The study involved two major segments in estimating the current size of the cold chain market. Exhaustive secondary research was done to collect information on the market, peer, and parent markets. The next step was to validate these findings, assumptions, and sizing with industry experts across the value chain through primary research. Both top-down and bottom-up approaches were employed to estimate the complete market size. After that, market breakdown and data triangulation were used to estimate the market size of segments and subsegments.
Secondary Research
This research study involved the extensive use of secondary sources—directories and databases such as Bloomberg Businessweek and Factiva—to identify and collect information useful for a technical, market-oriented, and commercial study of the cold chain market.
In the secondary research process, various sources such as annual reports, press releases & investor presentations of companies, white papers, food journals, certified publications, articles from recognized authors, directories, and databases, were referred to identify and collect information.
Secondary research was mainly used to obtain key information about the industry’s supply chain, the total pool of key players, and market classification and segmentation as per the industry trends to the bottom-most level, regional markets, and key developments from both market- and technology-oriented perspectives.
Primary Research
Extensive primary research was conducted after obtaining information regarding the cold chain market scenario through secondary research. Several primary interviews were conducted with market experts from both the demand and supply sides across major countries of North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, South America, and the Rest of the World. Primary data was collected through questionnaires, emails, and telephonic interviews. The primary sources from the supply side included various industry experts, such as Chief X Officers (CXOs), Vice Presidents (VPs), Directors, from business development, marketing, research, and development teams, and related key executives from distributors, and key opinion leaders. Primary interviews were conducted to gather insights such as market statistics, data on revenue collected from the services, market breakdowns, market size estimations, market forecasting, and data triangulation. Primary research also helped in understanding the various trends related to cold chain type, technology, application, temperature type, offering and region. Stakeholders from the demand side, such as dairy & frozen desserts, meat & seafood, fruits & vegetables, and bakery & confectionery products, pharmaceutical, chemical, art, flower & plants, electronics, and other temperature senisitive products manufacturers who avail the cold chain services were interviewed to understand the buyer’s perspective on the suppliers, services, and their current usage of cold chain and the outlook of their business which will affect the overall market.
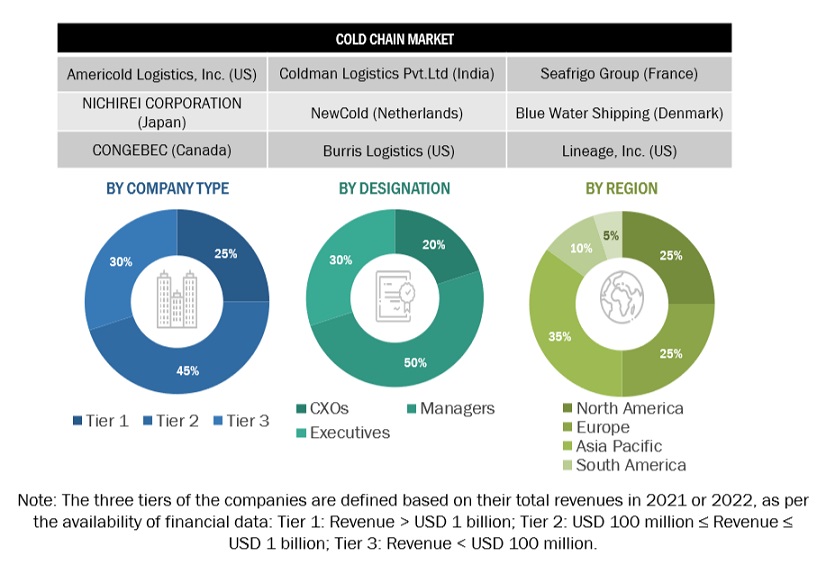
To know about the assumptions considered for the study, download the pdf brochure
|
COMPANY NAME
|
designation
|
|
Burris Logistics (US)
|
Territory Manager
|
|
Seafrigo Group (France)
|
Sales Manager
|
|
Coldman Logistics Pvt.Ltd (India)
|
General Manager
|
|
NICHIREI CORPORATION (Japan)
|
Head of logistics department
|
|
NewCold (Netherlands)
|
Marketing Manager
|
|
Americold Logistics, Inc. (US)
|
Sales Executive
|
Market Size Estimation
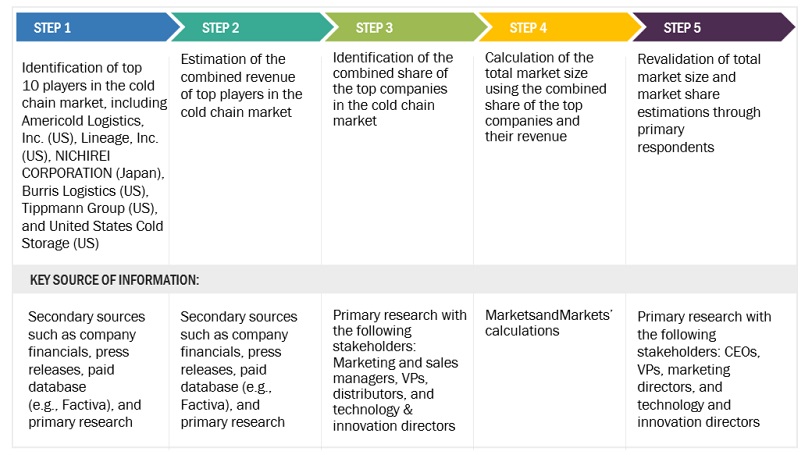
Both the top-down and bottom-up approaches were used to estimate and validate the total size of the cold chain market. These approaches were also used extensively to determine the size of various subsegments in the market. The research methodology used to estimate the market size includes the following details:
-
The key players in the industry and the overall markets were identified through extensive secondary research.
