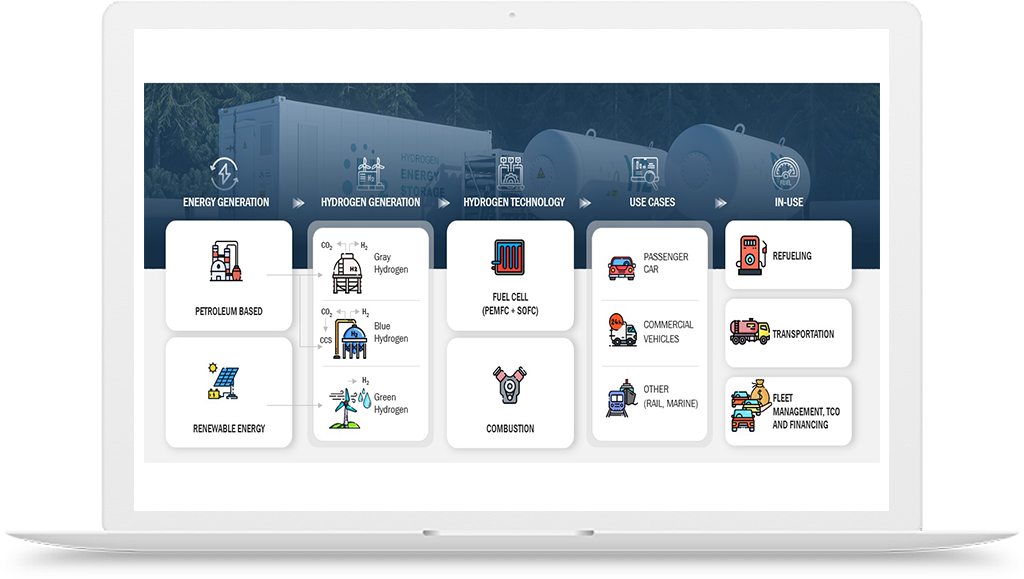
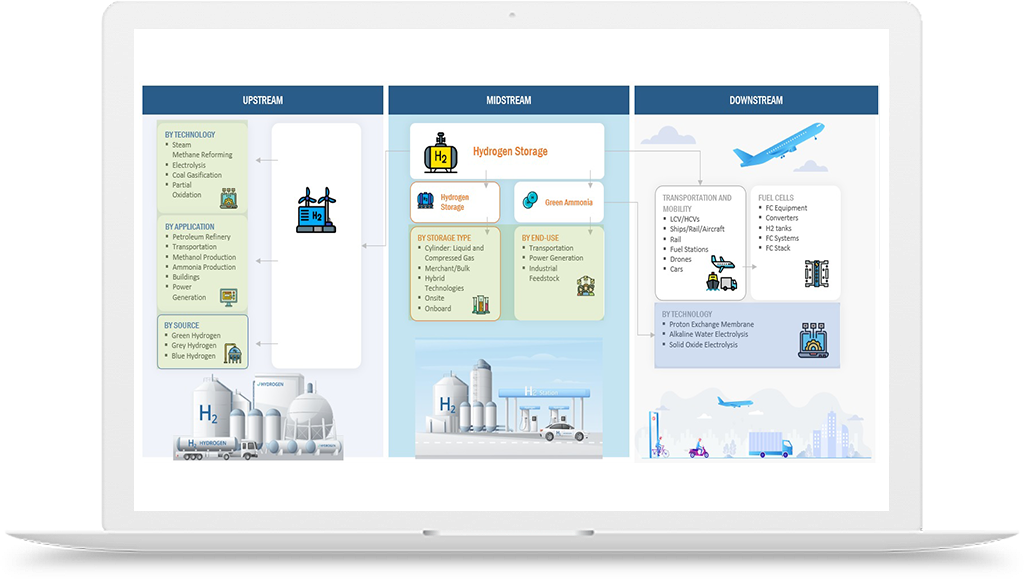
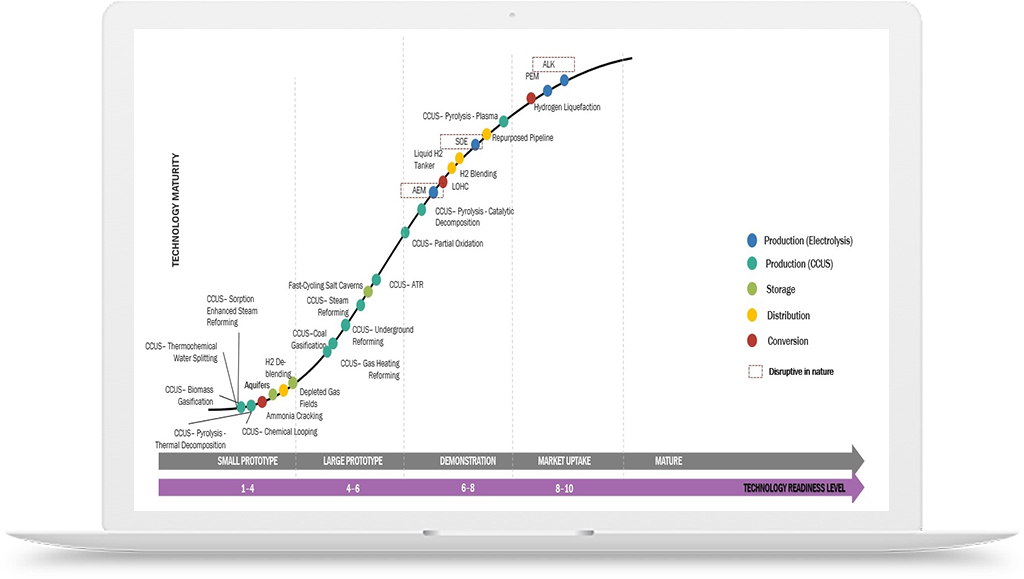
Hydrogen Application in Aerospace Defence Industry
Hydrogen application in aerospace Defence industry is becoming more and more common as fuel cell technology advances allow for the creation of more efficient and sustainable power systems for airplanes and military facilities.
