
Space Propulsion Market Size, Share, and Trends, 2025 To 2030
Space Propulsion Market by Propulsion Type (Solid, Liquid, Electric, Solar, Hybrid), Component (Bipropellant Thruster, Hall-Effect Thruster, Rocket Motor), Platform (Satellite, Launch Vehicle), End User, Services and Region - Global forecast to 2030




OVERVIEW

Source: Secondary Research, Interviews with Experts, MarketsandMarkets Analysis
The space propulsion market is estimated in terms of market size to be USD 10.21 billion in 2024 to USD 20.02 billion by 2030, at a CAGR of 11.9%. In terms of volume, the market is set to reach 5,394 units by 2030, from 3,257 units in 2024, at a CAGR of 8.8%. The space propulsion market is witnessing strong growth driven by rising satellite launches, advancements in electric and hybrid propulsion systems, and expanding government and commercial space programs worldwide.
KEY TAKEAWAYS
-
BY PLATFORMGrowing adoption of reusable launch vehicles and small satellite platforms is accelerating innovation in liquid rocket engines, solid rocket engines, and electric propulsion in space.
-
BY TYPEThe market is witnessing a major shift toward electric propulsion, ion propulsion systems, and hybrid rocket propellants for efficient and sustainable missions.
-
BY COMPONENTRise in demand for advanced electric thrusters, power processing units, and nuclear propulsion technologies is enhancing mission flexibility and endurance.
-
BY SUPPORT SERVICEExpansion of end-to-end propulsion integration, testing, and maintenance is supporting advancements in electric and rocket propulsion systems for deep-space applications.
-
BY END USERIncrease in participation from private companies and government agencies is driving large-scale deployment of future space propulsion systems across commercial and defense sectors.
-
BY REGIONNorth America is projected to lead, while Rest of the World emerges as a fast-growing market due to new national space programs.
-
COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPEMajor players in the space propulsion market have adopted both organic and inorganic strategies, including partnerships and investments. Safran and Northrop Grumman are among the key players in this market.
The growth of the space propulsion market will be fueled by rising satellite launches, deep-space exploration missions, and the transition toward reusable and electric propulsion technologies. Increasing government investments in space programs, the commercialization of low Earth orbit, and advancements in nuclear and green propellants are expected to drive demand.
TRENDS & DISRUPTIONS IMPACTING CUSTOMERS' CUSTOMERS
The global space propulsion market is experiencing robust growth, driven by the increasing commercialization of the space domain and government-funded deep space exploration programs. Private companies like SpaceX and Project Kuiper (Amazon) are planning to launch thousands of satellites each year for their respective satellite constellations, supporting the growth. Apart from these countries, such as Japan and Australia, are investing in their own space launch vehicle capabilities, supporting the growth of the space propulsion market.

Source: Secondary Research, Interviews with Experts, MarketsandMarkets Analysis
MARKET DYNAMICS
Level
-
Growing deployment of satellites

-
Advancements in propulsion technologies
Level
-
High development and manufacturing costs
-
Stringent regulatory and safety standards
Level
-
Increasing government investments in space programs
-
Emergence of nuclear thermal and nuclear electric propulsion
Level
-
Supply chain disruptions
-
Growing issues of space debris
Source: Secondary Research, Interviews with Experts, MarketsandMarkets Analysis
Driver: Expansion of deep space exploration missions
The growing number of deep space exploration missions by agencies such as NASA, ESA, and ISRO is driving demand for advanced propulsion technologies. These missions require high-efficiency systems capable of sustaining long-duration travel and maneuverability in distant orbits, boosting the need for both chemical and non-chemical propulsion solutions.
Restraint: High development and manufacturing costs of space propulsion systems
Developing propulsion systems involves complex engineering, expensive materials, and extensive testing, which significantly raise overall project costs. The high capital investment limits participation from smaller players and slows large-scale adoption of emerging propulsion technologies.
Opportunity: Increasing government investments in space programs
Rising government funding in national and international space programs is creating opportunities for propulsion manufacturers. Initiatives such as Artemis, Mars exploration, and satellite constellations are stimulating demand for efficient propulsion technologies across multiple mission types.
Challenge: Growing issues of space debris
The accumulation of space debris poses serious risks to propulsion system operations and orbital maneuvering. As debris management becomes a global concern, propulsion systems with deorbiting and collision avoidance capabilities are gaining strategic importance in future satellite and spacecraft designs.
Space Propulsion Market: COMMERCIAL USE CASES ACROSS INDUSTRIES
| COMPANY | USE CASE DESCRIPTION | BENEFITS |
|---|---|---|
 |
Provides chemical propulsion systems for satellites and launch vehicles, including thrusters used in geostationary and deep-space missions | Ensures reliable orbital maneuvering and mission longevity through proven propulsion efficiency |
 |
Develops solid rocket motors and propulsion subsystems for launch vehicles and missile defense applications | Delivers high-thrust performance and mission assurance for heavy-lift and defense launches |
 |
Supplies electric propulsion and power management solutions for next-generation satellites and spacecraft | Enables fuel-efficient and long-duration missions through precise orbital control |
 |
Manufactures liquid rocket engines and thrusters for national and commercial satellite programs | Offers compact, high-performance propulsion that supports Japan’s growing space missions |
 |
Integrated reusable propulsion systems like Merlin and Raptor engines for the Falcon and Starship launch vehicles | Reduces launch costs and enhances reusability, driving commercial space accessibility |
Logos and trademarks shown above are the property of their respective owners. Their use here is for informational and illustrative purposes only.
MARKET ECOSYSTEM
The key stakeholders in the market ecosystem are prominent companies, which are space propulsion OEMs, private and small enterprises, which have limited product portfolios, and end users, which include commercial and government & defense organizations.

