
Natural Gas Power Generation Market
Natural Gas Power Generation Market by Technology (Combined Cycle, Open Cycle, Cogeneration), End User (Power Utilities, Industrial, Residential & Commercial), Fuel Source (Pipeline, Liquefied), Power Output, and Region - Global Forecast to 2030




OVERVIEW

Source: Secondary Research, Interviews with Experts, MarketsandMarkets Analysis
The global natural gas power generation market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 4.8% between 2025 and 2030, as the industry is estimated to reach USD 96.95 billion from 2025 to USD 122.49 billion by 2030 due to the rising electricity demand and the ongoing transition from coal to cleaner fuels. Rapid urbanization and industrialization in emerging economies are further accelerating adoption, while technological advancements in combined-cycle gas turbines are enhancing efficiency, flexibility, and reliability. Supportive government policies, along with expanding LNG infrastructure, are also strengthening market prospects. Moreover, the integration of natural gas with renewable energy systems and advancements in hydrogen co-firing technologies are improving long-term sustainability. As a result, natural gas is expected to remain a critical transition fuel, balancing the need for low-carbon power generation with grid stability and energy security.
KEY TAKEAWAYS
-
BY TECHNOLOGYThe technology segment includes Combined Cycle, Open Cycle, and Cogeneration systems. Combined cycle plants dominate the market due to their higher efficiency, lower emissions, and ability to provide flexible power generation by utilizing both gas and steam turbines. Open cycle plants are mainly deployed for peak-load demand and faster startup, while cogeneration systems are gaining traction in industrial facilities for simultaneous electricity and heat generation.
-
BY FUEL SOURCEThe fuel source segment includes pipeline natural gas and liquefied natural gas (LNG). Pipeline gas holds the largest share, supported by extensive pipeline infrastructure and cost-effectiveness in fuel delivery. LNG is witnessing steady growth in regions with limited domestic gas supply, as it supports flexible imports and diversification of energy sources.
-
BY POWER OUTPUTThe power output segment is divided into Up to 50 MW, 51–200 MW, 201–500 MW, 501–1000 MW, and Above 1,000 MW. The 501–1,000 MW segment dominates the market, driven by demand for large-scale combined-cycle power plants that ensure efficiency, stability, and lower emissions. Smaller segments, such as up to 50 MW, are preferred for distributed and remote applications, while plants above 1000 MW are typically deployed in energy-intensive regions.
-
BY END USERThe end-user segment comprises power utilities, industrial, and residential & commercial consumers. Power utilities account for the largest share, as large-scale grid-connected natural gas plants provide reliable baseload and balanced power. The industrial sector is increasingly adopting captive gas-based plants to meet its process heating and power needs, while the residential & commercial segments benefit from distributed generation and microgrid applications.
-
BY REGIONThe regions considered are North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, South America, and Middle East & Africa. Asia Pacific leads due to Government policies supporting LNG imports, combined-cycle gas turbine (CCGT) installations, and integration of gas with renewables are accelerating growth. The region is emerging as a critical hub for natural gas power generation, supported by strong energy security initiatives and decarbonization strategies.
-
COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPEMajor market players use organic and inorganic strategies like partnerships and investments to drive growth in natural gas power generation. Companies such as GE Vernova, Wärtsilä, Ansaldo Energia, and Siemens energy, have entered various agreements, contracts and product launches to meet the increasing demand for ports in innovative uses.
The projected growth in the demand for natural gas power generation is driven by rising electricity consumption, the global shift from coal to cleaner fuels, and government commitments to reduce carbon emissions while ensuring energy security. Rapid industrialization, urbanization, and increasing renewable energy integration are further accelerating adoption, supported by investments in LNG infrastructure, hydrogen-ready technologies, and high-efficiency combined-cycle gas turbines
TRENDS & DISRUPTIONS IMPACTING CUSTOMERS' CUSTOMERS
The natural gas power generation market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 4.8% during the forecast period by value. The push for decarbonization, advancements in digital technologies such as IoT, AI, and predictive analytics for plant operations, and rising demand for flexible, low-carbon baseload capacity are fueling market expansion. Government-backed energy transition policies, along with private sector investments in advanced turbines, CCUS, and hybrid gas-renewable solutions, are expected to unlock significant opportunities for utilities, independent power producers, and technology providers.

