Confidential Computing Market by Component (Hardware, Software, Services), Application (Data Security, Secure Enclaves, Pellucidity Between Users), Deployment Mode, Vertical (Retail & Consumer Goods, BFSI) and Region - Global Forecast to 2028
Updated on : Feb 17, 2026
Confidential Computing Market - Worldwide | Future Scope & Trends
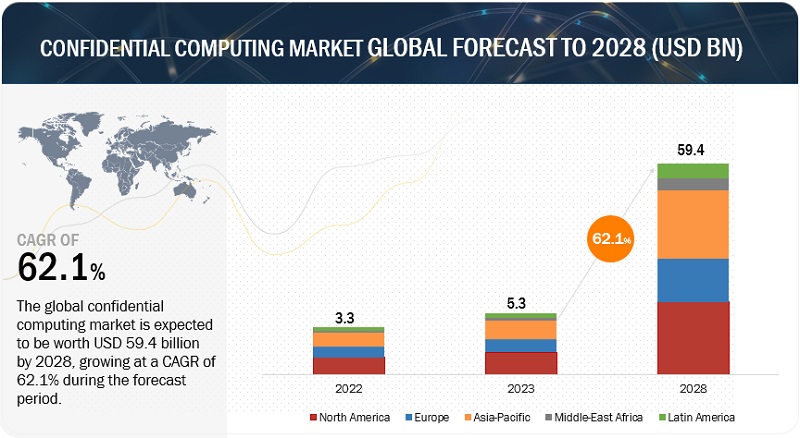
The Confidential Computing Market is projected to grow significantly, increasing from USD 5.3 billion in 2023 to USD 59.4 billion by 2028, with a robust CAGR of 62.1%. Confidential computing is an emerging field of technology that focuses on securing data while it is being processed, thereby protecting sensitive information from unauthorized access. It enables organizations to safeguard their data even when processed in untrusted environments such as cloud servers or third-party systems. Traditional computing models assume that the operating system, hypervisor, and hardware platforms are trustworthy. However, confidential computing acknowledges that these components can be compromised and employs various techniques to ensure data confidentiality, integrity, and privacy during processing. One of the key technologies in confidential computing is the concept of secure enclaves or trusted execution environments (TEEs). These hardware-based mechanisms create isolated environments within a computing system, protecting data and code from being accessed or modified by unauthorized entities. Popular implementations of TEEs include Intel SGX (Software Guard Extensions) and AMD SEV (Secure Encrypted Virtualization).
To know about the assumptions considered for the study, Request for Free Sample Report
To know about the assumptions considered for the study, download the pdf brochure
Recession Impact on the Confidential Computing Market
The global recession caused by the COVID-19 pandemic has had a mixed impact on the confidential computing market. During a recession, businesses are facing budget constraints and prioritizing cost-cutting measures. Investments in new technologies, including confidential computing solutions, may be deprioritized or delayed as organizations focus on essential expenses and core operations. In a recession, organizations reduce their overall IT spending, which impacts the adoption of emerging technologies such as confidential computing. Companies allocate their limited resources to areas perceived as more critical or directly tied to immediate cost savings. During a recession, businesses often emphasize cost efficiency and optimization. Confidential computing solutions need to demonstrate their value proposition in terms of cost savings, risk reduction, and improved operational efficiency to attract customers who are looking for tangible benefits amidst economic uncertainties. Economic downturns lead to increased competition as businesses seek to differentiate themselves and capture a smaller market. Confidential computing solution providers face intensified competition, which impacts pricing and market penetration strategies. The impact of a recession on the confidential computing market can be mixed. While budget constraints and reduced IT spending may pose challenges, increased security concerns, remote work trends, and regulatory compliance requirements create opportunities for confidential computing solution providers. Adapting to the economic landscape and effectively communicating the value proposition of data security and privacy will be crucial for the market's growth during recessionary periods.
Confidential Computing Market Dynamics
Driver: Increasing need to meet regulatory requirements
Data privacy regulations such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) require businesses to protect their customers' data. Confidential computing provides a secure and private processing environment that can help organizations comply with these regulations. For instance, GDPR requires that personal data be processed in a manner that ensures appropriate security of the data, including protection against unauthorized or unlawful processing. Confidential computing can help organizations meet this requirement by ensuring data is processed securely and privately. Various compliance regulations in different industries, such as healthcare, finance, and government, require organizations to protect sensitive data. For instance, the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) requires healthcare organizations to protect patient data. Confidential computing helps these organizations comply with HIPAA requirements by providing secure processing environments for sensitive data. Cloud security regulations such as the Federal Risk and Authorization Management Program (FedRAMP) and the Cloud Security Alliance (CSA) require cloud service providers to implement security controls to protect customer data. Confidential computing provides a layer of security for cloud service providers by ensuring that customer data is processed in a secure and private environment. Confidential computing enables organizations to protect their intellectual property. For instance, trade secrets are protected by law, and businesses must take reasonable steps to protect them. Confidential computing provides a secure processing environment that can help organizations protect their trade secrets from being accessed or compromised by unauthorized users.
