
LEO Satellite Market Size, Share & Trends, 2025 To 2030
LEO Satellite Market by Subsystem [Satellite Bus (Command & Data Handling, Electric Power System), Payload (Optical, Infrared, Radar), Solar Panel, Satellite Antenna], Satellite Mass, Application, End Use, Frequency, and Region - Global Forecast to 2030




OVERVIEW

Source: Secondary Research, Interviews with Experts, MarketsandMarkets Analysis
The LEO satellite market is projected to reach USD 20.69 billion by 2030, growing from USD 11.81 billion in 2025, at a CAGR of 11.9%. The LEO satellite volume is anticipated to grow from 3,722 units in 2025 to 5,175 units by 2030. The market is expanding rapidly, driven by demand for internet services, Earth observation, CubeSat miniaturization, and cost-efficient launches, positioning LEO networks as essential infrastructure for commercial connectivity and government applications worldwide.
KEY TAKEAWAYS
- North America is expected to account for a 36.3% share of the LEO satellite market in 2025.
- By mass, CubeSats are expected to exhibit the fastest growth, with a CAGR of 12.6%.
- By subsystem, the payloads segment is projected to be the fastest-growing segment, with a CAGR of 13.2%.
- By application, the communication segment is expected to account for the largest share of the LEO satellite market during the forecast period.
- SpaceX, Lockheed Martin Corporation, and Airbus Defence and Space were identified as star players in the LEO satellite market, given their strong market share and extensive product footprint.
- Kuiper Systems LLC, EnduroSat, and NanoAvionics, among others, have distinguished themselves among startups and SMEs by securing strong footholds in specialized niche areas, underscoring their potential as emerging market leaders.
The future outlook of the LEO satellite industry is robust, fueled by broadband demand, Earth observation, and IoT expansion. Advancements in miniaturization, frequency technologies, and cost-efficient launches will enhance scalability, resilience, and mission diversity, driving commercial and governmental adoption through 2030.
TRENDS & DISRUPTIONS IMPACTING CUSTOMERS' CUSTOMERS
The LEO satellite market is driven by mega-constellation deployments, cost-efficient SmallSat launches, and advanced payload technologies. Additionally, the rising demand for broadband, Earth observation, and IoT services, along with reusable launch systems and AI-enabled analytics, is reshaping operator strategies while unlocking new commercial and defense opportunities.

Source: Secondary Research, Interviews with Experts, MarketsandMarkets Analysis
MARKET DYNAMICS
Level
-
Elevated demand for satellite internet services

-
Need for Earth observation imagery and analytics
Level
-
Limited coverage and complexity of LEO satellites
-
Stringent government policies
Level
-
Booming 3D printing technology
-
Higher adoption of software-defined technology
Level
-
Concerns over growing space debris
-
Complex supply chain management
Source: Secondary Research, Interviews with Experts, MarketsandMarkets Analysis
Driver: Rising demand for satellite internet services
Global demand for affordable, high-speed broadband, especially in underserved regions, is accelerating LEO satellite adoption. Government initiatives, digital inclusion efforts, and growth in video streaming, e-learning, and remote work amplify demand. Companies like Starlink, OneWeb, and Amazon’s Kuiper are deploying mega-constellations, while technologies such as phased-array antennas and laser links enhance efficiency.
Restraint: Limited coverage and complexity of LEO satellites
LEO satellites offer low latency but require vast constellations for global coverage, driving costs higher than GEO systems. Short lifespans (5–7 years), atmospheric drag, and fuel demands add challenges. Complex ground infrastructure, network handoffs, and synchronization issues further limit scalability, making sustainability and long-term adoption difficult compared to more stable GEO systems.
Opportunity: Booming 3D printing technology
3D printing enables rapid prototyping, cost-effective small batch production, and mass customization of LEO satellite parts. It reduces weight, waste, and lead times while supporting CubeSat miniaturization. Advancements in aerospace-grade materials make it viable for structural, propulsion, and RF components, enhancing flexibility and resilience in satellite manufacturing, aligning with growing demand for affordable, agile missions.
Challenge: Concerns over increasing space debris
The surge in LEO satellites raises collision risks due to crowded orbits already filled with rocket remnants and debris. Traveling at extreme speeds, even small fragments threaten spacecraft. With ~14,000 trackable debris objects, replenishment cycles worsen congestion. Regulators and operators face pressure to implement space traffic management, disposal mechanisms, and debris removal to ensure sustainability.
LEO satellite market: COMMERCIAL USE CASES ACROSS INDUSTRIES
| COMPANY | USE CASE DESCRIPTION | BENEFITS |
|---|---|---|
 |
IoT satellites with SDR payloads | Enables real-time IoT connectivity and sensor data relay in remote areas |
 |
RF monitoring constellation | Provides global RF spectrum mapping and accurate signal detection |
 |
Ionosphere measurement nanosatellites | Delivers precision data on magnetic and electric fields |
 |
Earth observation satellites | Offers daily imagery for agriculture, climate, and defense |
 |
Nanosatellites for weather and tracking | Tracks weather, ships (AIS), and aircraft (ADS-B) |
 |
SAR Earth observation satellites | Provides all-weather, high-resolution radar imagery |
Logos and trademarks shown above are the property of their respective owners. Their use here is for informational and illustrative purposes only.
MARKET ECOSYSTEM
The LEO satellite market ecosystem includes primes like SpaceX, Airbus, and Lockheed Martin, with manufacturers such as GomSpace and AAC Clyde. Service providers like OneWeb and Eutelsat deliver connectivity, while governments, defense, and enterprises drive demand for global data services.

