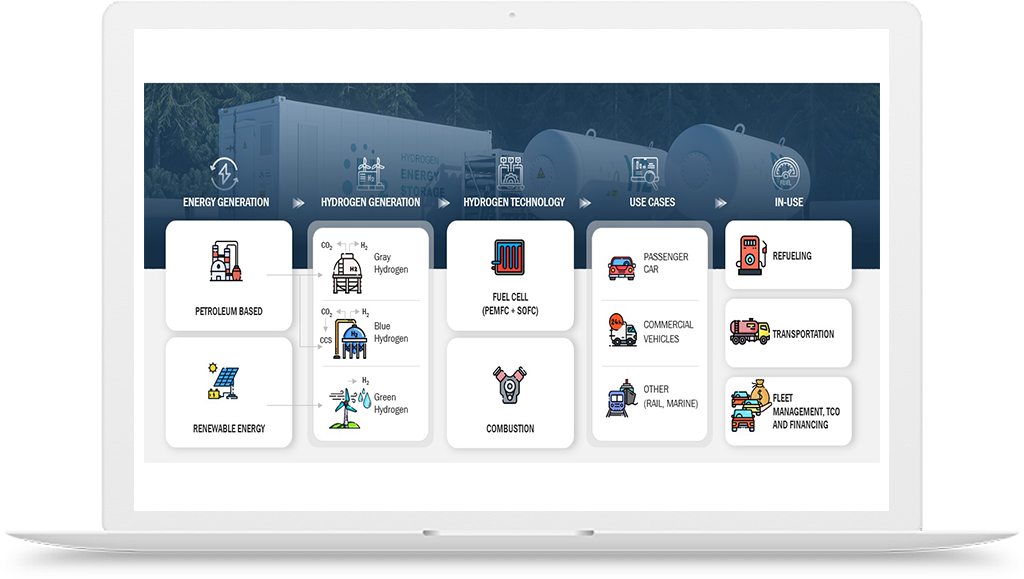
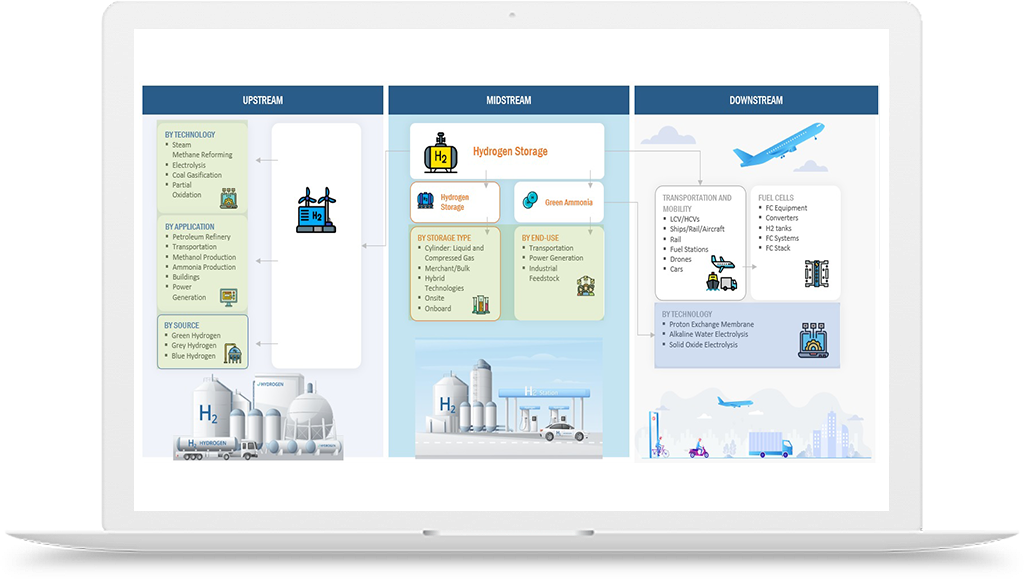
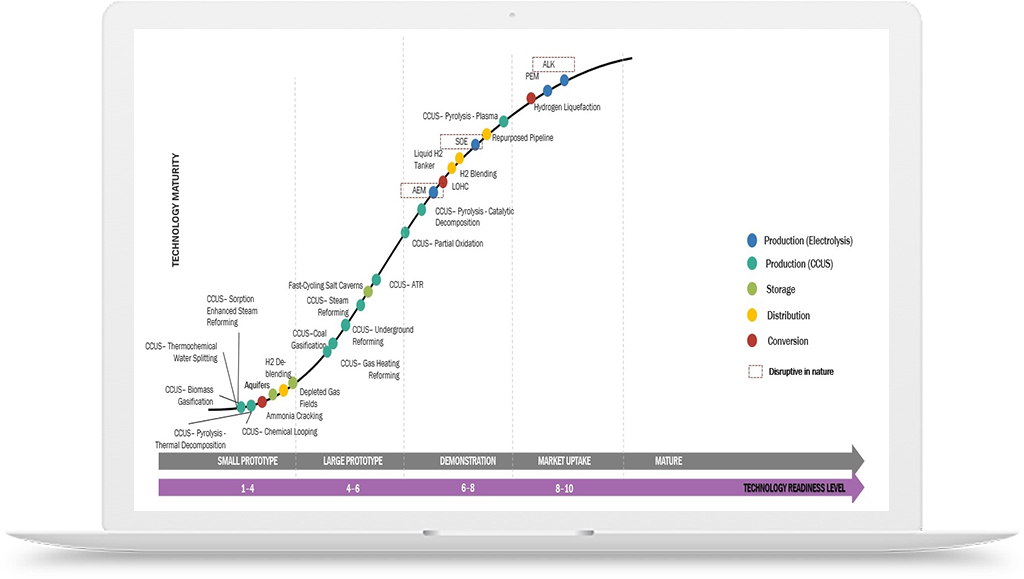
Green Hydrogen Growth Opportunities in Mobility Industry
Mobility and other industry operators across multiple industries can benefit from the opportunities presented by the Green Hydrogen space. The following are some significant prospects for Green Hydrogen Growth Opportunities in Mobility Industry:
-
Zero Emissions Transport:
Hydrogen Fuel Cell Vehicles: Fuel cell vehicles that run on hydrogen can use green hydrogen as a clean fuel that has the advantage of having a large driving range and quick refueling periods. Hydrogen-powered vehicles, including trucks, buses, and cars, can be investigated and commercialized by automakers.