Source: Secondary Research, Interviews with Experts, MarketsandMarkets Analysis
MARKET DYNAMICS
Level
-
Lower Carbon Emissions than Coal

-
High efficiency of combined-cycle plants
Level
-
Price Volatility
Level
-
Investing in Transitional Fuels to Accelerate Global Decarbonization
-
Strengthening Grid Reliability Through LNG Infrastructure Expansion
Level
-
Tightening Regulations and Net-Zero Commitments Reshape Gas’s Future
Source: Secondary Research, Interviews with Experts, MarketsandMarkets Analysis
Driver: Lower Carbon Emissions than Coal
Natural-gas power plants emit substantially less CO2 per unit of electricity than coal plants—approximately 50–60% less on a stack-emissions basis—positioning gas as a vital short-to-medium-term solution in decarbonization pathways where full electrification or zero-carbon firm capacity remains unfeasible. This significant emissions advantage, coupled with reduced local air pollutants such as SO2 and particulates, has spurred policy support and investment decisions globally. The 2024 regional demand trends, with a surge in North America, a moderate rise in Europe, and substantial growth in Asia Pacific as highlighted in the chart, reflect this strategic shift, underscoring gas’s role in meeting rising electricity needs while transitioning from coal. Recent developments further emphasize coal-to-gas switching as a near-term emissions reduction strategy, particularly in high-growth markets like China and India, where demand spikes are evident. Energy agencies advocate this transition, though they caution that methane leakage could undermine the CO2 benefit, necessitating robust management. This aligns with the chart’s data, showing steady demand in the Middle East & Africa and South America, where export and domestic balancing are key, driving the need for sustainable practices. Lifecycle studies from NGOs highlight the urgency of controlling upstream methane releases through enhanced fugitive-methane monitoring and mitigation, a critical focus for regulators and operators. This is especially relevant in regions like the Middle East & Africa and South America, where stable demand supports both export commitments and local power needs, as depicted in the 2024 chart. By addressing these challenges, the natural gas sector can maintain its transitional relevance, supporting global net-zero goals while infrastructure for renewables scales up.
Restraint: Price Volatility
Price Volatility remains one of the most significant restraints for the natural gas power generation market. Although natural gas is often promoted as a relatively cleaner and efficient alternative to coal, its heavy reliance on global supply-demand dynamics, geopolitical risks, and weather-driven consumption patterns makes prices highly unpredictable. This volatility directly impacts the operational costs and planning for utilities and independent power producers. According to the IEA, natural gas prices have fallen sharply from the record highs of 2022, supporting a partial recovery in demand. However, prices remain above historical averages. While this decline has encouraged some price-sensitive industrial demand, the uncertainty around sustained affordability discourages long-term commitments to gas-based generation, particularly in regions with growing renewables and stronger policy incentives for low-cost alternatives. In power generation specifically, gas use is forecast to rise only marginally, with higher consumption in Asia Pacific, North America, and the Middle East being partly offset by declines in Europe. This regional imbalance highlights how volatile prices can hinder consistent growth. For utilities, exposure to such fluctuations increases financial risk, reduces competitiveness against renewables, and undermines the case for new investments in gas-fired infrastructure.
