Hydrogen Industry Investments
Hydrogen Ecosystem Current and Future Investments
Current Investments in Hydrogen Ecosystem:
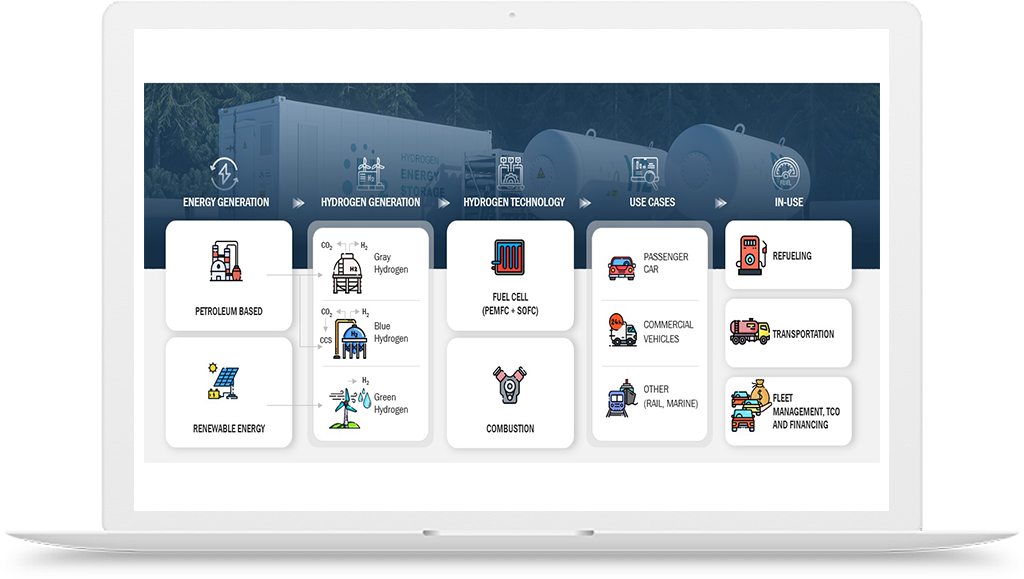
Hydrogen Production:
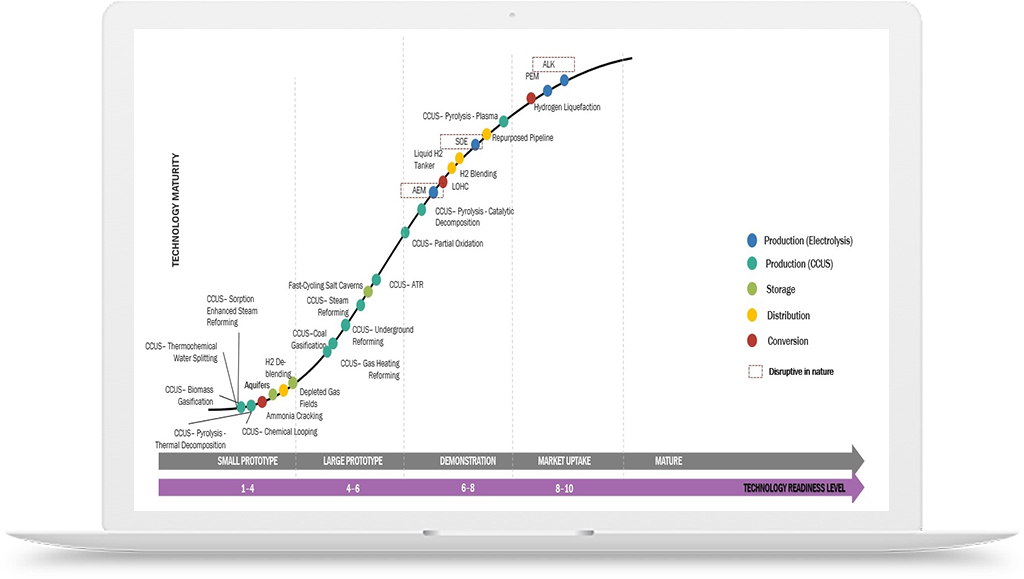
- Electrolysis: Investments in electrolysis technology have been rising in order to produce hydrogen. Because of their promise for scalable and effective hydrogen synthesis from renewable sources, proton exchange membranes (PEMs) and alkaline electrolyzers have drawn a lot of attention. Enterprises such as Nel ASA, ITM Power, and Plug Power have managed to raise capital to enhance their electrolyzer production capabilities and facilitate the advancement of extensive electrolysis initiatives.