Logos and trademarks shown above are the property of their respective owners. Their use here is for informational and illustrative purposes only.
MARKET SEGMENTS

Source: Secondary Research, Interviews with Experts, MarketsandMarkets Analysis
LEO Satellite Market, By Satellite Mass
Large satellites dominate as they provide higher payload capacity, extended mission lifespans, and advanced subsystem integration. Their ability to support communications, defense, and scientific missions makes them the preferred choice for both government and commercial operators.
LEO Satellite Market, By Subsystem
Satellite buses dominate as they provide the essential platform supporting payloads, power, thermal, and communication systems. Their scalability and reliability make them central to commercial constellations, defense missions, and scientific programs requiring efficient and long-term satellite operations.
LEO Satellite Market, By Application
Earth observation and remote sensing dominate as they enable high-resolution imaging, weather tracking, and geospatial analytics. Their critical role in agriculture, disaster management, and defense intelligence drives growing adoption across government, commercial, and environmental monitoring applications.
LEO Satellite Market, By End-Use
Commercial use dominates as businesses adopt satellites for broadband, navigation, and imaging services. Their ability to support telecom, aviation, maritime, and energy sectors makes them key enablers of digital transformation and global connectivity expansion.
LEO Satellite Market, By Frequency Band
Ku-band dominates as it provides reliable bandwidth for mobility and broadcast applications. Its ability to support aviation connectivity, maritime communications, and enterprise networks makes it a cornerstone frequency for expanding global satellite broadband services.
REGION
Middle East & Africa to be fastest-growing region in global LEO satellite market during forecast period
The Middle East & Africa LEO satellite market is set for fastest growth, driven by UAE’s Mars mission, military satellite investments, miniaturized payloads, broadband demand, and smart city initiatives enhancing regional connectivity and resilience.

LEO satellite market: COMPANY EVALUATION MATRIX
The company evaluation matrix for the LEO satellite market evaluates players based on product footprint and market share. It highlights their competitive positioning and ranks them according to market strength and growth strategies. SpaceX is positioned as a leading player with a strong focus on advanced satellite technologies, while OneWeb is recognized as an emerging leader in this market.

Source: Secondary Research, Interviews with Experts, MarketsandMarkets Analysis
KEY MARKET PLAYERS
List of Top LEO Satellite Market Companies
MARKET SCOPE
| REPORT METRIC | DETAILS |
|---|---|
| Market Size in 2024 (Value) | USD 10.22 Billion |
| Market Forecast in 2030 (value) | USD 20.69 Billion |
| Growth Rate | CAGR of 11.9% from 2025 to 2030 |
| Years Considered | 2021–2030 |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025–2030 |
| Units Considered | Value (USD Billion), Volume (Units) |
| Report Coverage | Revenue Forecast, Company Ranking, Competitive Landscape, Growth Factors, and Trends |
| Segments Covered |
|
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Middle East & Africa, and Latin America |
WHAT IS IN IT FOR YOU: LEO satellite market REPORT CONTENT GUIDE