Opportunity: Investing in Transitional Fuels to Accelerate Global Decarbonization
Natural gas is increasingly recognized as a pivotal transitional fuel in the global shift towards a sustainable energy future. While renewable sources like solar and wind are central to decarbonization efforts, their intermittent nature poses challenges for grid stability. Natural gas-fired power plants offer the flexibility needed to balance these fluctuations, ensuring a reliable and resilient energy supply. The International Energy Agency (IEA) highlights that natural gas emits less carbon than most other fossil fuels and may still be needed as backup for variable wind and solar power. This role is particularly crucial in regions undergoing rapid renewable energy integration, where maintaining grid stability is paramount. In the United States, for instance, natural gas is the single-largest source of energy used to generate electricity, comprising 43% of the nation's electricity generation in 2023. This dominance underscores the fuel's critical role in supporting renewable energy sources and maintaining grid reliability However, the integration of natural gas into the energy mix is not without challenges. Issues such as underutilization of existing gas-fired power plants and infrastructure limitations need to be addressed. Strategic investments in infrastructure and policy reforms are essential to optimize the use of natural gas, ensuring it effectively supports the transition to a sustainable energy future. In conclusion, while natural gas presents a viable solution to support renewable energy ambitions, its role must be carefully managed. By investing in infrastructure and implementing supportive policies, countries can harness the benefits of natural gas as a transitional fuel, ensuring a stable and sustainable energy future.
Challenge:Tightening Regulations and Net-Zero Commitments Reshape Gas’s Future
Global commitments to achieve net-zero emissions by mid-century are reshaping the outlook for natural gas power generation. The Paris Agreement, alongside national climate neutrality targets in regions such as the European Union, the United States, Japan, and South Korea, places mounting pressure on governments and utilities to accelerate the transition away from fossil fuels. Natural gas, while cleaner than coal, remains a carbon-emitting source, and its role as a “bridge fuel” is increasingly questioned in the context of ambitious decarbonization roadmaps. The International Energy Agency (IEA) has stressed in its Net Zero by 2050 Roadmap that unabated natural gas use in power must decline sharply, with gas generation without carbon capture falling by nearly 90% by 2040. Such policy-driven trajectories indicate that investments in conventional gas plants may face early retirement risks or reduced operational lifespans. This creates uncertainties for investors, utilities, and governments that have relied on natural gas to balance renewable variability. Several markets are already implementing stricter frameworks. The European Union’s “Fit for 55” package and carbon pricing through the EU Emissions Trading System are making natural gas-fired generation less competitive. Similarly, in the United States, recent EPA regulations targeting greenhouse gas emissions from power plants signal tightening compliance requirements. These developments highlight the risk that long-term policy directions may limit gas’s role despite its current importance in ensuring reliability. For the natural gas power generation market, climate neutrality goals represent a structural challenge. Without the widescale deployment of carbon capture and hydrogen blending, natural gas could gradually lose relevance, giving way to renewables and storage-backed solutions.
Natural Gas Power Generation Market: COMMERCIAL USE CASES ACROSS INDUSTRIES
| COMPANY | USE CASE DESCRIPTION | BENEFITS |
|---|---|---|
 |
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
|
|
Logos and trademarks shown above are the property of their respective owners. Their use here is for informational and illustrative purposes only.
MARKET ECOSYSTEM
The market map provides a quick snapshot of the key stakeholders involved in the natural gas power generation market, from component providers and end users to regulatory bodies/standards organizations. This list is not exhaustive and is meant to give an idea of the key market players.

Logos and trademarks shown above are the property of their respective owners. Their use here is for informational and illustrative purposes only.
MARKET SEGMENTS

Source: Secondary Research, Interviews with Experts, MarketsandMarkets Analysis
BY TECHNOLOGY
The technology segment includes combined cycle, open cycle, and cogeneration systems. Combined cycle plants continue to dominate the market due to their superior thermal efficiency, ability to utilize both gas and steam turbines, and reduced greenhouse gas emissions compared to conventional methods. They are increasingly being designed as hydrogen-ready, further strengthening their role in future low-carbon energy systems. Open cycle plants, though less efficient, remain vital for peaking power applications, emergency backup, and situations requiring rapid start-up. Cogeneration systems are gaining traction in industrial facilities, refineries, and district heating networks, as they enable the simultaneous generation of electricity and heat, thereby improving overall fuel utilization and reducing operational costs. The trend toward digital twin technology and predictive maintenance is further enhancing the efficiency and reliability of all three technologies.
