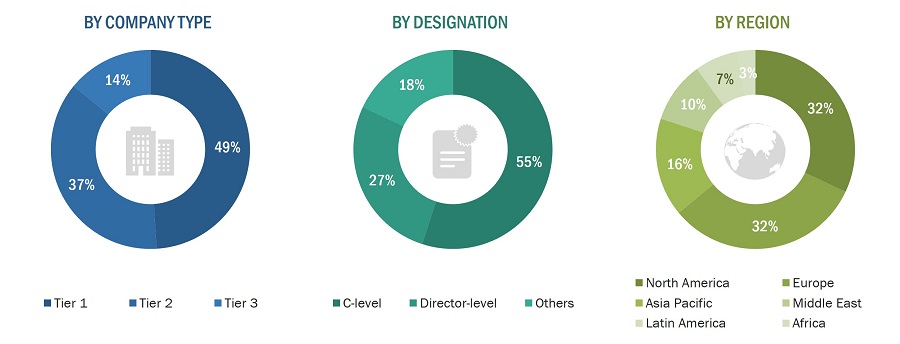
The research study conducted on the Space-Based Solar Power market involved extensive use of secondary sources, directories, and databases, such as D&B Hoovers, Bloomberg Businessweek, and Factiva, to identify and collect information relevant to the market. Publications of the International Energy Agency, American Oil & Gas Reporter, and Global Firepower, DNV GL are also considered in these secondary sources. Primary sources included industry experts from the market as well as suppliers, manufacturers, solution providers, technology developers, alliances, and organizations related to all segments of the industry’s value chain. In-dep.th interviews of various primary respondents, including key industry participants, subject matter experts (SMEs), industry consultants, and C-level executives, were conducted to obtain and verify critical qualitative and quantitative information about the market as well as to assess the growth prospects of the market.
Secondary Research
The market share for companies was determined based on secondary data made available through paid and unpaid sources and analysis of product portfolios of major companies and then rating them based on performance and quality. These data points were further validated by primary sources.
Secondary sources that were referred to for this research study included financial statements of companies with on-site hydrogen production, storage and conversion facilities and information from various trade, business, and professional associations, among others. The secondary data was collected and analyzed to arrive at the overall size of the Space-Based Solar Power market, which was validated by primary respondents.
Primary Research
Extensive primary research was conducted after obtaining information about the current scenario of the Space-Based Solar Power market through secondary research. Several primary interviews were conducted with market experts from the demand and supply sides across North America, Europe, and Asia Pacific, to obtain qualitative and quantitative information on the market. This primary data was collected through questionnaires, emails, and telephonic interviews. Primary sources from the supply side included various industry experts, such as vice presidents, directors, regional managers, technology providers, product development teams, distributors, and end users.
To know about the assumptions considered for the study, download the pdf brochure
Market Size Estimation
-
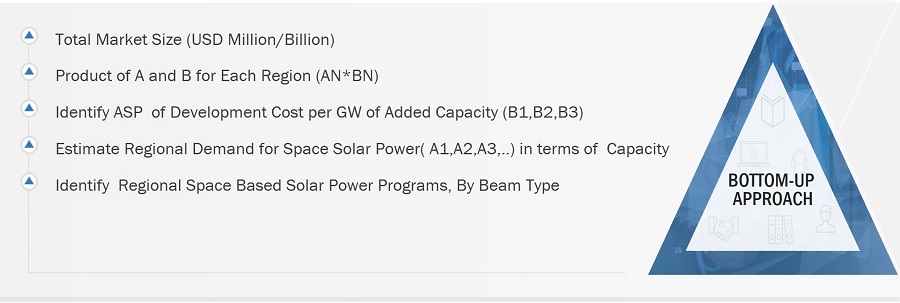
Both top-down and bottom-up approaches were used to estimate and validate the size of the Space-Based Solar Power market.
-
Key players were identified through secondary research, and their market ranking was determined through primary and secondary research. This included a study of annual and financial reports of the top market players and extensive interviews of leaders, including CEOs, directors, and marketing executives.
-
All percentage shares, splits, and breakdowns were determined using secondary sources and verified through primary sources. All possible parameters that affect the markets covered in this research study were accounted for, viewed in extensive detail, verified through primary research, and analyzed to obtain the final quantitative and qualitative data. This data was consolidated, enhanced with detailed inputs, analyzed by MarketsandMarkets, and presented in this report.
Market size estimation methodology: Bottom-up Approach
Market size estimation methodology: Top-down Approach

Data triangulation
After arriving at the overall size from the market size estimation process explained above, the total market was split into several segments and subsegments. The data triangulation and market breakdown procedures explained below were implemented, wherever applicable, to complete the overall market engineering process and arrive at the exact statistics for various market segments and subsegments. The data was triangulated by studying various factors and trends from both the demand and supply sides. Along with this, the market size was validated using both top-down and bottom-up approaches.
Market Definition
A Space-based solar power system is an energy collection, transmission and distribution hardware that uses satellites as well as ground infrastructure to focus solar radiation energy from the sun using special mirrors and direct the energy to terrestrial rectifying antennas (rectennas) via microwave and laser beams. The received energy can then be used for electricity and power generation for terrestrial uses. The key end users include government, defense and commercial entities that will utilize the novel technique as an alternative to traditional solar energy-based power generation. The technique offers specific advantages over traditional solar panel technologies including day and night operations and higher conversion efficiencies.
Stakeholders
Various stakeholders of the market are listed below:
-
Government Authorities
-
Regulatory Bodies
-
R&D Companies
-
Defense Organizations
-
Subsystem Manufacturers
-
Energy Providers and Utilities
-
Environmental Groups and Policymakers
-
Investors and Financial Institutions
-
Commercial Space Companies
Report Objectives
-
To define, describe, and forecast the size of the Space-Based Solar Power market based on beam type, application, end-user, and region from 2030 to 2040.
-
To forecast the size of market segments with respect to major regions, namely North America, Europe, and Asia Pacific
-
To identify and analyze key drivers, restraints, opportunities, and challenges influencing market growth.
-
To analyze opportunities for stakeholders in the market by identifying key market trends
-
To strategically analyze micromarkets1 with respect to individual growth trends, prospects, and their contribution to the global market
-
To analyze competitive developments such as contracts, acquisitions, agreements, and partnerships, product launches, and research and development (R&D) activities in the Space-Based Solar Power market.
-
To provide a detailed competitive landscape of the market, as well as an analysis of business and corporate strategies adopted by leading market players.
-
To strategically profile key market players and comprehensively analyze their core competencies2.
1. Micromarkets are defined as further segments and subsegments of the space-based solar power market included in the report.
2.Core competencies of the companies have been captured in terms of their key developments, SWOT analysis, and key strategies adopted by them to sustain their position in the market.
Available customizations
Along with the market data, MarketsandMarkets offers customizations as per the specific needs of companies. The following customization options are available for the report:
Product Analysis
-
Product matrix, which gives a detailed comparison of the product portfolio of each company.
Regional Analysis
-
Further breakdown of the market segments at the regional level
Company Information
-
Detailed analysis and profiling of additional market players (up to 5)



Growth opportunities and latent adjacency in Space-Based Solar Power Market