DELIVERED CUSTOMIZATIONS
We have successfully delivered the following deep-dive customizations:
| CLIENT REQUEST | CUSTOMIZATION DELIVERED | VALUE ADDS |
|---|---|---|
| LEO Satellite Market Customization (Asia Pacific – Historic & Forecast Market Numbers + Supply Chain Analysis) | Delivered a tailored LEO satellite market study for Asia Pacific, integrating historic and forecast sizing along with detailed supply chain mapping of satellite manufacturers, subsystem providers, and component suppliers. |
|
RECENT DEVELOPMENTS
- October 2024 : Thales Alenia Space received an ESA order for six satellites for Italy’s IRIDE Earth observation constellation.
- June 2024 : Airbus Defence and Space was contracted by Al Yah Satellite Communication Company PJSC for AY4 and AY5 telecom satellites.
- May 2024 : ESA awarded Airbus Defence and Space UK a contract for USD 368.5 million to develop the Vigil weather satellite.
- March 2024 : Thales Alenia Space won an ESA contract to deliver the LEO-PNT orbit demonstrator, covering satellites, ground segments, and in-orbit operations.
- March 2024 : Planet Labs PBC secured a contract with the US Navy’s Naval Information Warfare Center Pacific to supply satellite imagery for maritime surveillance and vessel monitoring via SeaVision platform.
Table of Contents

Methodology
This research study on the LEO satellite market involved extensive use of secondary sources, directories, and databases such as Hoovers, Bloomberg BusinessWeek, and Factiva to identify and collect information relevant to the market. The primary sources considered included industry experts, as well as service providers, manufacturers, solution providers, technology developers, alliances, and organizations related to all segments of the value chain of this market. In-depth interviews with primary respondents, including key industry participants, subject matter experts, industry consultants, and C-level executives, were conducted to obtain and verify critical qualitative and quantitative information pertaining to the LEO satellite market and assess its growth prospects.
Secondary Research
The secondary sources referred to for this research study on the LEO satellite market included the financial statements of companies offering delivery drone software, drone transportation and logistics services, transportation and logistics solution providers, and various trade, business, and professional associations. The secondary data was collected and analyzed to arrive at the overall size of the LEO satellite market, which was validated by primary respondents.
Primary Research
In the primary research process, various sources from the supply and demand sides were interviewed to obtain qualitative and quantitative information on the market. Primary sources from the supply side included CXOs, VPs, directors, regional managers, business development and product development teams, distributors, and vendors. Meanwhile, stakeholders from the demand side included telecommunication companies, government and defense agencies, broadcasting services, and others willing to adopt LEO satellites. These interviews were conducted to gather insights such as market statistics, data on revenue collected from the products and services, market breakdowns, market size estimations, market size forecasting, and data triangulation. These interviews also helped analyze the market by satellite mass, application, end use, subsystem, and frequency segments for five key regions
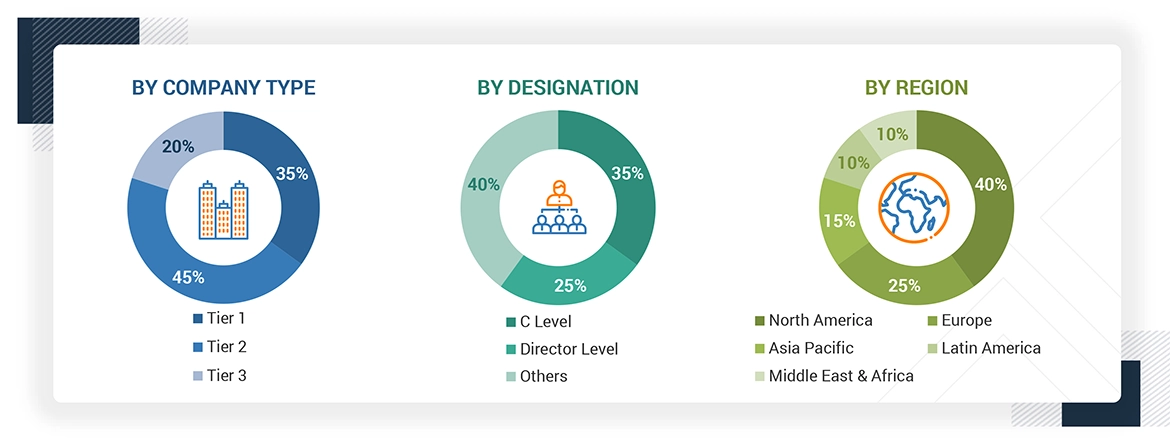
Note: Tier 1 = Company revenue over USD 1 billion, Tier 2 = Company revenue between USD 100 million and USD 1 billion, and Tier 3 = Company revenue less than USD 100 million.
To know about the assumptions considered for the study, download the pdf brochure
Market Size Estimation
Both top-down and bottom-up approaches were used to estimate and validate the total size of the LEO satellite market. These methods were also used to calculate the size of various segments and subsegments of the market. The research methodology used to estimate the market size includes the following details:
- The key players were identified through secondary research, and their market ranking was determined through primary and secondary research. This included a study of the annual and financial reports of the top market players and extensive interviews of leaders, including CEOs, directors, and marketing executives.
- All percentage shares, splits, and breakdowns were determined using secondary sources and verified through primary sources. All possible parameters that affect the markets covered in this research study were accounted for, viewed in extensive detail, verified through primary research, and analyzed to obtain the final quantitative and qualitative data. This data was consolidated, enhanced with detailed inputs, analyzed by MarketsandMarkets, and presented in this report.
LEO Satellite Market : Top-Down and Bottom-Up Approach