BY FUEL SOURCE
The fuel source segment comprises pipeline natural gas and liquefied natural gas (LNG). Pipeline gas dominates the market, owing to its cost efficiency, well-established infrastructure, and reliability for large-scale power plants. However, regions with limited domestic supply or cross-border connectivity are increasingly turning to LNG imports. LNG is playing a critical role in diversifying supply, ensuring energy security, and supporting markets in Asia-Pacific, Europe, and parts of Africa where demand is rising. The development of floating storage and regasification units (FSRUs) and small-scale LNG distribution networks is further accelerating LNG’s adoption in power generation. In addition, policies promoting cleaner fuels are driving investments in LNG-to-power projects across emerging economies
BY POWER OUTPUT
The power output segment is divided into Up to 50 MW, 51–200 MW, 201–500 MW, 501–1,000 MW, and Above 1,000 MW. The 501–1,000 MW segment holds the largest share, as utilities and independent power producers (IPPs) deploy large-scale combined-cycle plants for efficiency, stability, and grid support. Plants in this range also serve as reliable anchors for renewable integration. The 201–500 MW category is gaining traction in developing economies, where mid-sized plants are increasingly used for regional grids and industrial clusters. The Up to 50 MW and 51–200 MW segments are growing due to the rise of distributed generation, captive plants, and rural electrification projects, especially in areas with limited grid connectivity. At the other end, plants above 1000 MW are deployed in regions with large-scale industrial and urban demand, though their share is more limited due to high capital costs and long development timelines. Increasingly, these plants are being designed with carbon capture and storage (CCS) and hydrogen-blending capabilities to future-proof their operations.
BY END-USE APPLICATION
The end-use application segment comprises power utilities, industrial, and residential & commercial consumers. Power utilities represent the largest segment, driven by the rising demand for reliable baseload and mid-merit power to complement intermittent renewables such as wind and solar. Utilities are also investing heavily in flexible natural gas plants to stabilize grids and prevent outages. The industrial sector is showing strong adoption of captive natural gas plants, particularly in energy-intensive industries like steel, cement, and chemicals, where consistent power supply and process heat are essential. Meanwhile, the residential & commercial sector is benefiting from the growth of distributed generation, microgrids, and small-scale combined heat and power (CHP) units, which enhance energy efficiency and resilience in urban areas.
REGION
Asia Pacific to be fastest-growing region in global smart port market during forecast period
The natural gas power generation market in Asia Pacific is projected to witness strong growth over the forecast period, supported by rising electricity demand, rapid industrialization, and the transition from coal to cleaner energy sources. Countries such as China, Japan, and South Korea are leading investments in high-efficiency combined-cycle gas turbine (CCGT) plants, LNG import terminals, and hydrogen-ready infrastructure. China’s push to curb coal dependency and India’s initiatives to expand gas-based power capacity are creating robust opportunities for technology providers and utilities. The region is also becoming a global hotspot for LNG-to-power projects, particularly in Southeast Asia, where domestic gas resources are limited but energy demand is soaring. Floating storage and regasification units (FSRUs) are enabling quicker deployment of LNG-based generation capacity

Natural Gas Power Generation Market: COMPANY EVALUATION MATRIX
In the natural gas power generation market matrix, GE Vernova (Star) leads with a strong market presence and wide product portfolio, driving large-scale adoption across industries like industrial and utilities. Bechtel Corporation (Emerging Leader) is gaining traction with high efficiency in epc solutions. While GE vernova dominates with scale, Bechtel shows strong growth potential to advance toward the leaders' quadrant.