-
All shares, splits, and breakdowns were determined using secondary sources and verified through primary sources.
-
All possible parameters that affect the market covered in this research study were accounted for, viewed in extensive detail, verified through primary research, and analyzed to obtain final quantitative and qualitative data.
-
The research included the study of reports, reviews, and newsletters of top market players, along with extensive interviews for opinions from leaders, such as CEOs, directors, and marketing executives.
Global Cold Chain Market: Bottom-Up Approach.
To know about the assumptions considered for the study, Request for Free Sample Report
Global Cold Chain Market: Top-Down Approach.
Data Triangulation
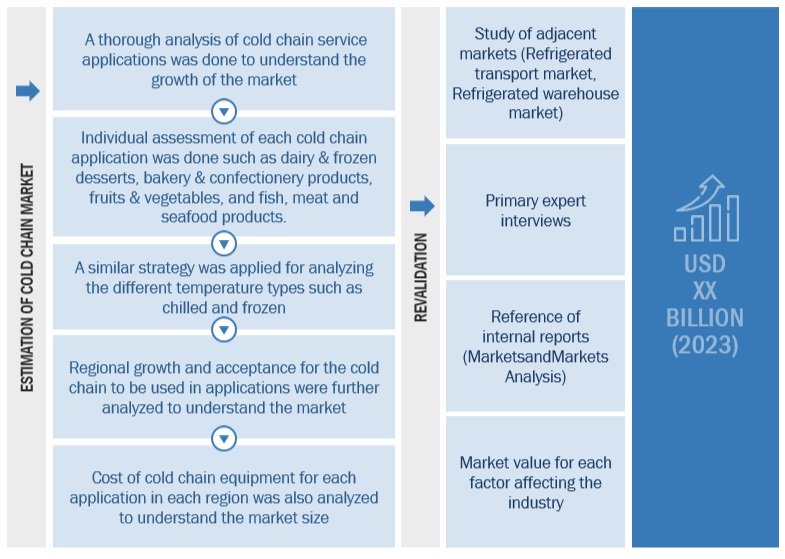
After arriving at the overall market size from the estimation process explained above, the total market was split into several segments and subsegments. Data triangulation and market breakdown procedures were employed to estimate the cold chain market and arrive at the exact statistics for all segments and subsegments. The data was triangulated by studying numerous factors and trends from the demand and supply sides. The market size was also validated using both the top-down and bottom-up approaches.
Market Definition
According to the Central Asia Regional Economic Cooperation (CAREC), “Cold chain refers to the transportation of temperature-sensitive products along a supply chain through thermal and refrigerated packaging methods and the logistical planning to protect the integrity of these shipments.”
It is an unbroken/uninterrupted series of refrigerated or chilled production, storage, and distribution activities, along with associated equipment and logistics, which maintain the desired low-temperature range.
Key Stakeholders
-
Cold chain service providers
-
Refrigerated transport service providers
-
Refrigerated warehouse and transport equipment providers
-
Refrigerated transport vehicle manufacturers
-
Logistics service providers
-
Associations and government agencies:
-
International Refrigerated Transport Association (IRTA)
-
Global Food Cold Chain Council (GFCCC)
-
Global Cold Chain Alliance
-
Refrigerated Foods Association (RFA)
-
The Refrigerated Warehouse & Transport Association of Australia Ltd (RWTA)
-
Southern African Refrigerated Distribution Association (SARDA)
-
International Association for Cold Storage Construction (IACSC)
-
International Association of Refrigerated Warehouses (IARW)
-
World Food Logistics Organization (WFLO)
-
European Cold Storage and Logistics Association (ECSLA)
-
Cool Chain Association (CCA)
-
American Association of Meat Processors (AAMP)
-
Frozen Potato Products Institute (FPPI)
-
Cold logistics players (shipping lines, transporters, and container companies)
-
Supply chain solution providers
-
Manufacturers and traders of dairy & frozen desserts, meat & seafood, fruits & vegetables, and bakery & confectionery products
-
Manufacturers of agricultural products
-
Manufacturers of pharmaceutical products
-
Manufacturers of temperature sensitive flowers & plants
-
Manufacturers of temperature sensitive chemicals, arts, electronics
Report Objectives
-
Determining and projecting the size of the cold chain market based on technology, type, offering, application, temperature type and region over a five-year period ranging from 2024 to 2029.
-
Identifying the attractive opportunities in the market by determining the largest and fastest-growing segments across the key regions
-
Analyzing the demand-side factors based on the following:
-
Impact of macro- and micro-economic factors on the market
-
Shifts in demand patterns across different subsegments and regions
-
Providing detailed information about the key factors influencing the growth of the market (drivers, restraints, opportunities, and industry-specific challenges)
Available Customizations:
With the given market data, MarketsandMarkets offers customizations according to company-specific scientific needs.
The following customization options are available for the report:
Service Analysis
-
Service Matrix, which gives a detailed comparison of the service portfolio of each company.
Geographic Analysis
With the given market data, MarketsandMarkets offers customizations according to company-specific scientific needs.
-
Further breakdown of the Rest of European market for cold chain into Ireland, Poland, Sweden, Switzerland and other EU & non-EU countries.
-
Further breakdown of the Rest of Asia Pacific market for cold chain into South Korea, Indonesia,, the Philippines, and Vietnam.
-
Further breakdown of the Rest of South American market for cold chain into Colombia, Peru, Chile, and Venezuela.
-
Further breakdown of the Rest of the World into the Middle East (Saudi Arabia, UAE, and the Rest of Middle East) and Africa (South Africa, Nigeria, and the Rest of Africa).
Company Information
-
Detailed analyses and profiling of additional market players (up to five)



Growth opportunities and latent adjacency in Cold Chain Market