Germany Microgrid Market to Reach $2.37 Billion by 2029
According to MarketsandMarkets, the Germany microgrid market is projected to grow from USD 1.10 billion in 2023 to reach USD 2.37 billion by 2029; it is expected to grow at a CAGR of 13.4 % from 2024 to 2029.
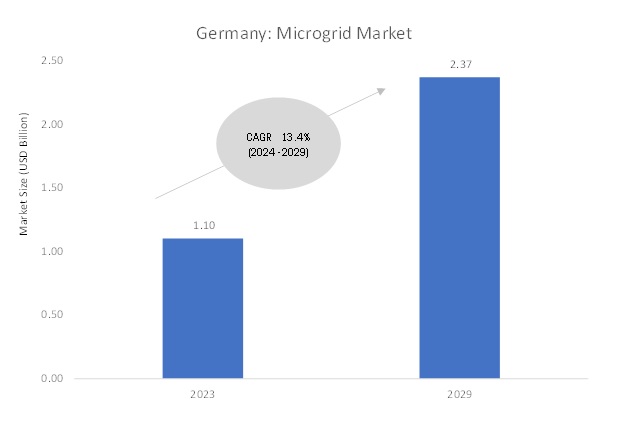
Germany’s Microgrid market to Germany’s focus on achieving a low-carbon economy through its "Energiewende" policy has driven significant investment in microgrid technology. The country’s energy transition aims to decentralize power generation and integrate renewable energy into the grid. Microgrids play a crucial role in achieving these objectives by providing localized solutions that optimize energy efficiency and enhance grid stability.
To know about the assumptions considered for the study download the pdf brochure
Germany’s industrial sector, known for its energy-intensive operations, has embraced microgrid technology to ensure uninterrupted power supply and reduce energy costs. Additionally, the rise of smart grid infrastructure and advancements in energy storage technologies are creating new opportunities for microgrid deployment across residential, commercial, and industrial applications.
Transition to Renewable Energy
Germany’s ambitious energy transition policy emphasizes renewable energy, targeting a 100% carbon-neutral grid by 2050. Microgrids enable efficient integration of distributed renewable energy resources, such as wind farms in the North Sea and solar arrays in southern Germany. Rural areas, in particular, benefit from microgrids by utilizing locally available resources and reducing dependence on centralized grids.
The flexibility offered by microgrids is also instrumental in addressing the intermittency challenges associated with renewable energy. For example, in Bavaria, microgrids are deployed to manage excess energy from solar farms, storing it for later use or feeding it back into the grid. These systems reduce wastage, enhance energy efficiency, and contribute to a more reliable grid infrastructure.
Industrial Demand for Energy Efficiency
Germany’s manufacturing industries, including automotive and chemical sectors, are some of the largest energy consumers globally. Microgrids allow industries to reduce energy costs and carbon emissions by integrating on-site renewable energy systems and advanced storage technologies. For instance, Siemens operates a microgrid at its headquarters in Erlangen, optimizing energy usage while maintaining operations during grid outages.
Industrial microgrids also enhance operational flexibility by providing real-time energy monitoring and load balancing. Facilities can manage peak loads more effectively, avoiding costly grid tariffs during high-demand periods. The automotive industry, led by companies like BMW and Volkswagen, is increasingly adopting microgrids to power their production facilities with renewable energy, meeting both environmental regulations and corporate sustainability goals.
Government Incentives and Technological Advancements
The German government actively supports microgrid development through initiatives like the Renewable Energy Sources Act (EEG), which offers subsidies, feed-in tariffs, and tax benefits, making microgrid adoption financially viable. Significant funding under the Climate Action Programme 2030 also promotes pilot projects focusing on smart grid integration and decentralized energy systems. Technological advancements, including smart meters for precise energy monitoring and flow batteries for improved storage, further drive market growth. Initiatives such as the "C/sells" project in southern Germany showcase how microgrids can integrate diverse energy resources, connecting producers, consumers, and storage systems to create a decentralized, efficient energy market.
Impact of AI on Microgrid Market
AI-driven systems have transformed microgrid operations by enabling real-time energy optimization, load forecasting, and demand-side management. AI tools help balance variable renewable energy supply, ensuring grid stability even during peak demand periods. Additionally, predictive maintenance enabled by AI reduces operational downtime, making microgrids more reliable and cost-effective.
Challenges for Microgrid Market in Germany
Germany faces challenges in scaling up microgrid adoption due to high installation costs and complex regulatory requirements. Integrating microgrids with existing energy infrastructure, especially in urban areas with dense populations, presents technical hurdles. Furthermore, lengthy permitting processes delay project timelines, impacting the overall pace of deployment.
Related Reports:
Microgrid Market by Connectivity (Grid Connected, Off-grid), Offering (Hardware (Power Generators, Controllers, Energy Storage Systems), Software, Services), Power Source, End User, Power Rating and Region - Global Forecast to 2029
Contact:
Mr. Rohan Salgarkar
MarketsandMarkets Inc.
1615 South Congress Ave.
Suite 103,
Delray Beach, FL 33445
USA : 1-888-600-6441
sales@marketsandmarkets.com
This FREE sample includes market data points, ranging from trend analyses to market estimates & forecasts. See for yourself.
SEND ME A FREE SAMPLE





