The study involved four major activities in estimating the current size of the train battery market. Exhaustive secondary research was done to collect information on the market, the peer market, and the parent market. The next step was to validate these findings, assumptions, and sizing with the industry experts across value chains through primary research. The bottom-up and top-down approaches were employed to estimate the complete market size. Thereafter, market breakdown and data triangulation processes were used to estimate the market size of segments and subsegments.
Secondary Research
The secondary sources referred to for this research study include corporate filings (such as annual reports, investor presentations, and financial statements), and trade, business, and industry associations. Secondary data has been collected and analyzed to arrive at the overall market size, which is further validated by primary research.
Primary Research
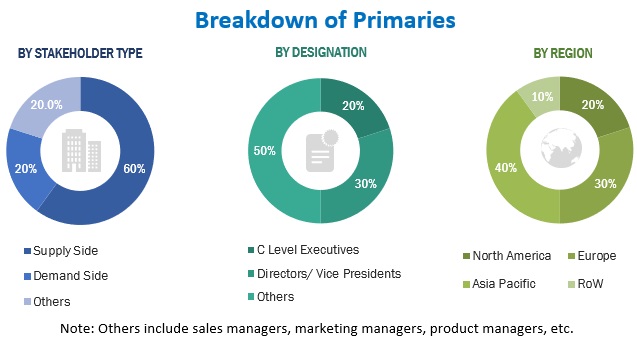
Extensive primary research has been conducted after acquiring an understanding of the train battery market through secondary research. Several primary interviews have been conducted with market experts from both, demand- (locomotive & rolling stock manufacturers) and supply-side (battery manufacturers) across major regions, namely, North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, and RoW. Approximately 60%, 20%, and 20% of primary interviews were conducted from the supply-side, demand-side, and others respectively. Primary data has been collected through questionnaires, emails, and telephonic interviews. In the primary research, we have strived to cover various departments within organizations, such as sales, operations, and administration, to enable a holistic approach in our report.
After interacting with industry experts, we also conducted brief sessions with highly experienced independent consultants to reinforce the findings through the primaries conducted by us. This, along with the opinions of in-house subject matter experts, led us to the findings that have been delineated in this report.
To know about the assumptions considered for the study, download the pdf brochure
Market Size Estimation
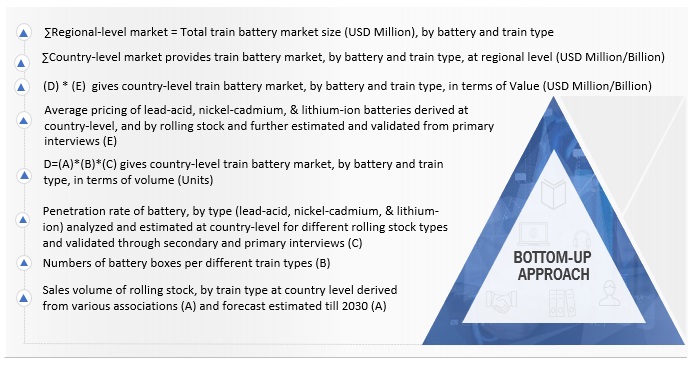
The study uses the bottom-up approach to estimate the market size and forecast the same for segments such as train type and battery type for each country considered under the scope of the study. The study covers the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the demand for various train types. The country-level forecast of train types is based on various secondary sources to understand the recovery period of the market and validate the same from industry experts. Once the base numbers were calculated, each train type was studied for the penetration of battery types in the same for all countries under the scope of the study. Then the Average Selling Price (ASP) was multiplied by each battery type for all train types to arrive at the country-wise value of the train and battery types. These numbers when collated represent the regional and global market size and forecast (volume as well as value) for train and battery types.
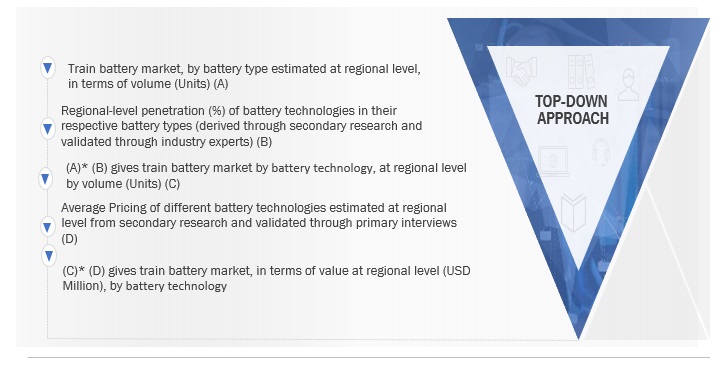
The top-down approach was used to estimate and validate the market size of the segment – battery technology. The market for battery type was arrived at using the bottom-down approach to estimate the battery technology market. For instance, the market for the three types of lead-acid batteries (conventional lead-acid, VRLA, gel tubular) was arrived at using the base number of lead-acid batteries. This is done by referring to multiple secondary sources and validating the penetration of battery technologies (in each battery type) from various industry experts.
