
Feeding The Future: Leveraging Micronutrients for Nutrient-Dense Crops & Sustainable Agricultural Practices
The global market for agricultural micronutrients, essential elements for optimal crop nutrition, is experiencing steady growth. The market growth is being driven by an increasing focus on sustainable agricultural practices and effective crop nutrient management. Integrated nutrition management strategies that incorporate micronutrients have become an absolute necessity to cater to the needs of a growing population. The adoption of comprehensive crop nutrition strategies holds immense potential to enhance crop yields, improve food quality, and promote long-term agricultural sustainability.
The global agricultural micronutrient market is estimated to be valued at USD 4.5 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach USD 6.9 billion by 2028, at a CAGR of 8.6%. Micronutrients act as catalysts in various biochemical processes within plants. Zinc, iron, manganese, and copper are among the micronutrients essential for optimal crop growth and development. The market has gained significant traction, primarily driven by soil micronutrient deficiency, the need for improved crop efficiency, increasing demand for food security, and an emphasis on sustainable agriculture. Government policies and initiatives support the adoption of micronutrient management practices through subsidies, programs, and research funding. These initiatives can include promoting soil testing, providing subsidies or incentives for micronutrient application, and offering educational programs to farmers. In India, the government supports micronutrient deficiency correction through policies and schemes such as the Soil Health Card Scheme, National Food Security Mission, and nutrient-based subsidies. The “Global Soil Partnership” was established by the FAO and the EU to focus specifically on soil challenges and advocate efficient soil management and land use. Advanced technologies in precision agriculture further allow for soil testing that accurately identifies exact micronutrient deficiencies. This enables targeted application, optimizing nutrient use, reducing waste, and improving cost-effectiveness.
The synergy of agricultural micronutrients and Integrated Nutrient Management (INM)
INM strategies combine organic and inorganic fertilizers to enhance the utilization of applied micronutrients in the soil. By improving soil microbial activity, organic matter (such as compost and manure) plays a crucial role in converting less available micronutrient forms into more accessible ones for plant uptake. This occurs through mechanisms such as chelation and improved soil structure for better root development. INM practices such as cover cropping and mulching further help minimize soil erosion and leaching, reducing the agricultural system’s micronutrient loss. INM approaches can significantly increase zinc availability and uptake in crops such as wheat and rice, improving yields and grain quality.
Innovation in biodegradable chelates to present growth opportunities
The use of biodegradable chelates in agricultural micronutrients presents significant opportunities for sustainable agriculture. The eco-friendly biodegradable chelates can enhance the bioavailability and uptake of essential micronutrients by crops. Additionally, these biodegradable chelates can address concerns about the persistence of non-biodegradable chelates in aquatic systems, which can lead to environmental contamination. Using biodegradable chelates, agricultural practices can become more environmentally responsible and align with circular and sustainable agriculture principles. NTA, EDDS, and ITS are the most recently developed and adopted agents widely promoted in the markets instead of non-biodegradable agents.
It is crucial to strike a balance between the use of biodegradable chelates and their potential environmental impact, as their accumulation can disrupt the delicate nutrient balance required for optimal plant growth. Sustainable and responsible agricultural practices in the application of biodegradable chelates are essential to ensure they support the growth of agricultural micronutrients.
Zinc to account for the largest market share among agricultural micronutrients
Accounting for around one-fourth of the global micronutrient demand, zinc is an essential micronutrient, playing a crucial role in the growth and development of plants. It is characterized by a diverse range of products and formulations tailored to meet specific crop requirements and soil conditions. Zinc supplements come in different forms, such as zinc chelates, sulfates, oxides, and complex compounds. They can be applied through various delivery methods such as foliar sprays and seed treatments, which help address zinc deficiencies efficiently. In addition, regulatory bodies and agricultural organizations are increasingly emphasizing the importance of balanced crop nutrient management practices that ensure adequate soil zinc levels. This has led to a greater focus on research & development efforts aimed at creating more efficient and environmentally friendly zinc supplements.
Increased bioavailability of chelated micronutrients to contribute to market productivity and profitability
Chelated micronutrients are readily absorbed by plants, fostering healthier growth and development. Chelation enhances the stability and availability of micronutrients, mitigating the risk of nutrient deficiencies in crops. Also, chelated micronutrients contribute to plant resistance against pests and diseases, improving crop protection. Their environmentally friendly characteristics, allowing for reduced application quantities, further emphasize their sustainability in crop nutrient management. Chelates encompass various application methods, including foliar sprays, seed treatments, and soil applications, catering to diverse farming needs. The bioavailability of micronutrients, such as Fe, Cu, Mn, and Zn, is increased due to chelation.
