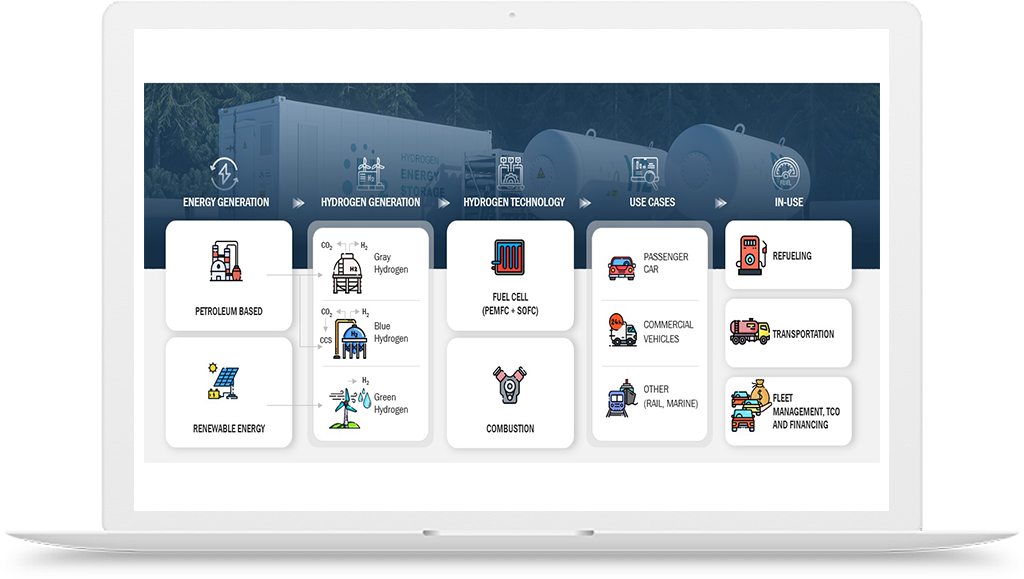
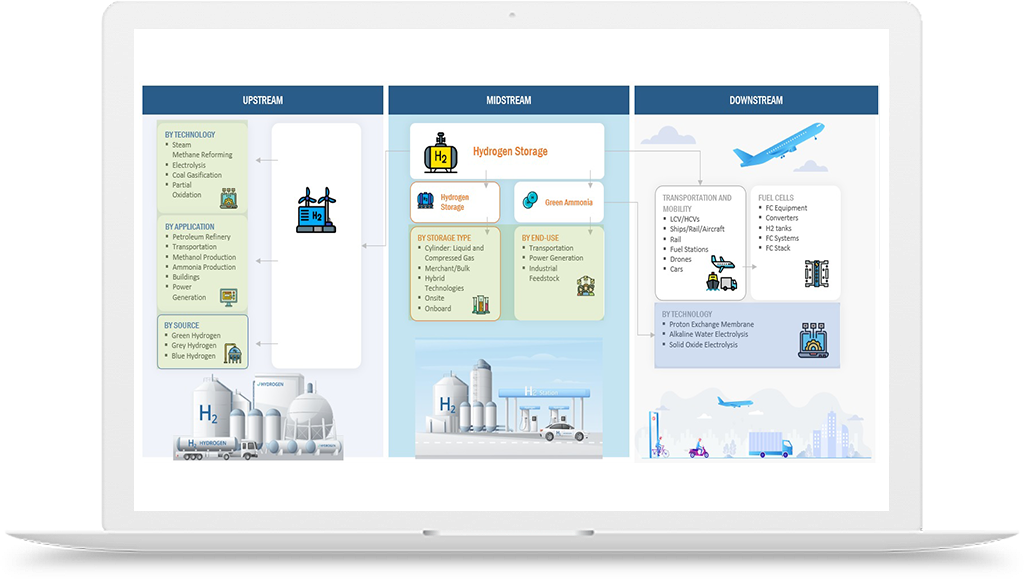
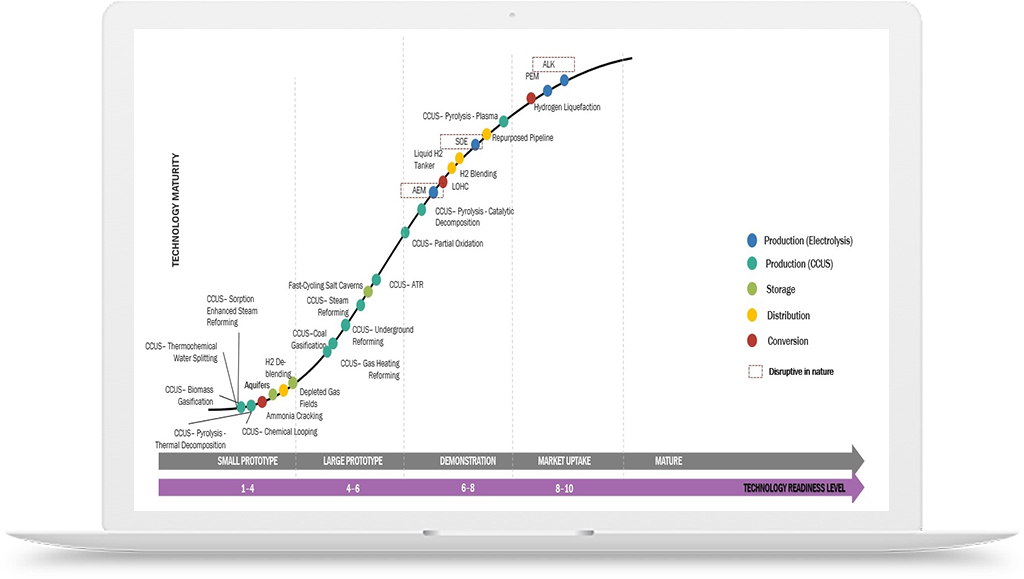
Hydrogen Application in Chemicals Industry
The hydrogen application in chemicals industry is growing in popularity, with an emphasis on utilizing its adaptability as a feedstock for a range of chemical processes to support the sector's sustainability efforts.