Logos and trademarks shown above are the property of their respective owners. Their use here is for informational and illustrative purposes only.
MARKET SEGMENTS

Source: Secondary Research, Interviews with Experts, MarketsandMarkets Analysis
Space Propulsion Market, by Platform
Launch vehicles are estimated to account for the largest share of the space propulsion market during the forecast period. The dominance is driven by increasing demand for solid and liquid rocket engines in orbital and deep-space missions. The growing number of commercial launches and reusable rockets is further boosting adoption. Advancements in hybrid rocket propellant technologies are also enhancing performance and cost efficiency.
Space Propulsion Market, by Support Service
The design, engineering, operation, and maintenance segment is projected to lead the market, supported by rising needs for system integration, hot firing tests, and propulsion validation. Growing demand for electric propulsion testing, including Hall-effect thrusters, requires advanced ground facilities and precision engineering support. Collaboration among space agencies and private firms is further boosting this segment. The transition toward future space propulsion systems, such as nuclear and hybrid technologies, enhances service opportunities.
Space Propulsion Market, by Component
Thrusters are estimated to dominate among the components in the market. The increasing adoption of electric thrusters, particularly Hall-effect thrusters and ion propulsion systems, is transforming satellite operations. These thrusters enable high efficiency, precise orbital adjustments, and extended mission lifespans.
Space Propulsion Market, by Type
The chemical propulsion segment is projected to dominate, driven by the proven reliability of liquid and solid rocket engines in launch vehicles and interplanetary spacecraft. However, innovations in hybrid rocket propellants are improving safety and reducing emissions. The hybridization of chemical and electric propulsion systems is gaining momentum to balance thrust power and mission efficiency. These advancements are shaping the evolution of next-generation rocket propulsion systems.
Space Propulsion Market, by End User
The commercial segment is expected to dominate due to the surge in private satellite constellations and commercial launch missions. Companies are increasingly deploying electric propulsion and Hall-effect thrusters for orbit raising and station-keeping. The rise of reusable launch vehicles and small satellite platforms is fueling steady market expansion. Continuous investments in advanced space propulsion technologies are further enhancing commercial competitiveness and operational cost savings.
REGION
Europe to be fastest-growing among major regions in global space propulsion market during forecast period
Among the four main regions studied in the global space propulsion market, Europe is projected to be the fastest-growing during the forecast period, driven by increasing investments from the European Space Agency (ESA) and national programs in France, Germany, and the UK. The region’s focus on developing electric propulsion systems, reusable launch vehicles, and sustainable propellants is accelerating technological progress.

Space Propulsion Market: COMPANY EVALUATION MATRIX
The company evaluation matrix for the space propulsion market evaluates players based on product footprint and market share. It highlights their competitive positioning and ranks them according to market strength and growth strategies. Safran leads the space propulsion market with a strong product portfolio, advanced technologies, and a broad customer base, while Airbus is recognized as an emerging leader in this market.

Source: Secondary Research, Interviews with Experts, MarketsandMarkets Analysis
KEY MARKET PLAYERS
MARKET SCOPE
| REPORT METRIC | DETAILS |
|---|---|
| Market Size, 2023 (Value) | USD 8.29 Billion |
| Market Forecast, 2030 (Value) | USD 20.02 Billion |
| Growth Rate | 11.9% from 2024 to 2030 |
| Years Considered | 2020–2030 |
| Base Year | 2023 |
| Forecast Period | 2024–2030 |
| Units Considered | Value (USD Million), Volume (Units) |
| Report Coverage | Revenue forecast, company ranking, competitive landscape, growth factors, and trends |
| Segments Covered |
|
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Middle East, Rest of the World |
WHAT IS IN IT FOR YOU: Space Propulsion Market REPORT CONTENT GUIDE

