Various secondary sources, directories, and databases have been used to identify and collect information for an extensive electric tractor market study. The study involved four main activities in estimating the current size of the electric tractor market: secondary research, validation through primary research, assumptions, and market analysis. Exhaustive secondary research was carried out to collect information on the market, such as different propulsion types and the upcoming technologies and trends. The next step was to validate these findings, assumptions, and market analysis with industry experts across the value chain through primary research. The top-down approach was employed to estimate the complete market size for different segments considered in this study.
Secondary Research
In the secondary research process, various secondary sources have been used to identify and collect information useful for an extensive commercial study of the electric tractor market. Secondary sources include company annual reports/presentations, press releases, industry association publications [such as publications on Committee for European Electric Off-highway Vehicle (CECE), Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), Agriculture Equipment Manufacturers Union (AXEMA), Association of Equipment Manufacturers (AEM), Italian Agricultural Machinery Manufacturers Federation (FEDERUNACOMA), Japan Agricultural Machinery Manufacturers Association (JAMMA), China Agricultural Machinery Distribution Association (CAMDA), VDMA (Verband Deutscher Maschinen- und Anlagenbau), Russian Association of Specialized Machinery and Equipment Manufacturers (ROSSPETSMASH), Brazilian Association of Industrial Machinery and Equipment (ABIMAQ), Agricultural Engineers Association (AEA). The electric tractor-related magazine articles, directories, technical handbooks, World Economic Outlook, trade websites, and technical articles. Additionally, secondary research has been carried out to understand the average cost of electric tractors, which come with different battery capacities, and the historical sales of vehicles.
Primary Research
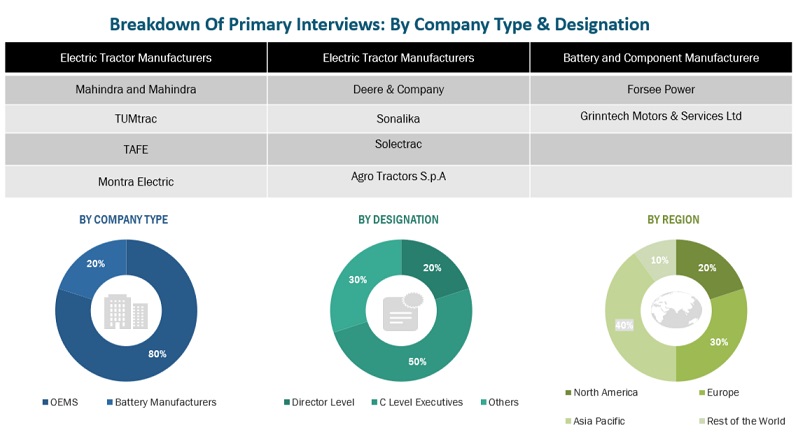
In the primary research process, various primary sources from both the supply and demand sides were interviewed to obtain qualitative and quantitative information on the market. The primary sources from the supply side included industry experts such as CXOs, vice presidents, directors from business development, marketing, product development/innovation teams, and related key executives from various key companies. Various system integrators, industry associations, independent consultants/industry veterans, and key opinion leaders were also interviewed.
In the primary research process, various sources from both the supply and demand sides have been interviewed to obtain qualitative and quantitative information for this report. The primary sources from the supply side include industry experts such as research and development experts, CEOs, CTOs, COOS, vice presidents, marketing directors, technology and innovation directors, and related key executives from different key companies operating in the electric tractor market.
After the complete market engineering, which includes calculations for market statistics, market breakdown, market size estimations, market forecasting, and data triangulation, extensive primary research has been conducted to gather information and verify and validate the critical numbers arrived at. Primary research has also been undertaken to identify and validate the segmentation, industry trends, key players, competitive landscape, and market dynamics, such as drivers, restraints, opportunities, challenges, industry trends, and key strategies. Extensive qualitative and quantitative analysis has been performed on the complete market engineering process to list key information/insights throughout the report.
After interacting with industry experts, we have also conducted brief sessions with highly experienced independent consultants to reinforce the findings from our primaries. This and the in-house subject matter expert’s opinions have led us to the conclusions described in this report's remainder.
To know about the assumptions considered for the study, download the pdf brochure
Market Size Estimation
A detailed market estimation approach was followed to estimate and validate the value of the electric tractor market and other dependent submarkets, as mentioned below:
-
Key players in the electric tractor market were identified through secondary research, and their global market shares were determined through primary and secondary research.
-
The research methodology included studying annual and quarterly financial reports, regulatory filings of major market players (public), and interviews with industry experts for detailed market insights.
-
All industry-level penetration rates, percentage shares, splits, and breakdowns for the electric tractor market were determined using secondary sources and verified through primary sources.
-
All key macro indicators affecting the revenue growth of the market segments and sub-segments have been accounted for, viewed in extensive detail, verified through primary research, and analyzed to get the validated and verified quantitative and qualitative data.
-
The gathered market data was consolidated and added with detailed inputs, analyzed, and presented in this report.