Restraint: High cost related to confidential computing
One of the key restraints in the confidential computing market is the high cost of implementing and maintaining these solutions. Confidential computing technologies often require significant investment in hardware, software, and personnel, making it difficult for small and medium-sized businesses to adopt them. The high costs of confidential computing solutions are driven by several factors, including:
- Hardware costs: Confidential computing solutions often require specialized hardware, such as secure enclaves or dedicated processors, to ensure the security and privacy of data and computations. This hardware can be expensive to procure and maintain and may require additional investments in infrastructure, such as data centers.
- Software costs: Besides specialized hardware, confidential computing solutions require software to manage and secure data and computations. This software may be proprietary and licensed by vendors, adding to the overall cost of implementation and maintenance.
- Personnel costs: Confidential computing solutions also require skilled professionals with expertise in data security, cryptography, and cloud computing to implement and maintain them. Hiring and retaining these professionals can be costly and require ongoing training to keep their skills up to date.
- Integration costs: Confidential computing solutions must also be integrated with the existing IT infrastructure, which can be time-consuming and expensive. This can involve adapting existing systems and applications to work with confidential computing solutions or developing new systems and applications from scratch.
- Ongoing maintenance costs: Maintaining confidential computing solutions requires ongoing monitoring, updates, and troubleshooting. This can be costly and time-consuming, especially if the solutions are complex or involve multiple components.
Opportunity: Growing need of confidential AI solutions
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is also on the rise, and there is a growing need for solutions that can help protect the confidentiality of AI models and data. Confidential AI solutions use secure enclaves and homomorphic encryption technologies to protect sensitive AI data. Confidential AI refers to a set of technologies and practices used to protect the confidentiality and privacy of sensitive data in artificial intelligence (AI) applications. AI models are typically trained on large datasets that contain sensitive information, such as personally identifiable information (PII) or proprietary business data. These models can then make predictions or decisions based on new data. However, using sensitive data in AI applications creates significant privacy and security risks. If an AI model is not properly secured, it could be vulnerable to attacks that compromise the confidentiality of the data it uses.
Challenge: Complexity associated with confidential computing technology
Confidential computing requires specialized knowledge and skills to implement and maintain, which, in turn, creates a barrier to entry for some businesses and organizations, particularly smaller ones with limited IT resources. There are several reasons which include the technology behind confidential computing is relatively new and constantly evolving. It requires specialized expertise in cryptography, secure enclaves, and trusted execution environments, which may not be widely available within many organizations. Additionally, confidential computing solutions often involve integrating with the existing IT infrastructure, which can be challenging. This requires extensive testing and debugging to ensure the solution functions as intended and not introduce new vulnerabilities or compatibility issues. The complexity of confidential computing can also create challenges around deployment and management.
Based on component, services is projected to witness the second highest CAGR during the forecast period
Services play a significant role in the implementation, deployment, and management of confidential computing solutions. They provide expertise, support, and specialized offerings to help organizations adopt and leverage confidential computing technologies. Confidential computing services offer consulting and advisory services to organizations, helping them understand the benefits, risks, and implications of adopting confidential computing. They provide guidance on selecting the right technologies, designing secure architectures, and defining security policies for confidential computing implementations. Services assist organizations in designing and integrating confidential computing solutions into their existing infrastructure and applications. They help identify use cases, develop architecture blueprints, and ensure seamless integration of secure enclaves or TEEs into the overall system design.
