscapeVeolia (France), AECOM (US), and Xylem (US) were identified as some of the star players in the PFAS filtration market (global), given their strong market share and product footprint.
-
Competitive LandscapeEurowater, Aquasana Inc., and Newterra Corporation, among others, have distinguished themselves among startups and SMEs by securing strong footholds in specialized niche areas, underscoring their potential as emerging market leaders
The PFAS filtration market is experiencing growth due to stringent environmental regulations, growing public awareness, technological advancement, and government grants for PFAS research and removal. North America is leading the PFAS filtration market, followed by Europe with strict REACH norms, while Asia Pacific is emerging as the fastest-growing regional market due to continuous industrial expansion and stringent environmental regulations.
TRENDS & DISRUPTIONS IMPACTING CUSTOMERS' CUSTOMERS
Changes in customer trends or disruptions impact consumers’ businesses. These shifts impact the revenues of end users. Consequently, the revenue impact on end users affects the revenues of PFAS filtration product suppliers, which, in turn, impacts the revenues of PFAS filtration product manufacturers.

Source: Secondary Research, Interviews with Experts, MarketsandMarkets Analysis
MARKET DYNAMICS
Level
-
Increasing regulatory scrutiny and tightening environmental regulations regarding PFAS contamination

-
Rising litigation and liability costs for polluters
Level
-
Expensive and complex filtration process
-
Limited availability of trained professionals
Level
-
Significant government funding and support for PFAS R&D and filtration efforts
-
Significant potential to expand globally
Level
-
Proper management of PFAS treatment residuals
-
Retrofitting existing water treatment plants for PFAS filtration
Source: Secondary Research, Interviews with Experts, MarketsandMarkets Analysis
Driver: Increasing regulatory scrutiny and tightening environmental regulations regarding PFAS contamination
Stringent regulatory pressure and strengthened environmental standards against PFAS pollution are fueling top-line growth for the PFAS filtration industry. PFAS are synthetic chemicals used across several industrial and consumer goods to provide heat, water, and oil resistance. However, their persistence in the environment and human tissue has led to highly critical ailments such as cancer, immune impairment, and developmental delays. Consequently, several regulatory bodies are instituting tighter controls to reduce exposure to PFAS, particularly in drinking water. In April 2024, the US EPA issued a rule adding two harmful PFAS chemicals—PFOA and PFOS—to the list of hazardous substances under the Comprehensive Environmental Response, Compensation, and Liability Act (CERCLA). This action promotes transparency and accountability in PFAS cleanup activities. The EPA also issued an enforcement discretion policy to ensure that cleanup burdens address the major contributors to PFAS pollution. In addition, through collaboration with the General Services Administration (GSA), the EPA introduced modifications requiring that cleaning products used in federal facilities be PFAS-free and that environmentally certified products—such as those carrying EPA’s Safer Choice or GreenSeal labels—be used. These federal initiatives, combined with rising public awareness and increasing pressure for industries to meet PFAS discharge limits, are driving demand for efficient PFAS filtration technologies and positioning the market for continued innovation and growth.
Restraint: Expensive and complex filtration process
The high operational expenses and extensive processing requirements of PFAS filtration systems create a major obstacle that prevents their widespread application in various end-use industries such as chemical, automotive, coatings, and others. The successful removal of PFAS contaminants from water requires treatment systems that use both granular activated carbon (GAC) and ion exchange resins, and high-pressure membrane technologies, which include reverse osmosis. The systems show operational efficiency while consuming high capital expenses through their establishment and operational requirements to treat extensive contaminated water stores and achieve extremely low PFAS disposal standards. The deployment of these systems demands specific equipment, which includes energy-consuming parts and special materials, and requires trained staff members to operate. The disposal of PFAS-contaminated filter media and PFAS-concentrated waste materials creates regulatory difficulties, which result in higher operational expenses and complicated treatment procedures. Industry operators encounter both financial challenges and operational difficulties, which prevent them from using complete filtration systems due to increasing regulatory requirements for PFAS and other hazardous environmental pollutants. The development of cost-effective and advanced PFAS treatment technologies, which can be expanded to larger applications, requires financial resources, grant opportunities, and supportive policy measures according to the current needs.
