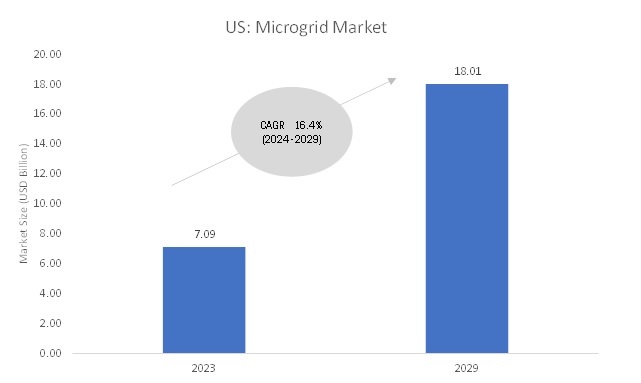
US Microgrid Market to Reach $18.01 Billion by 2029
According to MarketsandMarkets, the US microgrid market is projected to grow from USD 7.09 billion in 2023 to reach USD 18.01 billion by 2029; it is expected to grow at a CAGR of 16.4% from 2024 to 2029.
The United States has become one of the largest markets for microgrid technology, driven by increasing concerns about grid reliability, extreme weather events, and the transition to clean energy. Microgrids, with their ability to operate independently of the main power grid, are being deployed across a variety of sectors, including industrial, commercial, residential, and government facilities. The U.S. market is characterized by substantial investments in renewable energy, advancements in battery storage, and state-level initiatives promoting decentralized energy systems.
To know about the assumptions considered for the study download the pdf brochure
The growing focus on decarbonization has made microgrids critical to integrating renewable energy sources like solar and wind into local grids. Additionally, the rising costs of power outages—estimated to cause billions in economic losses annually—have positioned microgrids as a vital solution for ensuring energy resilience and reducing dependence on centralized grids. Federal funding and technological advancements further support the development and adoption of microgrid systems across the country.
Increasing Demand for Energy Resilience
Extreme weather events and natural disasters, such as hurricanes in the Gulf Coast, wildfires in California, and winter storms in Texas, have exposed vulnerabilities in the aging U.S. grid infrastructure. Microgrids provide a decentralized solution that ensures continuity of electricity supply during grid outages. Critical facilities such as hospitals, military bases, and data centers are increasingly adopting microgrids to safeguard operations. For example, the Marine Corps Air Station at Miramar, California, operates a microgrid that guarantees uninterrupted power to military operations during outages.
Federal and State-Level Incentives
Federal programs, including funding from the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE), are bolstering the development of microgrids. States like California, New York, and Massachusetts are leading in microgrid adoption through financial incentives, grants, and streamlined permitting processes. The California Energy Commission (CEC), for instance, funds numerous microgrid demonstration projects to promote renewable energy integration and grid resilience. At the federal level, tax credits under the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) further incentivize renewable energy components of microgrids, such as solar panels and battery storage systems.
Integration of Renewable Energy Sources
The U.S. has witnessed exponential growth in renewable energy, with over 250 GW of solar and wind capacity installed as of 2023. Microgrids are pivotal in managing these distributed energy resources by addressing intermittency challenges and ensuring reliable power supply. For example, the Stone Edge Farm Microgrid in California integrates solar, wind, and hydrogen storage to achieve 100% renewable energy operation. This capability supports the country’s decarbonization goals while reducing energy costs for consumers.
Impact of AI on Microgrid Market in the US
Artificial intelligence is reshaping the U.S. microgrid landscape by improving efficiency, reducing operational costs, and enhancing resilience. AI-enabled energy management systems allow microgrids to predict energy demand, optimize storage usage, and dynamically balance supply and demand. For instance, AI-powered platforms like Siemens’ Spectrum Power Microgrid Management System offer advanced analytics to improve grid reliability and integrate diverse energy sources seamlessly. AI also plays a critical role in detecting potential grid failures, enabling preemptive action to prevent outages.
Challenges for Microgrid Market in the US
Despite its potential, the U.S. microgrid market faces significant challenges. High upfront capital costs for installation and technology procurement remain a barrier, especially for small-scale users. Additionally, the lack of uniform regulatory frameworks across states complicates project implementation and integration with existing grid infrastructure. The resistance from utility companies, which view microgrids as a threat to traditional centralized power models, further hinders market growth.
Related Reports:
Microgrid Market by Connectivity (Grid Connected, Off-grid), Offering (Hardware (Power Generators, Controllers, Energy Storage Systems), Software, Services), Power Source, End User, Power Rating and Region - Global Forecast to 2029
Contact:
Mr. Rohan Salgarkar
MarketsandMarkets Inc.
1615 South Congress Ave.
Suite 103,
Delray Beach, FL 33445
USA : 1-888-600-6441
sales@marketsandmarkets.com
This FREE sample includes market data points, ranging from trend analyses to market estimates & forecasts. See for yourself.
SEND ME A FREE SAMPLE