Bottom-up approach: Train Battery market, by Battery type and region
To know about the assumptions considered for the study, Request for Free Sample Report
Top-down approach: by Battery Technology, Application
Data Triangulation
After arriving at the overall market size—using the market size estimation processes as explained above—the market was split into several segments and subsegments. To complete the overall market engineering process and arrive at the exact statistics of each market segment and subsegment, data triangulation and market breakdown procedures were employed, wherever applicable. The data was triangulated by studying various factors and trends from both the demand and supply sides
Market Definition:
According to Saft, rail batteries are an important component of energy storage systems that are used for end-use applications such as starters, lighting, air conditioning, access mechanisms, water-filling systems, isolators, connectors, and battery management control (BMC) systems.
According to Exide Industries, The Train battery is securely housed within a battery enclosure located beneath the coach. In railway application, the battery operates in a dusty environment, experiences moderate to high levels of vibration, encounters fluctuating temperatures, has limited windows for inspection and maintenance, and operates continuously in a charge-discharge cycle. This represents the most rigorous evaluation of a battery's performance and longevity, emphasizing the critical significance of reliability.
Key Stakeholders:
-
Sales Head
-
Marketing Head
-
Design Manager
-
R&D Head
Report Objectives
-
To define, segment, analyze, and forecast (2023–2030) the train battery market size, in terms of volume (units) and value (USD million) based on:
-
OE By Battery Type (Lead-Acid, Nickel-Cadmium, and Lithium-ion)
-
OE By Battery Technology (Conventional Lead-Acid, Valve Regulated Lead-Acid, Gel Tubular Lead-Acid, Sinter/PNE Ni-Cd Battery, Pocket Plate Ni-Cd Battery, Fiber/PNE Ni-Cd Battery, Lithium Iron Phosphate, Lithium, Titanate Oxide, and Others)
-
OE By Application (Starter, and Auxiliary)
-
OE By Engines/Head (Diesel Locomotive, Diesel Multiple Units (DMUs), Electric Locomotive, and Electric Multiple Units (EMUs))
-
OE By Application (Metro, High-Speed Trains, Light Rail/ Trams/Monorail, Passenger Coaches)
-
OE By Advanced Train Type (Fully Battery-Powered Train, and Hybrid Train)
-
Aftermarket By battery type (Lead-Acid, Nickel-Cadmium)
-
Aftermarket By application (Starter, and Auxiliary)
-
Aftermarket By Rolling Stock (Locomotives, Multiple Units, and Passenger Coaches)
-
Aftermarket By Region (Asia Pacific, Europe, and North America)
-
OE By Region (North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, and the Rest of the World (RoW))
-
To analyze the recession impact on the train battery market
-
To understand the market dynamics (drivers, restraints, opportunities, and challenges) of the train battery market
-
To study the following with respect to the market
-
Supply Chain Analysis
-
Market Ecosystem
-
Technology Analysis
-
Trade Analysis
-
Case Study Analysis
-
Patent Analysis
-
Buying Criteria
-
Regulatory Landscape
-
Bill of Material
-
To estimate the following with respect to the market
-
Average Price Analysis
-
Market Share Analysis
-
To analyze the competitive landscape and prepare a competitive evaluation quadrant for the global players operating in the train battery market.
-
To analyze recent developments, alliances, joint ventures, mergers & acquisitions, new product launches, and other activities carried out by key industry participants in the train battery market
Available Customizations
With the given market data, MarketsandMarkets offers customizations in accordance with a company’s specific needs.
The following customization options are available for the report:
Train Battery Market, By Application, By Rolling Stock
-
Engine Starter
-
Auxiliary Function
Note: The segment would be further segmented by region.
Train Battery Market, By Rolling Stock, By Battery Type
-
Lead Acid
-
Nickel-Cadmium
-
Lithium-Ion
Note: The segment would be further segmented by region
US Train Battery Aftermarket, By Rolling Stock, By Battery Type
-
Locomotives
-
Multiple Units
-
Passenger Coaches



Nilesh
Jun, 2019
We are interested in train battery market report, would like to understand how can we also gain a better understanding of "advanced train" application with the free customization you are offering.