- Steam Methane Reforming (SMR): Even though SMR is the most common way to produce hydrogen, efforts are being undertaken to enhance its environmental efficiency by utilizing carbon capture and storage (CCS) technologies. In order to improve the efficiency and lower the carbon footprint of SMR plants, businesses are spending money on research and development.
Hydrogen Storage and Transportation:
- Hydrogen Refueling Infrastructure: Infrastructure for hydrogen refueling is being developed with significant investments, especially in areas where fuel cell electric cars, or FCEVs, are becoming more and more popular. To assist the expansion of FCEVs, businesses including as Air Liquide, Linde plc, and Shell are investing in the installation of hydrogen filling stations.
- Hydrogen Pipelines and Transportation: Infrastructure for transportation and hydrogen pipeline development is receiving funding in order to facilitate the economical and efficient distribution of hydrogen. Enterprises are investigating the possibility of reusing already-existing natural gas pipes and constructing specific hydrogen pipelines for extended transit.
Hydrogen Utilization:
- Fuel Cell Electric Vehicles (FCEVs): Several automakers are investing in the research and development of fuel cell electric vehicles (FCEVs), including Toyota, Hyundai, and BMW. These expenditures go toward things like developing new vehicles, producing fuel cell stacks, and forming alliances to create FCEV supply chains.
- Industrial Applications: To investigate hydrogen uses for decarbonizing steel production, refining processes, and power generation, investments are being made in a number of industrial sectors. Businesses in the manufacturing, energy, and chemical industries are funding collaborations and pilot programs to show the feasibility of using hydrogen in industry for both practical and cost-effective reasons.
Future Investments in Hydrogen Ecosystem:
Green Hydrogen
Investments in green hydrogen production technologies are anticipated to rise sharply, with a focus on decarbonization. It is projected that significant investments in electrolysis driven by renewable energy sources will be made in order to reduce costs and increase production capacity. In order to achieve carbon neutrality in a number of industries, including transportation, manufacturing, and power generation, green hydrogen is anticipated to be extremely important.
Hydrogen Infrastructure Expansion
It is expected that more money will be spent on building hydrogen infrastructure, such as hubs and clusters, pipeline networks, and hydrogen recharging stations. The aforementioned expenditures are intended to establish a resilient and linked hydrogen ecosystem, which will facilitate the expansion of hydrogen production, storage, and delivery.
Cross-Sector Integration
It's anticipated that future investments would concentrate on integrating hydrogen technology with other industries, including power grids, industrial processes, and renewable energy sources. Power-to-hydrogen, hydrogen blending in natural gas pipelines, and the application of hydrogen in industries with difficult-to-abate emissions are some of the technologies that are required for this integration.
International Collaboration
It is envisaged that investments would be made in international cooperation and partnerships to promote the growth of international trade and cross-border hydrogen supply chains. To support the global transportation of hydrogen, this entails making investments in regulatory frameworks, certification processes, and hydrogen infrastructure.