Data Triangulation
After arriving at the overall size of the LEO satellite market from the market size estimation process explained above, the total market was split into several segments and subsegments. To complete the overall market engineering process and arrive at the exact statistics for various market segments and subsegments, data triangulation and market breakdown procedures explained below were implemented, wherever applicable. The data was triangulated by studying different factors and trends from both the demand and supply sides. The market size was also validated using both top-down and bottom-up approaches.
Market Definition
LEO satellites, or low Earth orbit satellites, are designed to operate in orbits that are relatively close to Earth, typically at altitudes of up to 2,000 kilometers (1,200 miles). These satellites are widely used for commercial communication, Earth observation, remote sensing, navigation, surveillance, meteorology, and scientific research. One defining feature of LEO satellites is their flexibility in orbit paths; unlike geostationary satellites that must orbit along the equator, LEO satellites can operate in tilted orbital planes, which allows for a greater variety of routes and coverage. This characteristic contributes to their popularity and utility across various sectors, including defense, civil, commercial, and governmental uses.
Key Stakeholders
- Satellite component manufacturers
- Satellite manufacturers
- Satellite integrators
- Launch service providers
- Government and civil organizations related to LEO satellite market
- Small satellite companies
- Payload suppliers
- Scientific institutions
- Meteorological organizations
- Component suppliers
- Technologists
- R&D staff
Report Objectives
- To define, describe, segment, and forecast the LEO satellite market based on satellite mass, subsystem, end use, application, frequency, and region
- To forecast the sizes of market segments with respect to five major regions: North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, the Middle East & Africa, and Latin America, along with major countries in each region
- To identify and analyze key drivers, restraints, opportunities, and challenges influencing market growth
- To analyze micromarkets1 with respect to individual growth trends, prospects, and their contribution to the overall market
- To analyze opportunities in the market for stakeholders by identifying market trends
- To profile key market players and comprehensively analyze their market shares and core competencies2
- To analyze the degree of competition in the market by identifying key growth strategies, such as acquisitions, contracts, investments, new installations & upgrades, and partnerships, adopted by leading market players
- To identify detailed financial positions, key products, and unique selling points of leading companies in the market
Customizations options
Along with the market data, MarketsandMarkets offers customizations to meet the specific needs of companies. The following customization options are available for the report:
Product Analysis
- Product matrix, which gives a detailed comparison of the product portfolio of each company
Regional Analysis
- Further breakdown of the market segments at the country level
Company Information
- Detailed analysis and profiling of up to five additional market players
Key Questions Addressed by the Report
- 3D-printed satellite manufacturing
- Development of CubeSat constellations
- Miniaturization in space technology
- Rising demand for satellite internet services
- Growing need for earth observation imagery and analytics
- Expanding satellite networks for internet access in underserved areas
- Increasing launches of CubeSats
Need a Tailored Report?
Customize this report to your needs
Get 10% FREE Customization
Customize This ReportPersonalize This Research
- Triangulate with your Own Data
- Get Data as per your Format and Definition
- Gain a Deeper Dive on a Specific Application, Geography, Customer or Competitor
- Any level of Personalization
Let Us Help You
- What are the Known and Unknown Adjacencies Impacting the LEO Satellite Market
- What will your New Revenue Sources be?
- Who will be your Top Customer; what will make them switch?
- Defend your Market Share or Win Competitors
- Get a Scorecard for Target Partners
Custom Market Research Services
We Will Customise The Research For You, In Case The Report Listed Above Does Not Meet With Your Requirements
Get 10% Free Customisation












Growth opportunities and latent adjacency in LEO Satellite Market