Electric Tractor Market: Bottom-Up Approach
To know about the assumptions considered for the study, Request for Free Sample Report
Electric Tractor Market: Top-Down Approach
Extensive secondary and primary research was conducted to understand the global market scenario and penetration for hybrid tractors per region. While estimating the regional market for hybrid electric tractors by power output, the regional shares of <50HP, 51 – 100HP, and >100HP power output were identified and multiplied by the regional market size in terms of the volume, of hybrid electric tractors. In terms of volume, the regional-level market size was then multiplied by the regional-level average selling price of the hybrid electric tractor mentioned above and the power output of the tractor. This resulted in regional-level market size, by powerout put, in terms of value. This information was validated through primary interviews with OEMs and Tier I suppliers.


Data Triangulation
After arriving at the overall market size, the market was split into several segments and sub-segments—using the market size estimation processes as explained above. Where applicable, data triangulation and market breakdown procedures were employed to complete the overall market engineering process and determine each market segment's and sub-segments exact statistics. The data was triangulated by studying various factors and trends.
Market Definition
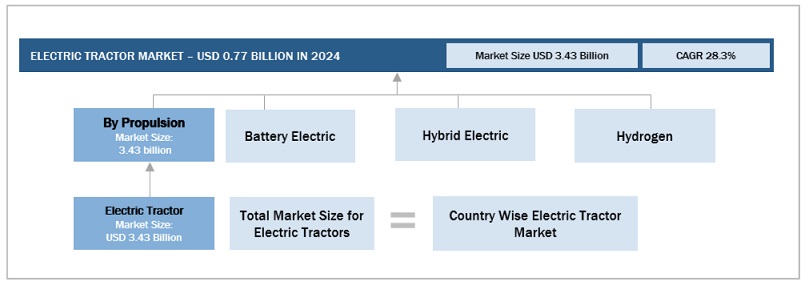
Electric tractors include both battery-electric and hybrid-electric tractors. The hybrid electric tractor is powered by an internal combustion engine (ICE) combined with one or more electric motors that use energy stored in batteries to meet the additional auxiliary power needs of the equipment, electronic devices, and power tools. The battery-electric tractor is fully electric, and the combustion engine is replaced with batteries and an electric motor that powers the movement of the machine and its attachments.
These tractors provide zero emissions, reduce carbon footprint, and contribute to sustainability goals. They also operate silently, improving the work environment and potentially complying with noise regulations. Functionally, electric tractors perform the same tasks as their diesel counterparts, including soil preparation, seeding, harvesting, and transporting materials. However, they come with distinct features such as regenerative braking that feeds energy back to the battery, multiple power levels catering to various needs, and connected data monitoring and optimization technologies.
Stakeholders
-
Electric Tractor Component Manufacturing Associations
-
Electric tractor Component Suppliers
-
Farm Tractor Dealers and Distributors
-
Government and Regulatory Authorities
-
Research Professionals
-
Farm Tractor Importers, Retailers, and Dealers
-
Tier 1 System Suppliers
-
Raw Material Suppliers for Electric Farm Tractor
-
Battery and Drivetrain Suppliers
-
Electric Tractor Manufacturers
-
Electric tractor Manufacturers
-
Traders, Distributors, and Suppliers of Electric tractor Systems/Components
-
Automotive Industry Associations, Government Authorities, and Research Organizations
Report Objectives
-
To define, describe, and forecast the electric tractor market in terms of value
(USD million), based on the following segments:
-
Propulsion (Battery Electric, Hybrid Electric, and Hydrogen)
-
Battery Chemistry (Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP), Lithium nickel manganese cobalt oxides (LI-NMC), and Others)
-
Hybrid Electric Tractor Market, by Power Output (<50 HP, 51-100 HP, and >100 HP)
-
Battery capacity (<50 KWH, 51-100 KWH, and >100 KWH)
-
Function (Agriculture & Forestry, Utility, and Industrial)
-
Region (Asia Pacific, Europe, and Americas)
-
To understand the market dynamics (Drivers, Restraints, Opportunities, and Challenges) and conduct Patent Analysis, Pricing Analysis, Recession Impact, Key Buying Criteria, Trade Analysis, Technology Analysis, ASP Analysis, Trades and Conferences, Case Study Analysis, Supply Chain Analysis, Regulatory Analysis, Key Conference and Events, Bill of Material, Total Cost of Ownership, Investment & Funding Scenario, Funding by Use Case Scenario, Battery Technology, and Ecosystem Mapping
-
To understand the dynamics of the market players and distinguish them into stars, emerging leaders, pervasive players, and participants according to their product portfolio strength and business strategies.
-
To strategically analyze markets concerning individual growth trends, prospects, and contributions to the total market
-
To analyze recent developments, such as partnerships, supply agreements, joint ventures/mergers and acquisitions, geographic expansions, and product developments of key players in the market
Available Customizations
Along with the market data, MarketsandMarkets offers customizations based on company-specific needs.
The following customization options are available for the report:
Electric Tractor Market By Region
Electric Tractor Market, By Battery Capacity
-
Asia Pacific (China, India, Japan, South Korea, Rest of Asia Pacific)
-
Europe (Germany, France, UK, Spain, Russia, Italy, Turkey, and Rest of Europe)
-
Americas (US, Canada, Mexico, Brazil, and Argentina)
-
Detailed Analysis And Profiling Of Additional Market Players (Up To 3)



Growth opportunities and latent adjacency in Electric Tractor Market