Hydrogen serves as a clean and effective substitute in processes like hydrogenation, ammonia production, and methanol synthesis, making its hydrogen application in chemicals industry essential for lowering carbon emissions.
Investigating hydrogen application in the chemicals sector offers game-changing possibilities, from improving manufacturing efficiency to facilitating the creation of green chemicals, all of which are in line with the larger objectives of creating a low-carbon and ecologically conscious sector.
Hydrogen plays a key role in the chemical industry as a raw material and an important energy source in many chemical processes. The use of hydrogen in the chemical industry offers numerous benefits, including improved efficiency, increased productivity and reduced environmental impact.
Here are some key applications of hydrogen in the chemicals industry:
"Green hydrogen," created by electrolysis using renewable energy sources, is gaining popularity as the industry focuses more on sustainability and cutting carbon emissions. As a cleaner hydrogen substitute made from fossil fuels, green hydrogen has the potential to become even more important in the chemical industry.
- Hydrogenation: One of the fundamental uses of hydrogen in the chemical industry is the hydrogenation process, in which hydrogen is added to unsaturated organic compounds. Hydrogenation produces a number of chemicals, including vegetable oils, margarine, and petroleum products. This process improves the quality of these products and reduces their environmental impact by reducing their carbon content.
- Ammonia Production: Ammonia is an important chemical raw material for the production of fertilizers, explosives and other chemicals. The Haber-Bosch process is the most common method of producing ammonia and requires large amounts of hydrogen. As demand for fertilizers and other ammonia-based products increases, demand for hydrogen in the chemical industry is also expected to increase.
- Methanol Production: Methanol is a multipurpose chemical that finds use in the manufacturing of plastics, solvents, and fuel. Although it can also be made using renewable energy sources from carbon dioxide and hydrogen, methanol is normally produced from coal or natural gas. The production of methanol from renewable hydrogen has a large positive impact on the environment and can lessen the chemicals industry's carbon footprint.
- Olefin Production: Olefins are a class of compounds that are used to make a variety of goods, such as fibers, rubber, and plastics. Large amounts of hydrogen are produced when hydrocarbons are cracked in order to produce olefins. Hydrogen provides substantial energy savings and environmental advantages in the olefins production process.
- Refining: Hydrogen is also used in the refining of petroleum products to remove impurities and improve the quality of the final products. The use of hydrogen in refining processes can also help reduce emissions and improve energy efficiency.
- Hydrogenation Reactions: In the synthesis of many different chemicals, hydrogenation reactions are frequent. Hydrogen gas can be used to hydrogenate unsaturated compounds when a catalyst is present. Edible oils and fats are produced using this process, for instance.
- Hydrogen Peroxide Production: Hydrogen peroxide is made with the use of hydrogen. An important chemical with a variety of uses, including as a bleaching agent, hydrogen peroxide is created when hydrogen reacts with anthraquinone in the anthraquinone process.
- Hydrogen in the Production of Synthetic Fuels: By converting hydrogen and carbon monoxide into hydrocarbons during procedures like Fischer-Tropsch synthesis, hydrogen can play a significant role in the creation of synthetic fuels.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ):
How is hydrogen used in the chemical industry?
Hydrogen is extensively used in the chemical industry as a key ingredient for various processes, including hydrogenation reactions to produce saturated fats, ammonia synthesis for fertilizer production, methanol synthesis as a precursor for chemicals and fuels, and as a reducing agent in numerous chemical reactions for the production of various compounds.
How is hydrogen gas valuable for the chemical industry?
Hydrogen gas is valuable for the chemical industry due to its versatility as a feedstock, reducing agent, and energy carrier. It enables the production of a wide range of chemicals, facilitates efficient reactions and transformations, and serves as a clean and sustainable option when produced from renewable sources, contributing to the decarbonization of the industry.
What chemicals are required for hydrogen production?
The chemicals required for hydrogen production depend on the method used. Commonly used chemicals include natural gas (methane) for steam methane reforming, water for electrolysis, and hydrocarbon feedstocks for processes like partial oxidation or coal gasification. The specific chemicals used vary based on the chosen hydrogen production technology.
What are the barriers to the hydrogen industry?
Barriers to the hydrogen industry include high production costs, limited infrastructure for storage and distribution, technological challenges in efficient hydrogen production and utilization, and the need for supportive policies and regulations to promote widespread adoption and investment in hydrogen technologies. Additionally, public acceptance and safety concerns are also important considerations for the industry's growth.