Foliar method to facilitate low-cost application and immediate response to applied nutrients
Foliar application is a dominant method in the agricultural micronutrients market, holding a significant market share. Ensuring quick reception of necessary micronutrients, foliar application enables precise and targeted nutrient delivery, addressing specific crop deficiencies. By minimizing excess runoff and waste, this method is more environmentally friendly and sustainable. It can be easily combined with other agricultural practices, such as crop nutrient management and pest and disease management. Foliar applications further benefit crops by preventing and correcting nutrient deficiencies, enhancing photosynthesis, and improving overall plant health.
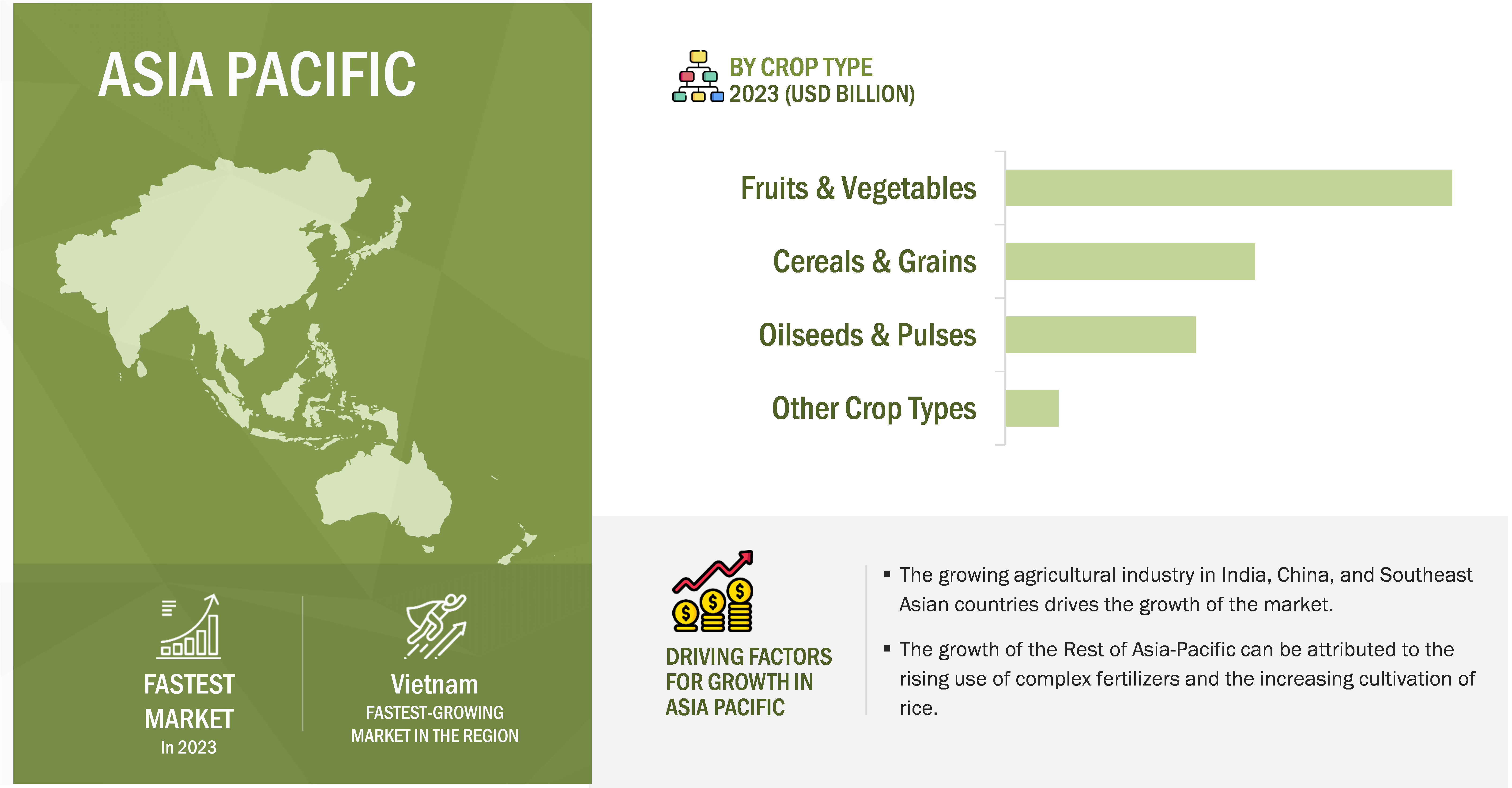
Asia Pacific to grow at the highest CAGR in the global agricultural micronutrient market
Factors such as soil type, crop system, local environmental conditions, and economic factors determine the use of micronutrients to correct deficiencies in different regions. There has been an increasing trend of using agricultural micronutrients in North America (US and Canada) due to factors such as a decrease in arable land, demand for high-quality food products, and changing agricultural practices, including precision agriculture and no-till management. The Common Agricultural Policy (CAP) adopted by Europe has made the growers shift toward sustainable agricultural practices due to the increase in leaching and runoff of chemical fertilizers, resulting in a nutrient deficiency in the soil; it has resulted in steady demand for micronutrients for holistic crop growth. The dominance of the Asia Pacific region is due to an increase in India and China’s agriculture industries. Also, the production of rice and fruits & vegetables in the region is growing, further propelling the demand for micronutrient fertilizers. The soil in the Asia-Pacific region is majorly deficient in zinc and boron. Zinc sulfate is the most commonly used Zn source, particularly in the Asian market, where price is the primary consideration in the choice of micronutrient products.