Source: Secondary Research, Interviews with Experts, MarketsandMarkets Analysis
KEY MARKET PLAYERS
MARKET SCOPE
| REPORT METRIC | DETAILS |
|---|---|
| Market Size in 2024 (Value) | USD 93.33 BN |
| Market Forecast in 2030 (Value) | USD 122.49 BN |
| Growth Rate | CAGR of 4.8% from 2025-2030 |
| Years Considered | 2021–2030 |
| Base Year | 2024 |
| Forecast Period | 2025–2030 |
| Units Considered | Value (USD Million) |
| Report Coverage | Revenue Forecast, Company Ranking, Competitive Landscape, Growth Factors, and Trends |
| Segments Covered | By Technology, By End-use Application,By Fuel Source, By Power Output and Region |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, South America, and Middle East & Africa |
| Driver | Lower Carbon Emissions than Coal |
| Restraint | Price Volatility |
WHAT IS IN IT FOR YOU: Natural Gas Power Generation Market REPORT CONTENT GUIDE

DELIVERED CUSTOMIZATIONS
We have successfully delivered the following deep-dive customizations:
| CLIENT REQUEST | CUSTOMIZATION DELIVERED | VALUE ADDS |
|---|---|---|
| US-based Natural Gas Power Generationsssassss Providers | Detailed company profiles of competitors (financials, product portfolio) | Identify interconnections and supply chain blind spots |
| End User Segmentation | Comprehensive list of customers with segmentation by end user | Insights on revenue shifts towards emerging composite applications |
| Natural Gas Power Generation System | Transformative improvements in efficiency and performance, balancing initial cost challenges with long-term operational and system-level economic advantages | Support entry into utilities value chain with tailored opportunity mapping |
| US-based Natural Gas Power Generation Technology Supplier | Global & regional capacity benchmarking | Strengthen forward integration strategy |
| Natural Gas Poer Generation Customer | Patent landscape & IP strength mapping in Natural Gas Power Generation Technology Supplier in various ports | Support backward integration into US-based Natural Gas Power Generation Technology Suppliersourcing |
RECENT DEVELOPMENTS
- September 2025 : In September 2025, Electricity Supply Board (ESB) of Ireland and GE Vernova partnered on a major life extension and modernization project for the Dublin Bay power plant to boost performance, reliability, output, and support Ireland’s Net Zero 2040 targets. Under a new service agreement, GE Vernova will deploy its GT26 High Efficiency (HE) upgrade, SEMIPOL technology for Static Excitation Equipment (SEE), and Startup Frequency Converter (SFC). The project, scheduled for completion in 2026, will modernize the facility, which was commissioned in 2002 and currently produces up to 415 MW with a single-shaft GT26 gas turbine.
- June 2024 : In June 2024, Saudi Arabia awarded Siemens Energy a USD 1.5 billion contract to supply technologies and 25-year maintenance services for the Taiba 2 and Qassim 2 combined-cycle power plants, each generating ~2,000 MW. The projects, executed with China Energy International Group, will add nearly
- August 2025 : In August 2025, GE Vernova Inc. announced that the first of three blocks at Taiwan Power Company’s Hsinta power plant, equipped with GE Vernova 7HA.03 combined cycle technology, has begun operations, supplying up to 1.3 GW to Taiwan’s grid. The new unit supports the transition from coal by gradually replacing existing coal-fired units, with the H-class blocks expected to cut emissions by 60% compared to the older facilities.
- March 2025 : In March 2025, Siemens Energy, with Harbin Electric International as EPC, won a contract to supply technologies for the Rumah 2 and Nairyah 2 gas-fired plants in Saudi Arabia, adding 3.6 GW to the grid.Core components will be produced at the expanding Siemens Energy Dammam Hub, ensuring local capacity and long-term maintenance over 25 years The plants will replace oil-fired stations, cutting CO2 emissions by up to 60% and being designed for future carbon capture compatibility
- July 2025 : In July 2025, Siemens Energy will supply a 280 MW electrolysis system to German utility EWE for its Emden plant, set to start operations in 2027, producing 26,000 tons of green hydrogen annually. The project is part of EWE’s “Clean Hydrogen Coastline” initiative, with the electrolyzer as its core, supported by compressors and cooling systems with 320 MW lifetime average consumption. Replacing fossil fuels with this hydrogen could avoid up to 800,000 tons of CO2 emissions per year, especially in the steel industry, and includes a 10-year service contract.