DELIVERED CUSTOMIZATIONS
We have successfully delivered the following deep-dive customizations:
| CLIENT REQUEST | CUSTOMIZATION DELIVERED | VALUE ADDS |
|---|---|---|
| Emerging Leader | Additional Company Profiles | Competitive information on targeted players to gain granular insights on direct competition |
RECENT DEVELOPMENTS
- August 2025 : Safran was selected by AstroForge to supply two EPS®X00 electric propulsion systems (including thrusters, power processing units, and fluid management subsystems) for the Vestri asteroid mission.
- July 2025 : Vaya Space was selected for a USD 1.2 million AFWERX Phase II contract to advance its hybrid-fueled ramjet/hypersonic propulsion technology.
- July 2025 : Rocket Propulsion Systems was awarded a USD 3 million contract by the US Space Force for work on an orbital transfer vehicle.
- October 2024 : Lockheed Martin acquire Terran Orbital, a global leader of satellite-based solutions primarily supporting the aerospace and defense industries.
- December 2024 : Vast, the pioneering space habitation technology company, announced that SpaceX’s Falcon 9 rocket would launch up to two Dragon missions to the International Space Station (ISS) in support of Vast’s future bid for NASA’s private astronaut missions (PAM).
Table of Contents

Methodology
The research study conducted on the Space Propulsion market involved the extensive use of secondary sources, directories, and databases, such as D&B Hoovers, Bloomberg, and Factiva, to identify and collect relevant information. Primary sources included industry experts from the market as well as suppliers, manufacturers, solution providers, technology developers, alliances, and organizations related to all segments of the value chain of this industry. In-depth interviews of various primary respondents, including key industry participants, subject matter experts (SMEs), industry consultants, and C-level executives, were conducted to obtain and verify critical qualitative and quantitative information pertaining to the market as well as assess the growth prospects of the market. A deductive approach, also known as the bottom-up approach combined with the top-down approach, was used to forecast the market size of different market segments.
Secondary Research
The share of companies in the Space Propulsion market was determined based on secondary data made available through paid and unpaid sources and an analysis of the product portfolios of major companies. These companies were rated based on their performance and quality. These data points were further validated by primary sources. Secondary sources for this research study included corporate filings, such as annual reports, investor presentations, and financial statements from trade, business, and professional associations. The secondary data was collected and analyzed to arrive at the overall market size, which was further validated by primary respondents.
Primary Research
Extensive primary research was conducted after obtaining information about the current scenario of the Space Propulsion market through secondary research. Several primary interviews were conducted with market experts from both, the demand and supply sides across different regions. This primary data was collected through questionnaires, emails, and telephonic interviews.
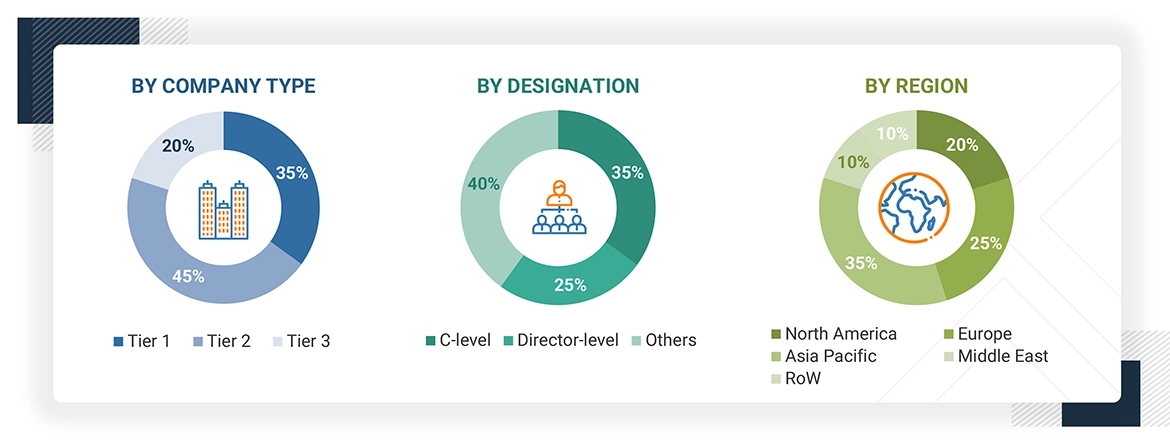
Note: Tiers of companies are based on their revenue in 2023. Tier 1: company revenue greater than USD 1 billion; tier 2: company revenue between USD 100 million and USD 1 billion; and tier 3: company revenue less than USD 100 million.
To know about the assumptions considered for the study, download the pdf brochure
Market Size Estimation
The top-down and bottom-up approaches were used to estimate and validate the size of the Space Propulsion market. The research methodology used to estimate the market size includes the following details.
Key players in the market were identified through secondary research, and their market share was determined through primary and secondary research. This included a study of the annual and financial reports of top market players and extensive interviews with industry stakeholders such as CEOs, technical advisors, military experts, and SMEs of leading companies operating in the Space Propulsion market.
All percentage shares, splits, and breakdowns were determined using secondary sources and verified through primary sources. All possible parameters that affect the markets covered in this research study were accounted for, viewed in extensive detail, verified through primary research, and analyzed to obtain the final quantitative and qualitative data on the Space Propulsion market. This data was consolidated, enhanced with detailed inputs, analyzed by MarketsandMarkets, and presented in this report.
Space Propulsion Market : Top-Down and Bottom-Up Approach