The utilization of hydrogen application in aerospace Defence industry goes beyond propulsion; cutting-edge uses like hydrogen fuel cells help boost energy efficiency and lessen environmental impact in a range of Defence operations.
The aerospace Defence industry is committed to lowering its carbon footprint and improving energy security. To that end, it is actively exploring hydrogen applications, which can provide strategic advantages for energy storage and power generation for Defence infrastructure.
Hydrogen has several potential applications in the aerospace and defense industry..
Below are some of the examples:
- Fuel cell technology: Aircraft powered by hydrogen fuel cells can have much lower carbon emissions than those powered by conventional jet engines. In addition, they can be utilized to power other defense-related vehicles and unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs). Additionally, military bases and other facilities can use fuel cells as a dependable source of electricity.
- Cryogenic hydrogen storage: Rockets and spacecraft can use cryogenic hydrogen storage for their propulsion and launch systems. It is a lightweight, highly effective substitute for conventional rocket fuel that produces fewer emissions and more efficiency.
- Ground support equipment: : Ground support equipment at airports and military installations can be powered by hydrogen fuel cells, which offer a more effective and environmentally friendly option to diesel generators.
- Energy storage: In the event of a power outage, military bases and aerospace facilities can utilize hydrogen for energy storage, giving them a dependable backup power source.
- Aerospace materials: It is possible to produce lightweight materials for spacecraft and airplanes using hydrogen. For instance, hydrogen can be used to make the polymer matrix for carbon fiber reinforced polymer, or CFRP.
- Hydrogen-powered drones: Drones, which are used in a variety of defense applications like intelligence gathering, reconnaissance, and surveillance, can also be powered by hydrogen fuel cells.
- Hydrogen-Powered Aircraft: The development of hydrogen-powered aircraft is still in progress. As replacements for conventional jet engines, hydrogen fuel cells and hydrogen combustion engines are being investigated. When compared to conventional fossil fuel-powered aircraft, hydrogen-powered aircraft have the potential to significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
- Unmanned Aerial Vehicles: When compared to conventional batteries, hydrogen fuel cells can give UAVs a longer operating lifespan. This is especially useful for missions involving surveillance and reconnaissance where long flight durations are essential.
- Missile Propulsion: Certain kinds of missiles use hydrogen as a propellant. Hydrogen's high energy density makes it a good choice for applications requiring strong and small propulsion systems.
There is growing pressure on the aerospace and defense sector to lower emissions and increase fuel efficiency. Hydrogen presents a sustainable and effective resolution to these issues. This industry has a lot of room for hydrogen growth, especially in the areas of fuel cells and cryogenic hydrogen storage for spacecraft and rockets. Additionally, the industry has a sizable budget for research and development, which may result in the creation of fresh, ground-breaking hydrogen technologies. All things considered, hydrogen could be very important for the aerospace and defense sectors in the future.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ):
What are the applications of hydrogen in aerospace?
Hydrogen has applications in aerospace, including its use as a rocket propellant for space exploration and satellite launches. It is also being explored as a potential fuel for aircraft propulsion, with hydrogen fuel cells and hydrogen combustion engines being studied for future aviation applications.
What are the military applications of hydrogen?
In military applications, hydrogen is used for various purposes such as rocket propulsion, fueling unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), powering portable power generators, and as a component of explosive materials. Additionally, hydrogen fuel cells are being explored for powering military vehicles and providing energy in remote or off-grid operations.
What are the advantages of using hydrogen as a fuel cell in aircraft?
Using hydrogen as a fuel cell in aircraft offers advantages such as zero-emission operation, increased energy efficiency compared to traditional combustion engines, and the potential for longer flight ranges due to the high energy density of hydrogen. Additionally, hydrogen fuel cells produce less noise and vibrations, contributing to a quieter and smoother flying experience.
What are the challenges of hydrogen-powered aircraft?
Hydrogen-powered aircraft face challenges such as the need for large onboard storage systems due to the low density of hydrogen, limited hydrogen refueling infrastructure, and concerns regarding the safety of handling and storing hydrogen on aircraft. Additionally, the high cost of hydrogen production and the development of efficient hydrogen fuel cell technology for aviation applications are ongoing challenges to be addressed.