Table of Contents

Methodology
This research study involved the use of extensive secondary sources such as press releases, investment reports, industry white papers, presentations, and other publicly available sources to identify and collect information useful for a technical, market-oriented, and commercial study of the natural gas power generation market. Primary sources include several industry experts from the core and related industries, preferred suppliers, manufacturers, distributors, service providers, technology developers, standards and certification organizations from companies, and organizations related to all the segments of this industry’s value chain. In-depth interviews were conducted with various primary respondents, which include key industry participants, subject-matter experts, C-level executives of key market players, and industry consultants, among other experts, to obtain and verify qualitative and quantitative information as well as assess prospects.
Secondary Research
Secondary sources referred to for this research study include annual reports, press releases, investor presentations of companies, white papers, certified publications, articles from recognized authors, and databases of various companies and associations. Secondary research has been mainly used to obtain key information about the industry’s supply chain to identify the key players offering various products and services, market classification and segmentation according to the offerings of major players, industry trends to the bottom-most level, regional markets, and key developments from market- and technology-oriented perspectives.
Primary Research
In the primary research process, various primary sources from both supply and demand sides were interviewed to obtain qualitative and quantitative information for this report. Primary sources from the supply side include industry experts such as chief executive officers (CEO), vice presidents, marketing directors, technology and innovation directors, and related key executives from various companies and organizations operating in the natural gas power generation market.
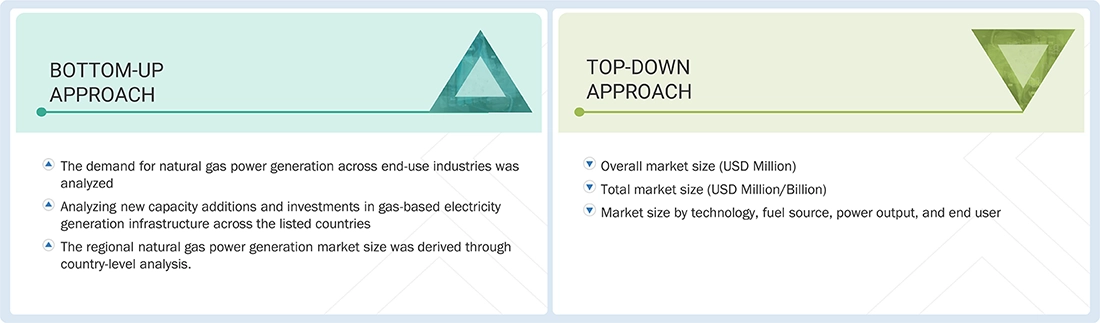
In the complete market engineering process, both top-down and bottom-up approaches were extensively used, along with several data triangulation methods, to perform the market size estimations and forecasts for all segments and subsegments listed in this report. Extensive qualitative and quantitative analyses were conducted to complete the market engineering process to list key information/insights throughout the report.
To know about the assumptions considered for the study, download the pdf brochure
Market Size Estimation
Both top-down and bottom-up approaches were used to estimate and validate the size of the global Natural gas power generation market and its dependent submarkets. The key players in the market were identified through secondary research, and their market shares in the respective regions were determined through both primary and secondary research. The research methodology included in the study is from the annual and financial reports of the top market players, and from interviews with industry experts, such as CEOs, VPs, directors, sales managers, and marketing executives, for key insights, both quantitative and qualitative, into the market. The following segments provide details about the overall market size estimation process employed in this study.