Opportunity: Significant government funding and support for PFAS R&D and filtration efforts
Increasing government investment and various institutional support to remove PFAS from the waste stream create growth opportunities for many industry players. Governments are boosting their research and remediation funding because they have discovered the extensive environmental risks and health dangers posed by PFAS man-made chemicals through their presence in firefighting foams, food packaging, and clothing products. The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) in the US has dedicated USD 50 million to combat PFAS pollution throughout the country. The funding supports both environmental cleanup work and the development of advanced technologies, which will improve PFAS detection, removal, and destruction capabilities. PFAS, or per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances, consist of almost 15000 chemical compounds that remain in the environment because they possess permanent chemical properties that allow them to build up in air, water, and soil. The National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences reports that people become exposed to these chemicals through their contact with contaminated drinking water, food, and consumer goods. Government-sponsored programs are not only accelerating technological innovation but also strengthening the regulatory and financing environment for companies and researchers involved in PFAS remediation.
Challenge: Proper management of PFAS treatment residuals
The PFAS filtration industry faces its most significant obstacle in the management process of treating waste materials that result from PFAS extraction operations. The process of PFAS removal from contaminated water using granular activated carbon (GAC) and ion exchange resins and reverse osmosis technology succeeds in separating PFAS from water, but it cannot destroy chemicals. The process creates residual waste streams that contain PFAS, which include used carbon and spent resins, and extremely contaminated brine. The process of handling PFAS-contaminated waste requires extensive resources to execute because it presents critical environmental hazards that must be managed to stop environmental contamination from recurring. The available disposal methods face tight government restrictions that make them difficult to access. The few methods that can break down PFAS compounds include high-temperature incineration, which requires a lot of energy to operate and incurs high costs while creating environmental risks through incomplete combustion and secondary pollutant emissions. The process of landfilling creates easier disposal options, but it will pollute water and soil. The environmental advantages of the PFAS filtration process become less effective when the residual management system fails to operate correctly. The development of safe technologies that can be scaled cost-effectively to manage PFAS waste requires urgent action to achieve sustainable solutions for PFAS remediation programs.
PFAS FILTRATION MARKET: COMMERCIAL USE CASES ACROSS INDUSTRIES
| COMPANY | USE CASE DESCRIPTION | BENEFITS |
|---|---|---|
 |
Implementation of advanced membrane and ion-exchange filtration systems for wastewater from specialty chemicals and coatings production. | Achieved regulatory compliance with EU PFAS limits. |
 |
Deployment of adsorptive and electrochemical PFAS removal technologies for process water at fluorochemical plants. | Strengthened environmental stewardship and ESG profile. |
 |
Adoption of industrial PFAS removal filters for textile dyeing and finishing wastewater treatment. | Reduced environmental and social risk exposure. |
Logos and trademarks shown above are the property of their respective owners. Their use here is for informational and illustrative purposes only.
MARKET ECOSYSTEM
The PFAS filtration ecosystem analysis involves identifying and evaluating the interconnected relationships among key stakeholders, including raw material suppliers, equipment suppliers, manufacturers, distributors, and end users. Raw material suppliers provide essential inputs such as filters, granular activated carbon (GAC), ion exchange resins, and other materials to PFAS filtration manufacturers. Distributors and suppliers play a critical role in connecting manufacturers with various end-use industries, helping streamline the supply chain and improve operational efficiency and profitability.

Logos and trademarks shown above are the property of their respective owners. Their use here is for informational and illustrative purposes only.
MARKET SEGMENTS