Agricultural Micronutrients Market Ecosystem
Basf SE (Germany), Nouryon (Netherlands), Nufarm (Australia), Yara International ASA (Norway), Coromandel International Limited (India), Land O’lakes, Inc. (US), Helena Agri-Enterprises, LLC (US), The Mosaic Company (US), and Haifa Negev Technologies Ltd (Israel) are among the key players. The key strategies used by companies in the agricultural micronutrient market include geographical expansion to tap the potential of emerging economies, strategic acquisitions to gain a foothold over the extensive supply chain, and new product launches as a result of extensive research and development (R&D) initiatives.
Ecosystem Map

Source: Secondary Research, Company Annual Reports, White Papers, Press Releases, and MarketsandMarkets Analysis
80% of the Forbes Global 2000 B2B companies rely on MarketsandMarkets to identify growth opportunities in emerging technologies and use cases that will have a positive revenue impact.
- Food Packaging Market Size Set for Strong Growth Through 2030 Amid Rising Demand for Convenience Foods
- Fertilizers Industry Set to Grow at 4.1% CAGR Through 2030
- Leading Automated Guided Vehicle Companies 2024: An In-depth Analysis
- CHARGED UP: SHIFT TO E-MOBILITY AND THE EVOLUTION OF TRANSPORTATION
- Global Automotive Market: Predictions For 2024
Agricultural Micronutrients Market Ecosystem
Basf SE (Germany), Nouryon (Netherlands), Nufarm (Australia), Yara International ASA (Norway), Coromandel International Limited (India), Land O’lakes, Inc. (US), Helena Agri-Enterprises, LLC (US), The Mosaic Company (US), and Haifa Negev Technologies Ltd (Israel) are among the key players. The key strategies used by companies in the agricultural micronutrient market include geographical expansion to tap the potential of emerging economies, strategic acquisitions to gain a foothold over the extensive supply chain, and new product launches as a result of extensive research and development (R&D) initiatives.

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What is the role of agricultural micronutrients in Integrated Nutrient Management Practices (INM) and sustainable agriculture globally?
Micronutrients added through INM strategies help address soil nutrient deficiencies caused by intensive farming practices, erosion, and imbalanced fertilizer use. Micronutrients are co-factors for numerous critical plant enzymes involved in photosynthesis, nitrogen fixation, and various metabolic processes. By providing these essential elements, INM strategies promote enhanced crop yields, improved nutritional value, and better visual appeal of agricultural products. INM practices often combine organic and inorganic fertilizers, creating a synergistic effect for micronutrient utilization for improved efficiency and reduced waste. Overall, the integration of micronutrients into INM strategies is essential for achieving sustainable agriculture globally by addressing soil deficiencies and optimizing nutrient use efficiency, enhancing crop yields, quality, and resilience, and promoting long-term soil health and environmental sustainability.
- How do agricultural micronutrients improve the efficacy and efficiency of Integrated Nutrient Management Practices (INM)?
Agricultural micronutrients significantly contribute to the efficacy and efficiency of integrated nutrient management (INM) through enhanced nutrient availability by chelation and improved soil structure, optimized nutrient use through synergy with organic matter, and reduced nutrient losses through less soil erosion and leaching.
By incorporating micronutrients strategically within INM frameworks, farmers and growers can achieve more efficient and sustainable crop nutrition management while contributing to global food security.