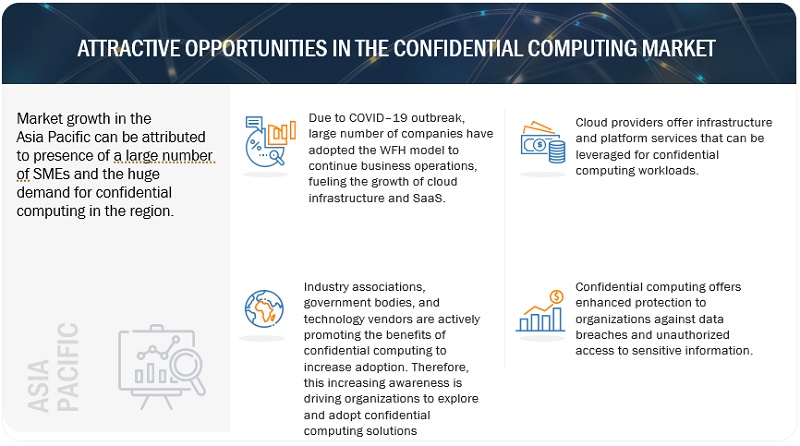
Based on vertical, the Retail & Consumer Goods vertical is projected to witness the highest CAGR during the forecast period.
Retail and consumer goods companies handle vast amounts of customer data, including personal information, purchasing history, and payment details. Confidential computing ensures the protection of this sensitive data, preventing unauthorized access and reducing the risk of data breaches, identity theft, and fraud. Confidential computing enhances the security of payment processing in the retail sector. By securely executing payment transactions within a trusted environment, confidential computing protects sensitive payment information, such as credit card numbers and authentication data, ensuring the privacy and integrity of customer transactions. The retail and consumer goods sector is also subject to data privacy regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS). Confidential computing assists companies in complying with these regulations by providing secure data processing and storage mechanisms, ensuring data privacy, and protecting against data breaches.
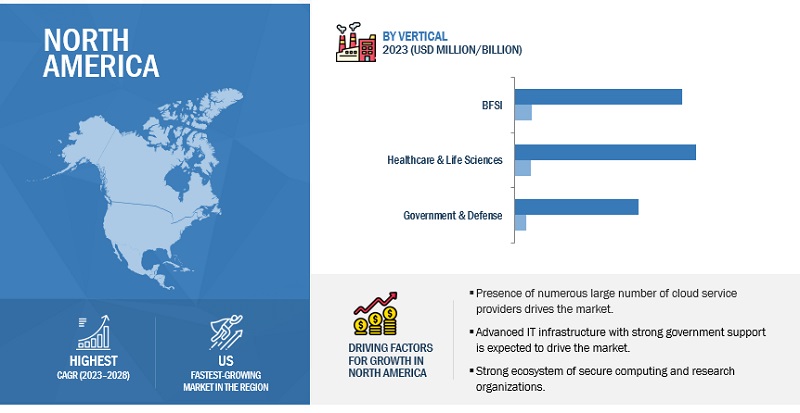
The US market is projected to contribute the largest share for the confidential computing market in North America.
North America is expected to lead the confidential computing market in 2023. The US is estimated to account for the largest market share in North America in 2023 in the confidential computing market, and the trend is expected to continue until 2028. Due to a number of factors, including advanced IT infrastructure, the existence of numerous businesses, and the availability of technical skills, it is the most developed market in terms of the adoption of confidential computing. Legal requirements, such as FedRAMP, a standardized approach to security assessment, authorization, and continuous monitoring for cloud products and services, also influence the adoption of confidential computing. The increasing need for data privacy and security, coupled with advancements in technology, has driven the demand for confidential computing solutions. Various industries in the US are adopting confidential computing to protect sensitive data and comply with data protection regulations. Industries such as finance, healthcare, government, and technology are among the leading adopters. Confidential computing enables secure data processing, storage, and analysis while preserving data privacy and confidentiality. Major cloud service providers in the US, including Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP), offer confidential computing services.
Key Market Players
The confidential computing market is dominated by a few globally established players such as Microsoft (US), IBM (US), Intel (US), Google (US), and AMD (US) among others, are the key vendors that secured confidential computing contracts in last few years. These vendors can bring global processes and execution expertise to the table, the local players only have local expertise. Driven by increased disposable incomes, easy access to knowledge, and fast adoption of technological products, buyers are more willing to experiment/test new things in the confidential computing market.
Scope of the Report
|
Report Metrics |
Details |
|
Market size available for years |
2019–2028 |
|
Base year considered |
2022 |
|
Forecast period |
2023–2028 |
|
Forecast units |
Million/Billion(USD) |
|
Segments Covered |
Component, Application, Deployment Mode, and Vertical |
|
Geographies Covered |
North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Middle East & Africa, and Latin America |
|
Companies Covered |
Some of the major vendors offering confidential computing across the globe include Some of the major vendors offering confidential computing across the globe are Microsoft (US), IBM (US), Intel (US), Google (US), AMD (US), Fortanix (US), AWS (US), Arm (UK), Alibaba Cloud (China), Swisscom (Switzerland), OVHcloud (France), pheonixNAP (US), AMI (Georgia), and more. |
This research report categorizes the confidential computing market based on component, application, deployment mode, verticals, and regions.