Natural Gas Power Generation Market : Top-Down and Bottom-Up Approach
Data Triangulation
After arriving at the overall market size from the estimation process explained below, the total market was split into several segments and subsegments. The data triangulation and market breakdown procedures were employed, wherever applicable, to complete the overall market engineering process and arrive at the exact statistics for all the segments and subsegments. The data was triangulated by studying various factors and trends from both the demand and supply sides. Along with this, the market was validated using both the top-down and bottom-up approaches.
Market Definition
According to IEA, the natural gas power generation market encompasses the production of electricity through the combustion of natural gas, primarily methane (CH4), which is the largest component of natural gas. Natural gas is a fossil fuel energy source consisting of various hydrocarbons, with methane being the most prevalent. It is easily stored and can be delivered through pipelines or liquefied and transported by ship. Gas-fired power plants are valued for their ability to turn on and off quickly, making them a convenient way to respond to both seasonal and short-term demand fluctuations. Natural gas accounts for about a quarter of global electricity generation and plays a significant role in providing a reliable and flexible power supply.
Stakeholders
- Natural Gas Suppliers & Producers
- Power Generation Companies / Utilities
- Engineering, Procurement, and Construction (EPC) Contractors
- Turbine & Equipment Manufacturers
- Operation & Maintenance (O&M) Service Providers
- Consulting Companies
- Energy Regulators & Authorities
- Government and Research Organizations
- Industry Associations & Power/Utility Forums
- Standards & Certification Bodies
- Technology & Innovation Partners
Report Objectives
- To define, describe, segment, and forecast the size of the natural gas power generation market, by technology, fuel source, power output, end user, and region, in terms of value
- To segment and forecast the size of the natural gas power generation market by region, in terms of volume
- To forecast the market sizes for five key regions, namely North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Middle East & Africa, and South America
- To provide detailed information regarding key drivers, restraints, opportunities, and challenges influencing the growth of the natural gas power generation market
- To offer the supply chain analysis, trends/disruptions impacting customer business, ecosystem analysis, regulatory landscape, patent analysis, case study analysis, technology analysis, key conferences & events, the impact of AI/Gen AI, macroeconomic outlook, pricing analysis, Porter’s five forces analysis, and regulatory analysis, the impact of the 2025 US tariff on the market
- To analyze opportunities for stakeholders in the natural gas power generation market and draw a competitive landscape of the market
- To benchmark market players using the company evaluation matrix, which analyzes market players on broad categories of business and product strategies adopted by them
- To compare key market players for the market share, product specifications, and end uses
- To strategically profile key players and comprehensively analyze their market ranking and core competencies
- To analyze competitive developments, such as contracts, agreements, partnerships, and joint ventures, in the natural gas power generation market
Available Customizations
MarketsandMarkets offers customizations according to the specific needs of the companies with the given market data.
The following customization options are available for the report:
Product Analysis
- Product matrix, which gives a detailed comparison of the product portfolio of each company
Geographic Analysis as per Feasibility
- Further breakdown of the natural gas power generation market, by North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Middle East & Africa, and South America.
Company Information
- Detailed analysis and profiling of additional market players (up to five)
Need a Tailored Report?
Customize this report to your needs
Get 10% FREE Customization
Customize This ReportPersonalize This Research
- Triangulate with your Own Data
- Get Data as per your Format and Definition
- Gain a Deeper Dive on a Specific Application, Geography, Customer or Competitor
- Any level of Personalization
Let Us Help You
- What are the Known and Unknown Adjacencies Impacting the Natural Gas Power Generation Market
- What will your New Revenue Sources be?
- Who will be your Top Customer; what will make them switch?
- Defend your Market Share or Win Competitors
- Get a Scorecard for Target Partners
Custom Market Research Services
We Will Customise The Research For You, In Case The Report Listed Above Does Not Meet With Your Requirements
Get 10% Free Customisation












Growth opportunities and latent adjacency in Natural Gas Power Generation Market