Source: Secondary Research, Interviews with Experts, MarketsandMarkets Analysis
PFAS Filtration Market, By Remediation Technology
Reverse osmosis (RO) and nanofiltration (NF) are two advanced PFAS treatment methods that effectively eliminate multiple PFAS substances, including short-chain PFAS that standard techniques fail to capture. The membrane-based technologies use pressure to drive polluted water through semi-permeable membranes, which prevent PFAS molecules and other pollutants from passing through. RO eliminates more than 90% of PFAS compounds, which makes it the ideal choice for both municipal and industrial water treatment systems. The increasing need for ultra-low PFAS detection in drinking water, combined with the development of more effective treatment systems, has led to greater usage of RO and NF systems. The traditional method for removing PFAS involves the use of granular activated carbon (GAC) and ion exchange resins, which effectively remove long-chain PFAS but fail to handle short-chain compounds. The RO and NF systems deliver advanced treatment capabilities that function effectively under different water quality conditions. The RO and NF technologies are expanding because they provide superior PFAS removal capabilities and operational flexibility, which makes them essential for upcoming PFAS remediation efforts as regulations increase.
PFAS Filtration Market, By Technology Type
The requirement to remove PFAS hazardous substances from water sources has led to rapid progress in PFAS water treatment technologies. The field of water treatment uses standard technologies, which include granular activated carbon (GAC), ion exchange resins, DEXSORB, reverse osmosis (RO), and nanofiltration (NF) systems. GAC serves as a main choice because it enables cost-efficient operations, while its strong adsorption capacity enables the removal of long-chain PFAS compounds. The PFAS removal system uses ion exchange resins because they provide better selectivity and efficiency for different PFAS compounds through their ability to remove PFAS molecules via ion exchange. The PFAS filtration industry currently experiences rapid market growth from nanofiltration and reverse osmosis systems, which represent the most advanced filtration technologies. The membrane-based systems force water to pass through semi-permeable membranes, which achieve 99% PFAS compound removal efficiency for both long- and short-chain variants. The RO and NF systems provide complete filtration solutions that businesses require to comply with government rules about PFAS pollution and to address growing public health concerns. Reverse osmosis and nanofiltration systems achieve high removal efficiency while providing scalable capacity, which results in their rapid installation for municipal and industrial water treatment systems to become key elements of future PFAS water treatment solutions.
REGION
Asia Pacifi to be fastest-growing region in global PFAS filtration market during forecast period
The PFAS filtration market in the Asia Pacific region (APAC) is experiencing strong development due to robust industrial growth and growing public awareness of health risks associated with PFAS contamination. The extensive use of PFAS chemicals in various applications is causing China, India, and South Korea to experience increasing levels of PFAS contamination. The public's growing concern about health risks linked to PFAS is leading regional governments to implement more stringent water quality standards and wastewater treatment requirements. Public utilities and private industries are investing in advanced PFAS filtration technologies because infrastructure expansion and stronger Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) commitments create a need for better waste treatment systems. The combination of government regulations, increased demand for fresh water, and industry accountability advancements has established APAC as the region with the fastest development of PFAS filtration systems.

PFAS FILTRATION MARKET: COMPANY EVALUATION MATRIX
In the PFAS filtration market matrix, Veolia (Star), a France-based company, leads the market through its high-quality PFAS filtration products, such as RO, carbon adsorption, and ion exchange resin, which find extensive applications in various end-use industries such as industrial, municipal, and others. Cyclopure (Emerging Leader) is gaining traction with its technological advancements in PFAS filtration.

Source: Secondary Research, Interviews with Experts, MarketsandMarkets Analysis
KEY MARKET PLAYERS
- Veolia (France)
- AECOM (US)
- WSP (Canada)
- Clean Earth (US)
- Wood (UK)
- Xylem (US)
- Jacobs (US)
- TRC Companies, Inc. (US)
- Battelle Memorial Institute (US)
- Cyclopure, Inc. (US)
- Ecolab (US)
- Ion Exchange (India)
- Calgon Carbon Corporation (US)
- Regenesis (US)
- Mineral Technologies, Inc. (US)
- Pentair (UK)
MARKET SCOPE
| REPORT METRIC | DETAILS |
|---|---|
| Market Size in 2025 (Value) | USD 2.17 Billion |
| Market Forecast in 2031 (Value) | USD 3.28 Billion |
| Growth Rate | CAGR of 7.0% from 2026 to 2031 |
| Years Considered | 2022-2031 |
| Base Year | 2025 |
| Forecast Period | 2026-2031 |
| Units Considered | Value (USD Million/Billion), Volume (Kilotons) |
| Report Coverage | Revenue forecast, company ranking, competitive landscape, growth factors, and trends |
| Segments Covered |
|
| Regions Covered | North America, Asia Pacific, Europe, South America, Middle East & Africa |
WHAT IS IN IT FOR YOU: PFAS FILTRATION MARKET REPORT CONTENT GUIDE