Detailed use case analyses related to current and future investments in the hydrogen ecosystem:
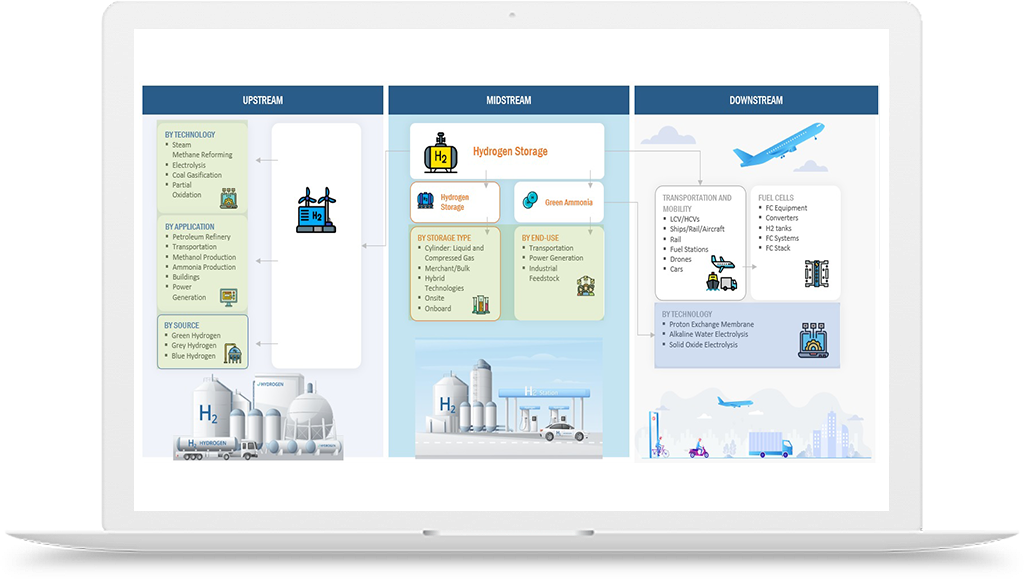
Hydrogen Production
- Electrolysis Plants: Investing in electrolysis facilities is essential to increasing the production of green hydrogen. These plants separate water into hydrogen and oxygen using renewable electricity. They make it possible to produce hydrogen that is free of carbon, which has a variety of uses in the transportation, industrial, and power generation sectors. Electrolysis plants are being used on a variety of scales, from large-scale facilities for regional or national hydrogen production to small-scale projects for local consumption.
- Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS) in Hydrogen Production: The development and implementation of carbon capture and storage technologies for the production of hydrogen from fossil fuels are being funded. By capturing and storing carbon emissions, the creation of hydrogen is intended to become a low-carbon or carbon-neutral process. Blue hydrogen can serve as a stopgap measure until a more environmentally friendly hydrogen economy is established, and CCS technologies make this possible.
Hydrogen Infrastructure
- Hydrogen Refueling Stations: Fuel cell electric vehicle (FCEV) adoption depends on investments in hydrogen refueling facilities. Compared to battery electric vehicles, FCEVs can drive longer distances and refill more quickly because to the infrastructure these stations provide for hydrogen filling. With an emphasis on important transit corridors, metropolitan areas, and places with favorable regulations and market demand for FCEVs, efforts are being undertaken to broaden the network of hydrogen refueling stations.
- Hydrogen Pipelines and Storage: For hydrogen to be transported and distributed efficiently, storage facilities and pipelines must be invested in. Hydrogen may be transported great distances to supply-demand hubs using dedicated hydrogen pipelines or by repurposing existing natural gas pipelines. Subterranean hydrogen storage facilities are also being invested in, in an effort to offset the intermittent nature of renewable energy sources and guarantee a steady supply during moments of high demand.
Industry and Manufacturing
- Green Hydrogen for Industrial Applications: The goal of investing in green hydrogen production is to reduce the carbon footprint of industrial activities. Refineries, steel, and ammonia manufacturing are among the industries investigating the use of green hydrogen as a fuel or feedstock in place of fossil fuels. These investments make it possible for these industries to reduce their carbon emissions, which results in more ecologically friendly and sustainable production methods.
- Power-to-X Technologies: Investing in power-to-x technologies entails turning excess renewable energy into hydrogen or goods generated from hydrogen, such as feedstocks, chemicals, or synthetic fuels. Power-to-x technologies facilitate the integration of renewable energy sources into the energy system by storing renewable energy as hydrogen or its derivatives. This allows for the exploitation of excess renewable energy.
International Hydrogen Trade
- Cross-Border Hydrogen Infrastructure: To enable global hydrogen trade, investments are being made to build cross-border infrastructure. Nations endowed with copious amounts of renewable energy resources are making significant investments in the construction of green hydrogen production plants and related transportation infrastructure. The objective of these investments is to establish a hydrogen supply chain that links locations with strong demand but limited domestic production capabilities with hydrogen production centers.