Hydrogen Infrastructure: The establishment of a hydrogen refueling station network is essential to facilitating the uptake of hydrogen-powered automobiles.
-
Industrial Applications:
Hydrogen-Powered Industrial Vehicles: Industrial machinery, such as forklifts, warehouse vehicles, and other material handling equipment, can transition to green hydrogen. This shift reduces emissions within industrial facilities, contributing to a cleaner and more sustainable mobility landscape within industrial settings.
Incorporating green hydrogen into logistics and supply chain operations presents growth opportunities. Hydrogen-powered vehicles can streamline transportation within industrial complexes, offering an environmentally friendly alternative for the movement of goods and materials.
-
Energy Storage:
Power-to-Hydrogen Energy Storage: Green hydrogen has the ability to be stored and subsequently transformed back into power when required. To maintain grid stability and balance sporadic renewable energy sources, industrial players can invest in large-scale hydrogen energy storage systems.
Grid Services Based on Hydrogen: Green hydrogen can offer grid services including peak shaving, frequency management, and load balancing. Businesses might look at ways to improve grid resilience and dependability by using hydrogen as a flexible energy supply.
-
Research and Development:
Technologies for Electrolyzers: The broad use of green hydrogen depends on the creation of creative solutions for the safe and effective distribution, transportation, and storage of hydrogen. To overcome these obstacles, businesses should concentrate on their R&D activities.
Distribution and Safety of Hydrogen: The broad use of green hydrogen depends on the creation of creative solutions for the safe and effective distribution, transportation, and storage of hydrogen. To overcome these obstacles, businesses should concentrate on their R&D activities.
The growing emphasis on decarbonization and the demand for sustainable energy sources are what are driving this potential in the green hydrogen market. Engaging in the research, use, and deployment of green hydrogen technologies allows industrial actors to take the lead in the shift to a low-carbon economy.
Some examples of Green Hydrogen Growth Opportunities in Mobility Industry:
With so many growth prospects that coincide with sustainability objectives, green hydrogen is starting to take the mobility industry by storm. Green hydrogen offers a viable option for powering many forms of mobility as people look for greener substitutes for conventional fossil fuels. The following are some instances of Green Hydrogen Growth Opportunities in Mobility Industry:
-
Zero Emissions Transport:
Hyundai and Toyota: These automakers have made significant investments in hydrogen fuel cell vehicles. Hyundai offers the NEXO SUV, while Toyota introduced the Mirai sedan, showcasing their commitment to zero-emission transport powered by green hydrogen.
-
Clean Power Generation:
Ørsted: This Danish energy company is developing the H2RES project, combining offshore wind turbines with an electrolyzer to produce green hydrogen. The hydrogen will be used for power generation, heating, and transportation, highlighting the integration of renewable energy and hydrogen.
-
Industrial Applications:
Thyssenkrupp: The German corporation is investigating the application of green hydrogen in its steel manufacturing process. Thyssenkrupp wants the steel industry's carbon emissions to be drastically reduced by using hydrogen in place of coal.
-
Energy Storage:
E.ON and RWE: These energy corporations are looking into storing excess renewable energy via large-scale hydrogen storage. During times of high generation, they want to store excess energy as hydrogen and convert it back to electricity when needed.
-
Research and Development:
Siemens Energy: The energy technology company is actively engaged in research and development of advanced electrolyzer technologies. Siemens Energy aims to increase the efficiency and performance of electrolysis systems to support the widespread adoption of green hydrogen.
-
Hydrogen Infrastructure:
Air Liquide: These multinational industrial gases company is involved in developing hydrogen infrastructure, including hydrogen production and distribution facilities. They have implemented hydrogen refueling stations in various locations, supporting the growth of hydrogen-powered mobility.
-
Infrastructure for Hydrogen:
The development of hydrogen infrastructure, including facilities for hydrogen generation and delivery, is being undertaken by the international industrial gases company Air Liquide. They've put in place hydrogen filling stations across the city to encourage the expansion of hydrogen-powered vehicles