DELIVERED CUSTOMIZATIONS
We have successfully delivered the following deep-dive customizations:
| CLIENT REQUEST | CUSTOMIZATION DELIVERED | VALUE ADDS |
|---|---|---|
| Leading PFAS filtration products supplier |
|
Supported go-to-market strategy and positioning vs. competitors |
| Country-level insights for high-growth regions | Provided detailed market sizing and forecasts for North America and Asia Pacific | Helped the client identify region-specific growth hotspots and investment opportunities |
| Identify emerging PFAS filtration technologies | Conducted technology scouting and feasibility analysis | Supported investment decisions and innovation roadmap for clients |
| Evaluate regulatory compliance for new market entry | Compiled local emission, safety, & efficiency standards per country | Ensured smooth market entry and minimized legal risks |
RECENT DEVELOPMENTS
- June 2024 : AECOM, a globally trusted infrastructure consulting firm, and Aquatech, a leader in water and process technology, partnered to fast-track the deployment of per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) destruction technology. This collaboration combined AECOM’s top-ranked water and environmental practice, along with its innovative DE-FLUORO PFAS destruction technology, and Aquatech’s expertise in process and electrochemical technology, as well as its proven track record in scaling end-to-end technology solutions and services. The combined strengths of these two industry leaders will help accelerate DE-FLUORO as a premier solution for PFAS destruction.
- January 2024 : Clean Earth launched Resolve, a new program that offers a toolbox of innovative solutions to treat and remediate PFAS, and a website detailing news, updates, and guidance on PFAS in the US.
- June 2023 : Veolia Water Technologies expanded its mobile water services fleet in China by adding new modular trailer-mounted reverse osmosis (RO) systems. This expansion enhanced the company's range of mobile solutions tailored for the Chinese market. By integrating the latest modular trailer-mounted RO units, Veolia reinforces its commitment to delivering innovative water treatment solutions to its customers in China. Alongside the RO units, the fleet also features filtration, ultrafiltration, and deionization systems. The addition of these new RO mobile units will boost capacity to meet the increasing demand for dependable and efficient water treatment solutions across China.
- January 2023 : Xylem acquired Evoqua, a leader in mission-critical water treatment solutions and services. Under the agreement, Xylem will acquire Evoqua in an all-stock transaction that reflects an implied enterprise value of approximately USD 7.5 billion. This acquisition creates a transformative global platform to address water scarcity, affordability, and resilience at an even greater scale.
- September 2022 : WSP announced the acquisition of the environment & infrastructure business of John Wood. With this, WSP expanded its environmental leadership. This move will also enable the company to further seize opportunities in the fast-growing environmental and water sectors.
Table of Contents

Methodology
The study involved two major activities in estimating the current market size for the PFAS filtration market. Exhaustive secondary research was carried out to collect information on the market, peer market, and parent market. The next step involved validating these findings, assumptions, and sizing with industry experts across the value chain through primary research. Both top-down and bottom-up approaches were employed to estimate the complete market size. Following this, market breakdown and data triangulation were employed to determine the market size of segments and subsegments.
Secondary Research
Secondary sources referred to for this research study included financial statements of companies offering PFAS filtration and information from various trade, business, and professional associations. Secondary research was used to obtain critical information about the industry’s value chain, the total pool of key players, market classification, and segmentation according to industry trends to the bottom-most level and regional markets. The secondary data was collected and analyzed to arrive at the overall size of the PFAS filtration market, which was validated by primary respondents.
Primary Research
Extensive primary research was conducted after obtaining information regarding the PFAS filtration market scenario through secondary research. Several primary interviews were conducted with market experts from both the demand and supply sides across major countries of North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, the Middle East & Africa, and South America. Primary data was collected through questionnaires, emails, and telephonic interviews. The primary sources from the supply side included various industry experts, such as Chief X Officers (CXOs), Vice Presidents (VPs), Directors from business development, marketing, product development/innovation teams, and related key executives from PFAS filtration industry vendors, material providers, distributors, and key opinion leaders. Primary interviews were conducted to gather insights, including market statistics, revenue data from products and services, market breakdowns, market size estimations, market forecasting, and data triangulation. Primary research also helped in understanding the various trends related to materials, sources, manufacturing processes, applications, and regions. Stakeholders from the demand side, such as CIOs, CTOs, CSOs, and installation teams of the customers/end users who are seeking PFAS filtration, were interviewed to understand the buyer’s perspective on the suppliers, products, component providers, and their current usage of PFAS filtration products and future outlook of their business, which will affect the overall market.
Breakup of Primary Research:
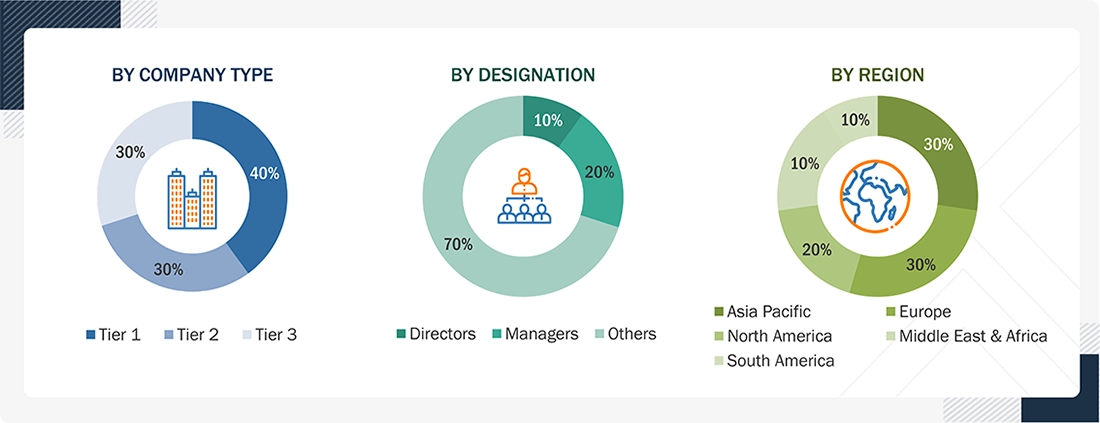
To know about the assumptions considered for the study, download the pdf brochure
Market Size Estimation
The research methodology used to estimate the size of the PFAS filtration market includes the following details. The market sizing of the market was undertaken from the demand side. The market was upsized based on the demand for PFAS filtration products in different applications at a regional level. Such procurements provide information on the demand aspects of the PFAS filtration industry for each end-use industry. For each end-use industry, all possible segments of the PFAS filtration market were integrated and mapped.
PFAS Filtration Market : Top-Down and Bottom-Up Approach