Data Triangulation
After arriving at the overall size of the Space Propulsion market from the estimation process explained above, the total market was split into several segments and subsegments. The data triangulation and market breakdown procedures explained below were implemented, wherever applicable, to complete the overall market engineering process and arrive at the exact statistics for various market segments and subsegments. The data was triangulated by studying various factors and trends from the demand and supply sides. Along with this, the Space Propulsion market size was validated using the top-down and bottom-up approaches.
Market Definition
Space propulsion is the technology and systems used to produce thrusts and manipulate spacecraft, satellites, and launch vehicles in the vacuum of space or while ascending through the atmosphere of Earth. Spacecraft can make the necessary movement in the vacuum of space by expelling mass in the opposite direction as per the Third Law of Motion of Newton. A general classification for space propulsion systems yields chemical propulsion (solid, liquid, and hybrid rocket engines), and non-chemical propulsion (electric, nuclear, and solar sail propulsion). Since chemical propulsion presents high thrust, it is naturally suited for the launch of vehicles as well as orbital maneuvers, whereas non-chemical propulsion makes a much more efficient use of energy on long missions, such as clean-space exploration or satellite station-keeping. Propagation technology is getting advanced and the new generation of propulsion systems being introduced are highly efficient, reusable, and environmentally friendly, thus serving the growing requirements pertaining to commercial, scientific, and defense-oriented tasks in space.
Key Stakeholders
- Propulsion System Manufacturers
- Satellite Operators
- Raw Material Providers
- Component Providers
- National Space Agencies
- Launch Service Providers
- Original Equipment Manufacturers
- Regulatory Bodies
- Departments of Defense
- Space Propulsion Service Providers
Report Objectives
- To define, describe, segment, and forecast the size of the Space Propulsion market based on platform, propulsion type, component, end user, support services, and region.
- To forecast the size of market segments based on five regions: North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Middle East, and Rest of the World, along with key countries in each region.
- To identify and analyze key drivers, restraints, opportunities, and challenges influencing the growth of the market across the globe.
- To identify industry trends, market trends, and technology trends that are currently prevailing in the market.
- To provide an overview of the regulatory landscape with respect to drone regulations across regions.
- To analyze micro markets with respect to individual growth trends, prospects, and their contribution to the overall market.
- To analyze opportunities in the market for stakeholders by identifying key market trends.
- To profile key market players and comprehensively analyze their market shares and core competencies.
- To analyze the degree of competition in the market by identifying key growth strategies, such as acquisitions, product launches, contracts, and partnerships, adopted by leading market players.
- To identify detailed financial positions, key products, and unique selling points of leading companies in the market.
- To provide a detailed competitive landscape of the market, along with market ranking analysis, market share analysis, and revenue analysis of key players.
Available Customizations
Along with the market data, MarketsandMarkets offers customizations as per the specific needs of companies. The following customization options are available for the report:
Product Analysis
- Product matrix, which gives a detailed comparison of the product portfolio of each company
Regional Analysis
- Further breakdown of the market segments at country-level
Company Information
- Detailed analysis and profiling of additional market players (up to 5)
Key Questions Addressed by the Report
- Growing satellite deployments.
- Increasing advancements in propulsion technologies.
- Expansion of deep space exploration missions.
- Growing demand for diverse propellant options for long duration missions.
Need a Tailored Report?
Customize this report to your needs
Get 10% FREE Customization
Customize This ReportPersonalize This Research
- Triangulate with your Own Data
- Get Data as per your Format and Definition
- Gain a Deeper Dive on a Specific Application, Geography, Customer or Competitor
- Any level of Personalization
Let Us Help You
- What are the Known and Unknown Adjacencies Impacting the Space Propulsion Market
- What will your New Revenue Sources be?
- Who will be your Top Customer; what will make them switch?
- Defend your Market Share or Win Competitors
- Get a Scorecard for Target Partners
Custom Market Research Services
We Will Customise The Research For You, In Case The Report Listed Above Does Not Meet With Your Requirements
Get 10% Free Customisation












Growth opportunities and latent adjacency in Space Propulsion Market