- Hydrogen Export Projects: The development of large-scale hydrogen export projects is the focus of investments. Nations that possess abundant renewable energy resources and are in close proximity to prospective buyers of hydrogen are investigating the possibility of establishing export-oriented hydrogen production facilities. In order to support the development of a global hydrogen economy, these projects entail the production, liquefaction, and transportation of hydrogen to foreign markets.
The financial commitments made by different stakeholders, such as governments, private enterprises, and investors, to support and advance the growth of the hydrogen sector are referred to as hydrogen industry investments. These expenditures are going to be used for things like R&D, building infrastructure, setting up production facilities, and implementing hydrogen technology. The objective is to support the development of a sustainable hydrogen industry that can aid in the pursuit of clean energy, decarbonization initiatives, and the shift to a low-carbon economy.
How do these investments benefit market participants? Which countries and players have taken the lead in government and direct private sector investments?
Investments in the hydrogen ecosystem benefit market participants in several ways, including the following:
- Market Growth and Expansion: The infrastructural and technological advancements related to hydrogen fuel support the market's expansion. Market players have greater opportunity to enter new markets, develop cutting-edge solutions, and gain market share as more funds are devoted to research, development, and deployment.
- Technological Advancements: Technological developments in hydrogen technologies include reduced fuel cell costs, enhanced electrolysis efficiency, and advances in hydrogen storage and delivery. Market players gain from these developments since they improve the efficiency, dependability, and affordability of hydrogen solutions.
- Cost Reduction: Across the hydrogen value chain, investments lead to cost savings through economies of scale and innovation. Hydrogen solutions are more cost-competitive than traditional energy sources, which increases market demand and adoption. Cost reductions can boost market competitiveness and profitability for participants in the market.
- Job Creation and Economic Growth: The expansion of the hydrogen industry through investments generates employment possibilities in a number of value chain categories, such as manufacturing, R&D, infrastructure implementation, and service delivery. These employment options promote employment and revenue development while also supporting regional and national economic progress.
Regarding government and private sector investments, the lead has been taken by several countries and companies:
Government Investments:
- Germany: Government investments in the hydrogen industry have been led by Germany. In order to encourage research, development, and demonstration initiatives, they have committed significant resources and developed the National Hydrogen Strategy. Germany has committed billions of euros to investments in hydrogen technology with the goal of leading the world in this field.
- Japan: With its Basic Hydrogen Strategy, Japan has made significant investments in the hydrogen industry. The nation is concentrating on creating a society that uses, stores, transports, and produces hydrogen. Japan has allocated public funds to assist the development of hydrogen infrastructure, as well as research and experimental initiatives.
- European Union: As part of its Green Deal and European Hydrogen Strategy, the European Union (EU) has set high goals for the deployment of hydrogen. The European Union intends to make significant investments through public-private partnerships in hydrogen technologies, infrastructure, and projects. The European Commission has allotted billions of dollars to member state efforts pertaining to hydrogen.
Private Sector Investments:
- Energy Companies: Significant investments have been made in the hydrogen industry by well-known energy firms like BP, TotalEnergies, and Shell. Their portfolios are becoming more diverse, and they are making investments in infrastructure, apps, and hydrogen generation. By using their resources and experience, these businesses are propelling the growth of the hydrogen industry.
- Automotive Manufacturers: Several automakers have made significant investments in hydrogen fuel cell infrastructure and technology, including Toyota, Hyundai, and BMW. To assist with the commercialization of fuel cell electric vehicles (FCEVs), these firms are developing FCEVs and making investments in infrastructure for hydrogen refueling.
- Industrial Players: To decarbonize their processes, major industrial players in industries including steel, chemicals, and refining are investing in hydrogen-related projects. Businesses like Siemens Energy, Air Liquide, and Thyssenkrupp are developing low-carbon hydrogen supply chains by working with partners, investing in hydrogen technology, and testing hydrogen-based industrial processes.
These instances show the initiative and financial commitments made by public and private sector participants to propel the expansion of the hydrogen ecosystem. The development and commercialization of hydrogen technologies and infrastructure are being actively shaped by market participants who are combining government backing, legislative frameworks, and private sector innovation.