Based on the Component:
- Hardware
- Software
- Services
Based on the Deployment Mode:
- On-Premises
- Cloud
Based on the Application:
- Data Security
- Secure Enclaves
- Pellucidity Between Users
- Other Applications
Based on the Vertical:
- BFSI
- Government & Defense
- Healthcare & Life Sciences
- IT & Telecommunications
- Manufacturing
- Retail & Consumer Goods
- Education
- Other Verticals
Based on the Region:
-
North America
- United States
- Canada
-
Europe
- Germany
- UK
- France
- Rest of Europe
-
Asia Pacific
- Japan
- China
- India
- Rest of Asia Pacific
-
Middle East & Africa
- Middle East
- Africa
-
Latin America
- Brazil
- Rest of Latin America
Recent Developments:
- In May 2023, Intel announced the release of a new security-as-a-service solution called Project Amber. The solution is an independent trust authority, designed to remotely verify whether a compute asset in the cloud, network’s edge or on-premises environment is trustworthy.
- In April 2023, Microsoft announced the expansion of its confidential VM family with the launch of the DCesv5-series and ECesv5-series in preview. Featuring 4th Gen Intel Xeon Scalable processors, these VMs are backed by an all-new hardware-based Trusted Execution Environment called Intel Trust Domain Extensions (TDX). Organizations can use these VMs to seamlessly bring confidential workloads to the cloud without any code changes to their applications.
- In April 2023, Google and Intel collaborated on a new research project to identify potential security vulnerabilities in Intel's new confidential computing technology, Intel Trust Domain Extensions (Intel TDX). In addition to an expanded feature set, Intel Tdx offers full vm compute models without requiring any code changes.
- In April 2023, Microsoft announced to align with Kata Confidential Containers to achieve zero trust operator deployments with AKS. The goal of the Kata Confidential Containers (CoCo) project is to standardize confidential computing at the container level and simplify its consumption in Kubernetes. This is to enable Kubernetes users to deploy confidential container workloads using familiar workflows and tools. We are also taking our Confidential containers on Azure Container Instances (ACI) learning to community with container enforcement policy/full attestation and OCI image snapshotter with DM verity enforcement.
- In February 2923, Arm published the initial Confidential Computing Architecture (CCA) code for the Linux kernel so there can be KVM virtualization integration around Arm CCA, a KVM user-space ABI for managing Realms, and Linux guest support for Arm Realms.
- In January 2023, Intel has launched its 4th Gen Intel Xeon Scalable Processors and the Intel Max Series CPUs and GPUs, alongside the launch of a VM isolation solution and an independent trust verification service to help build their most comprehensive confidential computing portfolio.
- In December 2022, Fortanix announced that its Fortanix Data Security Manager was approved for the G-Cloud Framework and available on G-Cloud 13. The UK Government G-Cloud eases procurement of cloud computing solutions by public sector organizations in the UK. Specifically, G-Cloud 13 is an online catalogue where public sector buyers can buy services including many that are off the shelf, pay-as-you-go cloud solutions.
- In December 2022, IBM collaborated with Cloud Security Alliance, a global non-profit organization dedicated to defining standards, certifications, and best practices to help ensure secured cloud computing, which aims to further advance security and risk management of cloud within financial services.
- In October 2022, Google announced Confidential Space, the next solution in Confidential Computing portfolio. It enables organizations to perform tasks such as joint data analysis and ML model training with trust guarantees that the data, they own can stay protected from their partners including hardened protection against cloud service provider access.
- In May 2022, Fortanix partnered with Keyfactor and this new integration allows leading enterprises and managed service providers to effectively manage all machine identities across hybrid and multi-cloud infrastructure while reducing complexity in ensuring sensitive private keys remain protected
- In May 2022, AMD unveiled confidential virtual machines on Google Cloud, powered by AMD Epyc processors VMs are on the existing the N2D and C2D VMs on Google Cloud. These VMs extend the AMD Epyc processor portfolio of confidential computing on Google Cloud with the performance of 3rd Gen Epyc processors in compute optimized VMs.