Data Triangulation
The PFAS filtration market encompasses various technologies, media, systems, and related services designed to remove PFAS compounds from water and environmental media. This process aims to meet stringent regulatory standards that protect public health and enable safe discharge or reuse. The solutions include various adsorption media, such as granular activated carbon, ion exchange resins, DEXSORB, and engineered treatment systems. These are complemented by additional technologies and support services that cater to municipal drinking water, industrial wastewater, groundwater remediation, and various other sectors.
Key Stakeholders
- PFAS Filtration Product Manufacturers
- PFAS Filtration Product Distributors and Suppliers
- Universities, Governments, and Research Organizations
- Associations and Industrial Bodies
- R&D Institutes
- Environmental Support Agencies
- Investment Banks and Private Equity Firms
- Research and Consulting Firms
Report Objectives
- To define, describe, and forecast the PFAS filtration market size in terms of volume and value
- To provide detailed information regarding the key factors, such as drivers, restraints, opportunities, and challenges influencing market growth
- To analyze and project the market based on technology, remediation technology, contaminant type, environmental medium, place of treatment, service type, end-use industry, and region
- To forecast the market size concerning five main regions (along with country-level data), namely, North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Middle East & Africa, and South America, and analyze the significant region-specific trends
- To strategically analyze micromarkets with respect to individual growth trends, prospects, and contributions of the submarkets to the overall market
- To analyze the market opportunities and competitive landscape for stakeholders and market leaders
- To assess recent market developments and competitive strategies, such as agreements, contracts, acquisitions, partnerships & collaborations, and product developments/launches, to draw the competitive landscape
- To strategically profile the key market players and comprehensively analyze their core competencies
Available customizations:
MarketsandMarkets offers the following customizations for this market report:
- Additional country-level analysis of the PFAS filtration market
Product Analysis
- Product matrix, which provides a detailed comparison of the product portfolio of each company's market
Key Questions Addressed by the Report
Need a Tailored Report?
Customize this report to your needs
Get 10% FREE Customization
Customize This ReportPersonalize This Research
- Triangulate with your Own Data
- Get Data as per your Format and Definition
- Gain a Deeper Dive on a Specific Application, Geography, Customer or Competitor
- Any level of Personalization
Let Us Help You
- What are the Known and Unknown Adjacencies Impacting the PFAS Filtration Market
- What will your New Revenue Sources be?
- Who will be your Top Customer; what will make them switch?
- Defend your Market Share or Win Competitors
- Get a Scorecard for Target Partners
Custom Market Research Services
We Will Customise The Research For You, In Case The Report Listed Above Does Not Meet With Your Requirements
Get 10% Free Customisation














Growth opportunities and latent adjacency in PFAS Filtration Market