- In January 2022, Microsoft and HashiCorp have partnered and HashiCorp Vault is now a supported third-party integration with Azure Key Vault Managed HSM. Hardware-backed keys stored in Managed HSM can now be used to automatically unseal a HashiCorp Vault. This offers customers the convenience of using a Microsoft Cloud key manager for automatic unsealing while keeping keys within a secure hardware boundary and Microsoft further out of the Trusted Computing Base.
- In January 2021, IBM and DIA, a Switzerland-based open-source financial information platform have announced that DIA migrated its platform to IBM cloud and is leveraging IBM Cloud Hyper Protect Services to manage how financial data is sourced, stored, processed, and published. The migration of DIA's platform to a cloud environment backed by IBM cloud confidential computing capabilities is designed to protect data and applications from potential malicious inside and external attacks.
- In October 2020, UC San Francisco’s Center for Digital Health Innovation (CDHI), Fortanix, Intel, and Microsoft Azure have formed a collaboration to establish a confidential computing platform with privacy-preserving analytics to accelerate the development and validation of clinical algorithms.
- In September 2020, Google made two announcements: the general availability of the beta version of its Confidential GKE Nodes and general availability of Confidential VMs.
- In September 2019, IBM announced IBM z15, which is a mainframe computer that has been designed with security and privacy in mind. It features hardware-assisted encryption, secure boot, and secure key management to protect data and applications running on the system.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ):
What is Confidential Computing?
A cloud computing technology that isolates sensitive data in a protected CPU enclave during processing. The contents of the enclave—the data being processed, and the techniques used to process it—are accessible only to authorized programming code and are invisible and unknowable to anything or anyone else, including the cloud provider. Confidential computing focuses on software and hardware-based security and ensures data is secured and encrypted against risks such as malicious insiders, network vulnerabilities or any threat to hardware- or software-based technology that could be compromised. Confidential computing applications include data security, secure enclaves, pellucidity between users, and other applications which include blockchain applications with enhanced record privacy and code integrity, privacy-preserving advertising technology, and confidential databases.
Which country is early adopters of Confidential Computing?
The US is at the initial stage of the adoption of Confidential Computing.
Which are key verticals adopting Confidential Computing?
Key verticals adopting the Confidential Computing market include: -
- BFSI
- Government & Defense
- Healthcare & Life Sciences
- Manufacturing
- IT & Telecommunications
- Retail & Consumer Goods
- Education
- Other Verticals
Which are the key vendors exploring Confidential Computing?
Some of the major vendors offering confidential computing across the globe are Microsoft (US), IBM (US), Intel (US), Google (US), AMD (US), Fortanix (US), AWS (US), Arm (UK), Alibaba Cloud (China), Swisscom (Switzerland), OVHcloud (France), pheonixNAP (US), AMI (Georgia), Applied Blockchain (UK), R3 (US), Decentriq (Switzerland), Hub Security (Israel), Edgeless Systems (Germany), Cysec (Switzerland), Opaque Systems (US), Profian (US), Super Protocol (US), Secretarium (UK), Anjuna Security (US), and Tresorit (Switzerland).
What is the total CAGR expected to be recorded for the Confidential Computing market during 2023-2028?
The Confidential Computing market is expected to record a CAGR of 62.1% from 2023-2028.
To speak to our analyst for a discussion on the above findings, click Speak to Analyst

The study involved four major activities in estimating the size of the confidential computing market. Exhaustive secondary research was done to collect information on the market, peer market, and parent market. The next step was to validate these findings, assumptions, and sizing with industry experts across value chains through primary research. The bottom-up approach was employed to estimate the overall market size. After that, market breakdown and data triangulation were used to estimate the market size of segments and subsegments.
Secondary Research
The market size of companies offering confidential computing solutions and services was arrived at based on the secondary data available through paid and unpaid sources, and by analyzing the product portfolios of major companies in the ecosystem and rating the companies based on their product capabilities and business strategies.
In the secondary research process, various sources were referred to, for identifying and collecting information for the study. The secondary sources included annual reports, press releases, investor presentations of companies, and product data sheets, white papers, journals, certified publications, and articles from recognized authors, government websites, directories, and databases.
Secondary research was mainly used to obtain key information about the industry’s supply chain, the total pool of key players, market classification and segmentation according to industry trends to the bottom-most level, regional markets, and key developments from both market- and technology-oriented perspectives, all of which were further validated by primary sources.
Primary Research
In the primary research process, various primary sources from both supply and demand sides were interviewed to obtain qualitative and quantitative information for this report. The primary sources from the supply side included industry experts, such as Chief Executive Officers (CEOs), Vice Presidents (VPs), marketing directors, technology and innovation directors, and related key executives from various key companies and organizations operating in the confidential computing market.
Primary interviews were conducted to gather insights, such as market statistics, the latest trends disrupting the market, new use cases implemented, data on revenue collected from products and services, market breakups, market size estimations, market forecasts, and data triangulation. Primary research also helped in understanding various trends related to technologies, segmentation types, industry trends, and regions. Demand-side stakeholders, such as Chief Information Officers (CIOs), Chief Technology Officers (CTOs), and Chief Security Officers (CSOs); the installation teams of governments/end users using confidential computing solutions and services; and digital initiatives project teams, were interviewed to understand the buyer’s perspective on suppliers, products, service providers, and their current use of software solutions, which would affect the overall confidential computing market.
To know about the assumptions considered for the study, download the pdf brochure
Market Size Estimation
Both top-down and bottom-up approaches were used to estimate and forecast the confidential computing market and other dependent submarkets. The bottom-up procedure was deployed to arrive at the overall market size using the revenues and offerings of key companies in the market. With data triangulation methods and validation through primary interviews, the exact value of the overall parent market size was determined and confirmed using this study. The overall market size was then used in the top-down procedure to estimate the size of other individual markets via percentage splits of the market segments.
Data Triangulation
After arriving at the overall market size—using the market size estimation processes as explained above—the market was split into several segments and subsegments. Data triangulation and market breakdown procedures were employed, wherever applicable, to complete the overall market engineering process and arrive at the exact statistics of each market segment and subsegment. The data was triangulated by studying various factors and trends from the demand and supply in Banking, Financial Services, and Insurance (BFSI), Healthcare & Life Sciences, Government & Defense, IT & Telecommunications, Manufacturing, Retail & Consumer Goods, Education, and Other Verticals.
Market Definition
A cloud computing technology that isolates sensitive data in a protected CPU enclave during processing. The contents of the enclave—the data being processed and the techniques used to process it—are accessible only to authorized programming code and are invisible and unknowable to anything or anyone else, including the cloud provider. Confidential computing focuses on software and hardware-based security and ensures data is secured and encrypted against risks such as malicious insiders, network vulnerabilities or any threat to hardware- or software-based technology that could be compromised. Confidential computing applications include data security, secure enclaves, pellucidity between users, and other applications which include blockchain applications with enhanced record privacy and code integrity, privacy-preserving advertising technology, and confidential databases.”
Key Stakeholders
- Confidential computing solution providers
- Confidential computing service providers
- Confidential Computing Consortium (CCC) members
- Network and system integrators
- Cloud solution and service providers
- Project managers and developers
- Data security specialists
- Regional associations
- Consulting companies
- Information Technology (IT) infrastructure providers
- Investors and venture capitalists
- Government organizations and standardization bodies
- Value-added resellers and distributors
Report Objectives
- To define, describe, and forecast the global confidential computing market based on components (software, hardware, and services), applications (data security, secure enclaves, pellucidity between users, and other applications), deployment modes, verticals, and regions
- To forecast the market size of the five major regional segments: North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Middle East & Africa, and Latin America
- To strategically analyze the market subsegments with respect to individual growth trends, prospects, and contributions to the total market
- To provide detailed information related to the major factors influencing the growth of the market (drivers, restraints, opportunities, and challenges)
- To strategically analyze macro and micromarkets1 with respect to growth trends, prospects, and their contributions to the overall market
- To analyze industry trends, patents and innovations, and pricing data related to the confidential computing market
- To analyze the opportunities in the market for stakeholders and provide details of the competitive landscape for major players
- To profile key players in the market and comprehensively analyze their market share/ranking and core competencies.
- To track and analyze competitive developments, such as mergers and acquisitions, new product developments, and partnerships and collaborations in the market
Available Customizations
With the given market data, MarketsandMarkets offers customizations as per the company’s specific needs. The following customization options are available for the report:
Product Analysis
- Product matrix provides a detailed comparison of the product portfolio of each company
Geographic Analysis
- Further breakup of the Asia Pacific market into countries contributing 75% to the regional market size
- Further breakup of the North American market into countries contributing 75% to the regional market size
- Further breakup of the Latin American market into countries contributing 75% to the regional market size
- Further breakup of the Middle Eastern & African market into countries contributing 75% to the regional market size
- Further breakup of the European market into countries contributing 75% to the regional market size
Company Information
- Detailed analysis and profiling of additional market players (up to 5)














Growth opportunities and latent adjacency in Confidential Computing Market